Under the background of population aging, rising labor costs, energy conservation and emission reduction, China’s precast buildings have started again and entered people’s vision again.
Driven by policy, precast buildings have developed rapidly in recent years and made some achievements, but there are still many pain points in the implementation process.
Focusing on the trend and pain points of the cast construction industry, this paper expects the industry to work together to promote the high-quality development of the industry.
At 8:00 next Monday, continue to update the response strategy for improving the quality of precast construction projects.
01 industry trend throughout the long history of the development of China’s construction industry, precast construction has become the main trend of the development of today’s construction industry.
The promulgation and implementation of national precast construction policy documents point out the direction for the development of precast construction industry in various provinces and cities, and its development presents the characteristics of multi-level and multi angle.
Under the background of “stricter environmental protection and labor shortage”, the policy has made great efforts to promote precast buildings.
China’s early extensive economic development with high energy consumption and high pollution has brought serious environmental and air pollution problems.

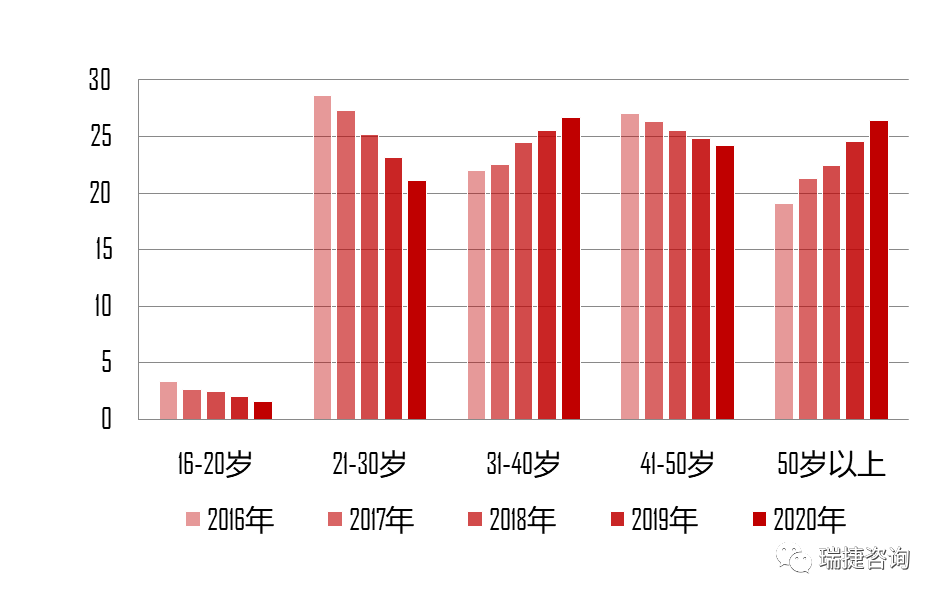
At the same time, the problem of population aging is becoming more and more prominent, the labor cost continues to rise, and the labor shortage is becoming more and more serious, which affects the healthy development of the construction industry.
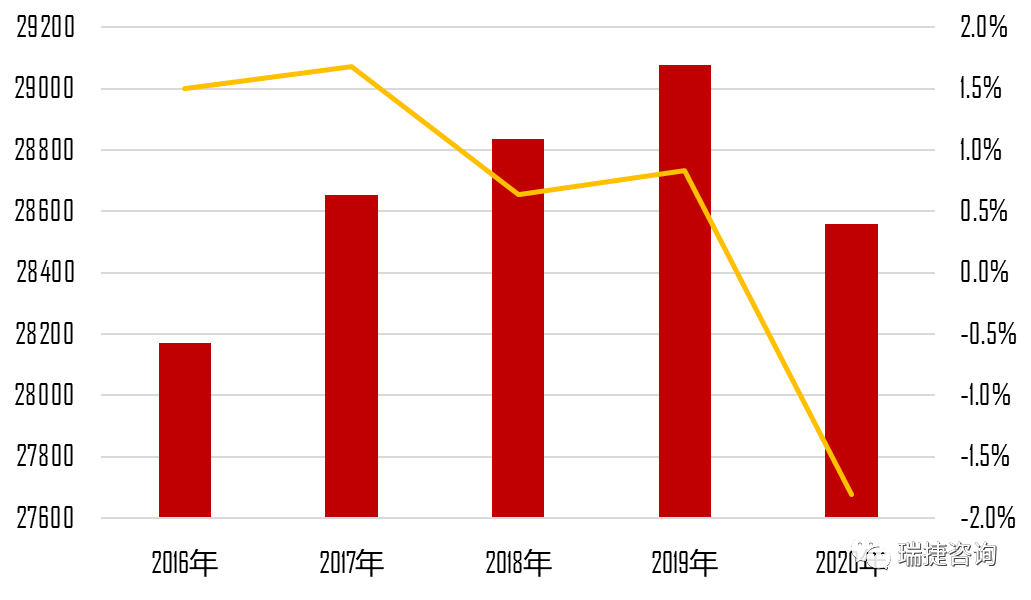
Data source: Bureau of statistics, monitoring and investigation report on migrant workers in 2020 ▲ data source on the scale and growth rate of migrant workers: Bureau of statistics, monitoring and investigation report on migrant workers in 2020 ▲ compared with the traditional cast-in-situ construction method, the cast construction method has obvious advantages in improving construction efficiency, improving project quality, reducing labor and energy conservation and emission reduction.
In 2016, the State Council made it clear that it will strive to make the proportion of precast buildings in new buildings reach 30% in about 10 years.

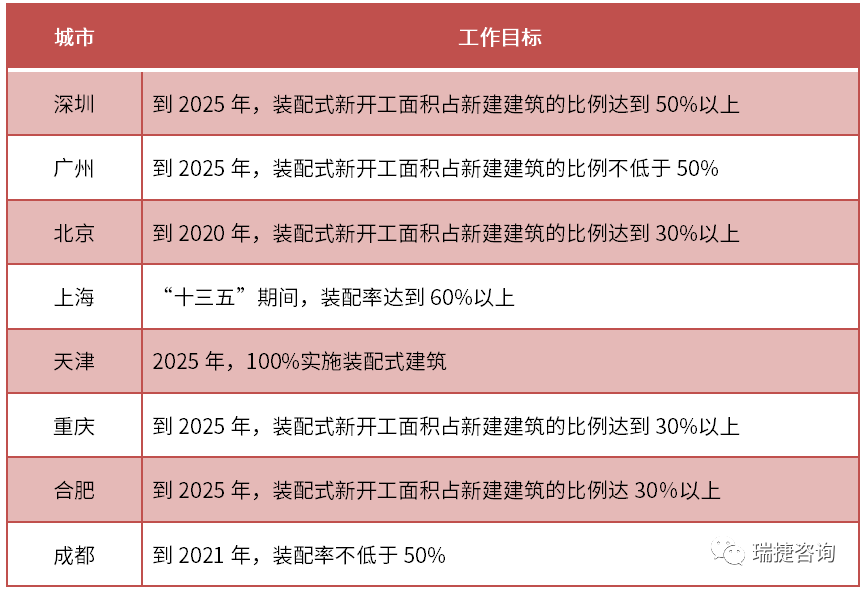
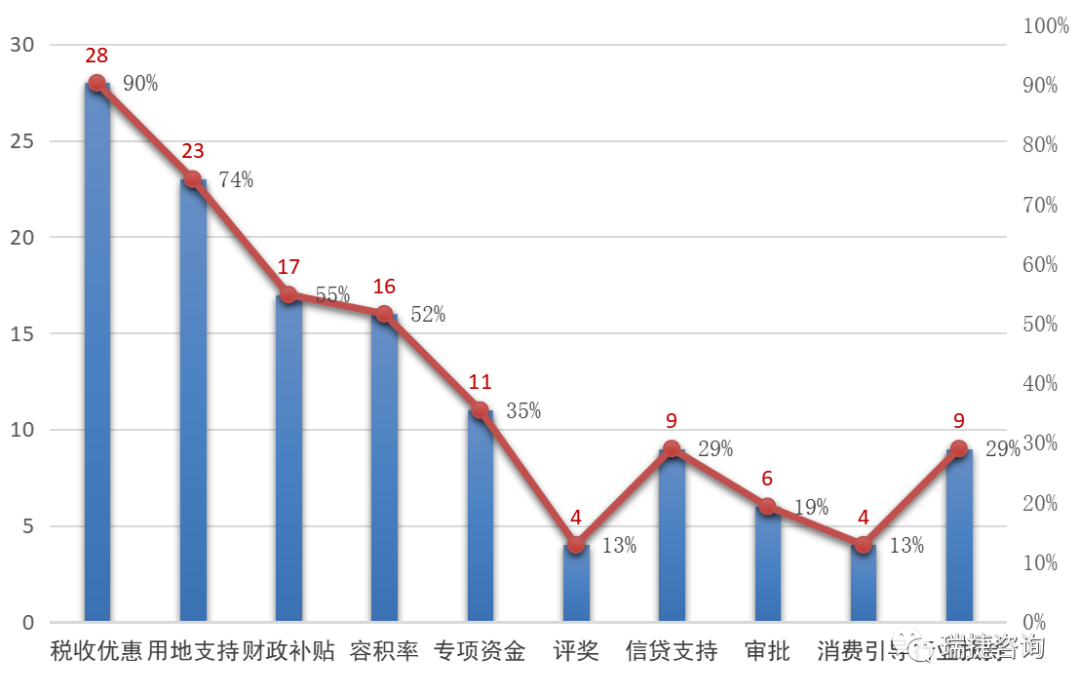
The promotion efforts of local governments have been increasing, and the rigid requirements and subsidy support have been promoted in coordination.
Since 2016, local governments have successively issued policies to encourage the promotion of precast buildings, and formulated work objectives and support policies.
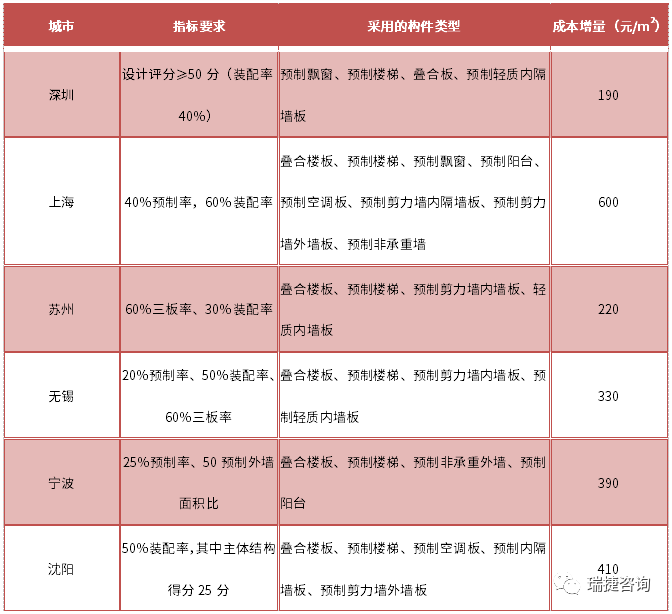
▲ summary and analysis of precast building planning policies in some cities data source: sort out according to local government documents ▲ under the “double carbon” goal of the number of provinces and cities providing relevant support policies for precast buildings and coverage, the precast building industry will usher in greater development.
At the United Nations General Assembly in September 2020, China promised that China will improve its national independent contribution, Adopt more effective policies and measures, strive to peak carbon dioxide emissions by 2030, and strive to achieve carbon neutralization by 2060.
As a major carbon emitter, the construction industry has the problems of large resource consumption and high pollution emission.
At present, it is generally believed that the carbon emission in the whole life cycle of buildings accounts for more than 50%.
There is a lot of space to reduce carbon emission in the preparation and construction stages of building materials.
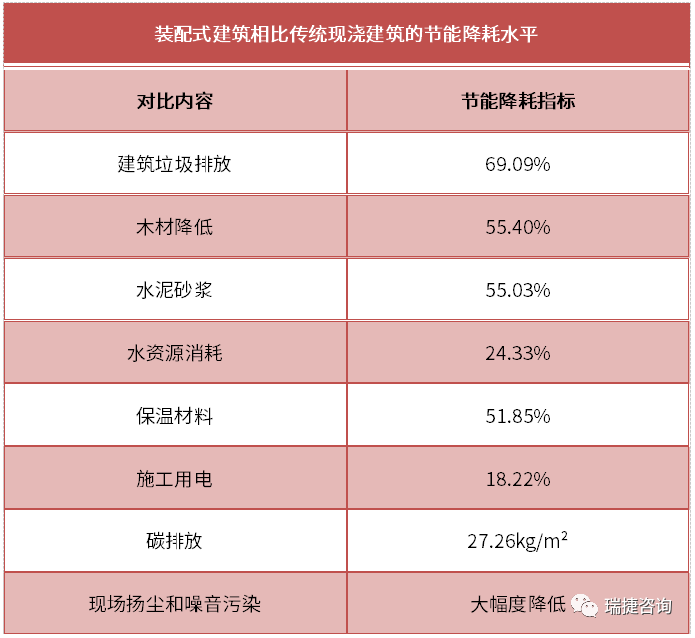
Source: Ministry of housing and urban rural development investment estimation index for precast construction projects (Draft for comments) ▲ compared with traditional cast-in-situ buildings, the energy-saving and consumption reduction level of precast buildings.
The precast building market is developing rapidly and will still show high growth in the future.
In 2020, the newly started precast building area in China will reach 630 million M ², It is 50% higher than that in 2019, accounting for about 20.5% of the new construction area in China.
According to the action plan for precast buildings in the 13th five year plan issued by the Ministry of housing and urban rural development, the proportion of precast buildings in new buildings will reach 30% by 2025; According to the prediction and analysis, the new construction area of precast will reach 1.17 billion m by 2025 ²。 Data source: Ministry of housing and urban rural development, Ruijie Research Institute, unit: 10000 m ² ▲ in recent years, the new construction area of precast buildings in China and the prediction of national standards in the next five years have been gradually improved, Promote the high-quality development of precast buildings code for acceptance of construction quality of concrete structures (gb50204-2015) was implemented in 2015, while the large-scale implementation of precast concrete buildings began in 2016.
Due to the continuous emergence of new technologies in the precast construction industry, the acceptance code lags behind, the coverage of some detection indicators is not comprehensive, and the fit with the market is not enough.
Therefore, relevant national departments have started to review the code for acceptance of construction quality of concrete structures The revision of (gb50204-2015) has entered the stage of revising the draft for comments.
Considering the actual situation, the newly revised code is more reasonable.
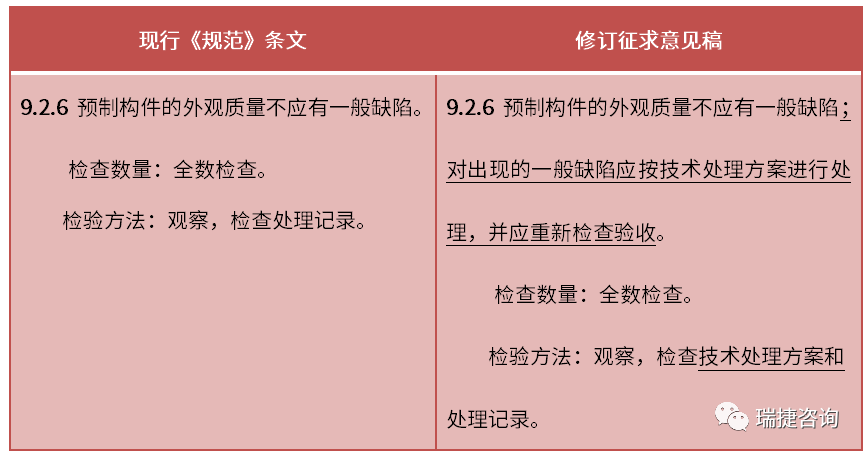
For example, article 6.2.6 of the new code supplements the inspection of the technical treatment scheme for general defects in the appearance of precast components.
Source: Draft for comments on code for acceptance of construction quality of concrete structures ▲ code for acceptance of construction quality of concrete structures The newly revised specifications of the old and new rules and regulations are more in line with the market.
The forming process of the rough surface of precast components washed by water is complex and the process is cumbersome.
The flushing tank must be set in the factory, and the components need secondary transportation, which will also cause some pollution.
The newly revised specification shall supplement the rough surface form according to the actual situation, and the methods of roughening, roughening and indentation can be adopted.
The new regulation 9.2 Article 8 revised the number of keyways of precast components and the treatment of rough surfaces.
02 pain point analysis precast building is the transformation and upgrading of the industry, the construction mode has changed from traditional manual operation to industrialized construction, and the management mode has also changed from extensive to fine.
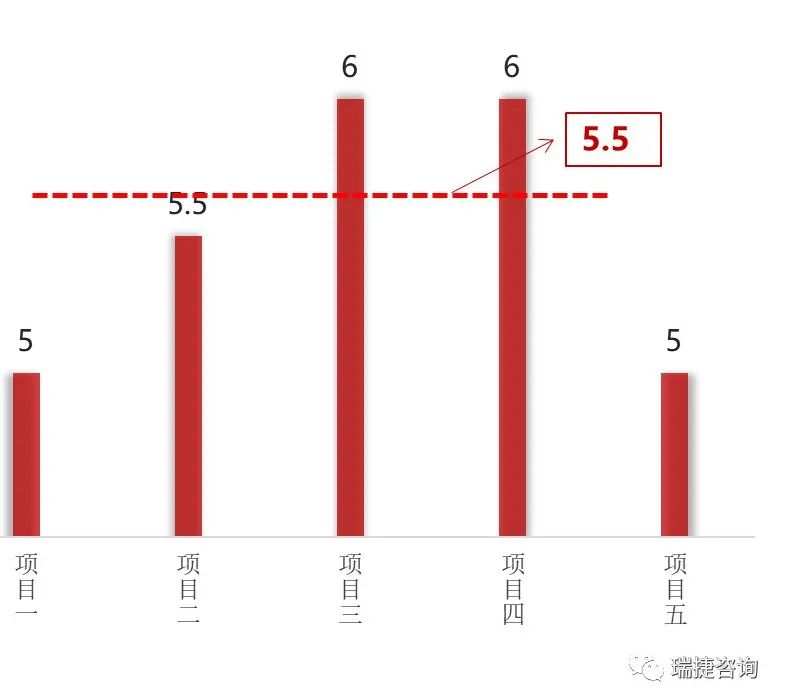
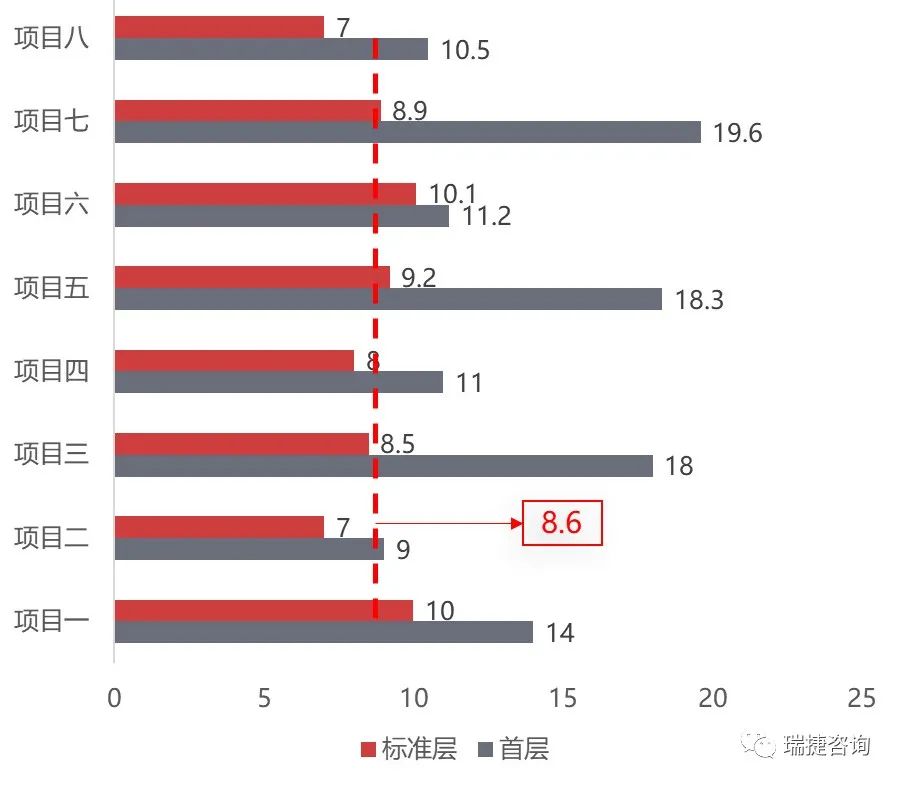
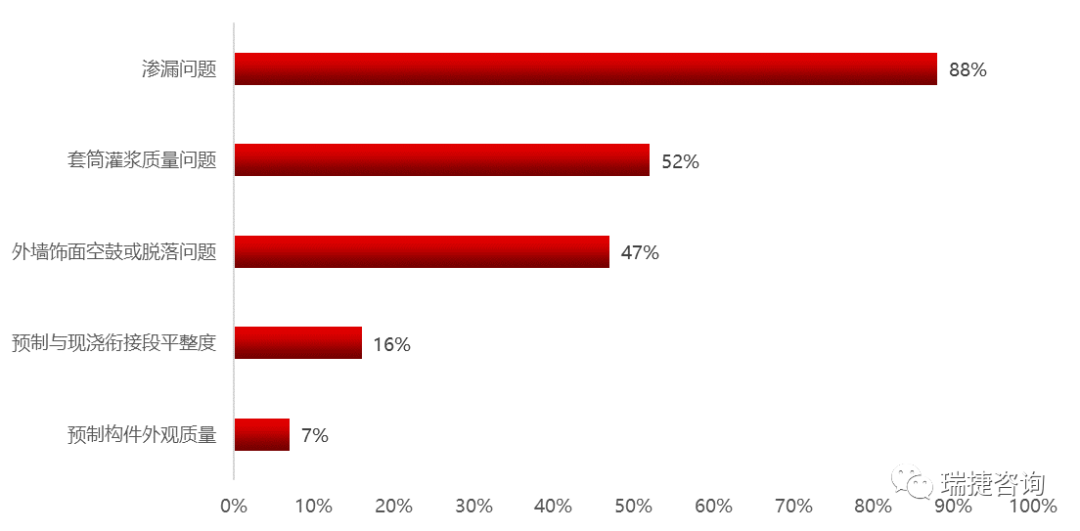
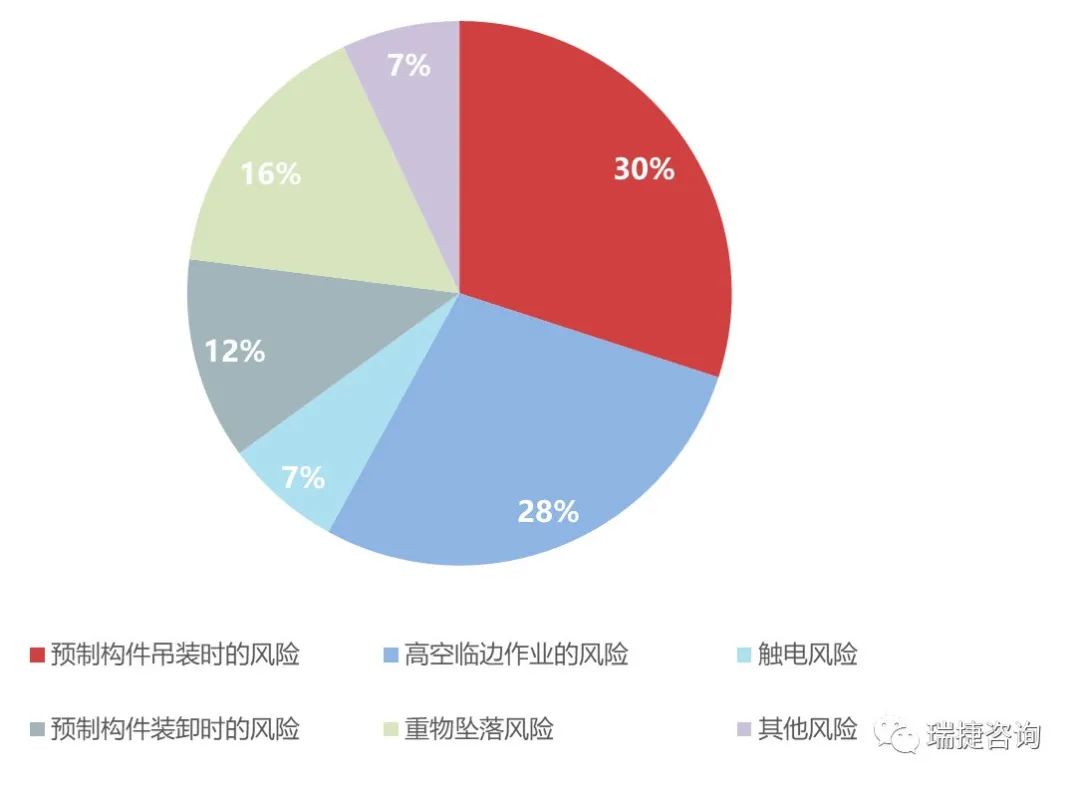
As China’s precast buildings are in the primary stage, compared with the traditional cast-in-place method, there are many pain points in the implementation process, such as high cost, long construction period, uneven quality, high safety risk and so on.
The cost of precast projects is higher than that of traditional cast-in-situ projects.
The cost is the constraint point.
Compared with cast-in-situ buildings, precast buildings have high integration and higher technical requirements.
The connection of all links from design, production, transportation to construction is not smooth, which will increase the cost.
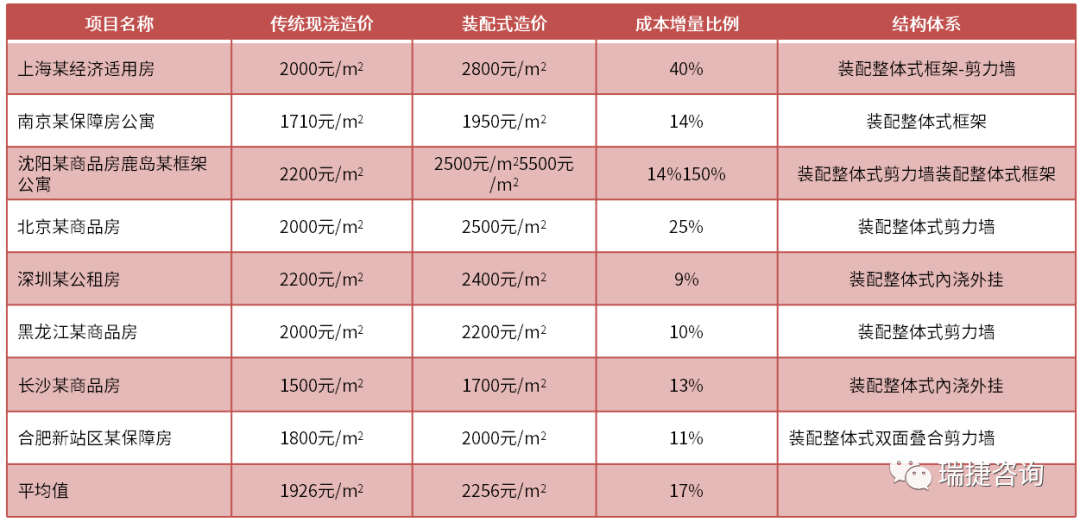
Due to the low level of standardization, integration, modularization and industrialization of precast buildings in China, the cost of precast concrete buildings is higher than that of cast-in-situ buildings, and even more than 30% in some areas or projects..



