In order to further improve the popularization rate of automatic manufacturing of non-standard components in port machinery products and improve the current situation that the manufacturing of non-standard products of shore bridge completely depends on manual work, the application limitations of traditional welding robots in non-standard components are analyzed, and the difficulties and pain points of realizing automatic manufacturing of non-standard components are clarified.

3D visual recognition technology and intelligent composite sensing mode are adopted to realize the intelligent recognition, tracking and welding functions of welds with different shapes such as arc, circle and ellipse of non-standard lifting lug components, so as to effectively improve the welding efficiency of structural parts and make the production process smoother.

Introduction Shanghai Zhenhua heavy industry (Group) Co., Ltd.

(ZPMC), as a well-known enterprise in the heavy equipment manufacturing industry, its shore container bridge crane (shore bridge) products account for more than 70% of the global market.

The structure of shore bridge is complex, and a large number of lifting and transfer operations are involved in the process of structure manufacturing and structure transfer; After the production of shore bridge products, the whole machine is shipped on board, which also involves a large number of shipping and binding operations.

Therefore, a large number of lifting lug components are designed on the shore bridge structure for lifting and binding operations.
At the same time, according to the needs of users, the lifting capacity and design requirements of different shore bridge products are different, resulting in different lifting capacity of lifting lug components, and various lifting lug sizes and weld types.

As the lifting lug component is a typical small non-standard product of shore bridge, it can not rely on traditional robots to realize the intelligent production of lifting lug.

At present, it still completely depends on labor and the production process is backward.
A large number of welders are required to ensure the progress.

The welders have high labor intensity and unstable welding quality.

A large number of welding repair and grinding operations are required after welding.

At this stage, with the labor cost rising year by year, the situation of “difficult recruitment and labor shortage” of high-risk types of work such as welders and grinders is becoming more and more prominent.

In the production of shore bridge product components, it is urgent to use automatic production technology to reduce personnel, increase efficiency and reduce production costs.
In recent years, with the development of high-efficiency welding methods and flexible welding systems, traditional welding robots are widely used in automobile and steel structure industries because of their advantages of high stability, high production quality and high efficiency.

Through teaching, arc tracking, laser tracking and other weld tracking methods, single pass automatic welding of thin plate can be realized, but there are few successful examples of welding robots applied to non-standard products, The reason is that the traditional welding robot has the limitations of long teaching time, complex programming and high assembly requirements on non-standard products.

It is difficult to ensure the production efficiency while realizing the automatic production of non-standard components.
Moreover, the traditional robot has high requirements for workers’ programming operation and is not suitable for the automatic production of industrial non-standard components.
At present, laser tracking and arc tracking are mostly suitable for the welding of single weld.
How to realize the autonomous welding of port crane lifting lug components based on traditional robots is an urgent production pain point for enterprises.
The robot feasibility test of the lifting lug component shows that the overall production efficiency of the traditional teaching robot is low; At present, the fastest parametric programming also requires the operator to input the corresponding size according to the component size information before welding, call the corresponding welding process, and need the tooling fixture suitable for the workpiece for positioning, resulting in a large workload of pre welding assembly.
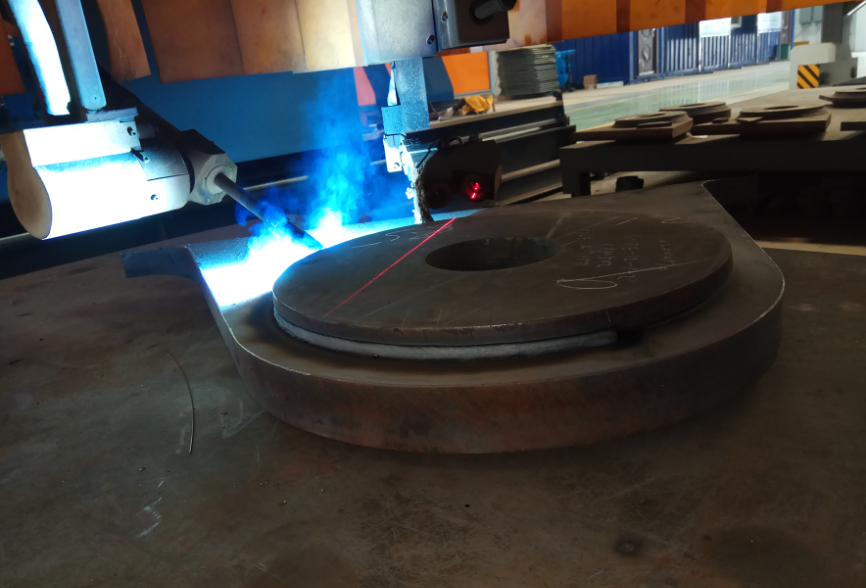
Therefore, for the structural parts of the lifting lug of the port machinery, a composite sensing method of visual panoramic camera recognition technology combined with 3D laser vision technology is proposed to achieve the purpose of accurate measurement and tracking of the weld and eliminate the pre welding programming teaching link.
In addition, through the matching of workpiece contour and groove size information model, combined with a variety of intelligent functions such as automatic motion path planning, automatic sequencing of welding sequence, automatic arrangement of weld bead and automatic call of process specification, the teaching free intelligent welding of lifting lug components with different shapes such as arc, circle and ellipse can be realized quickly.
Through the combined application of 3D visual recognition technology and multi-layer and multi pass automatic welding process, the labor intensity of manual operation can be significantly reduced, the weld forming quality can be improved, and there is no need to polish and repair after welding, which not only saves the cost of labor and welding materials, but also improves the production efficiency by more than 40%.
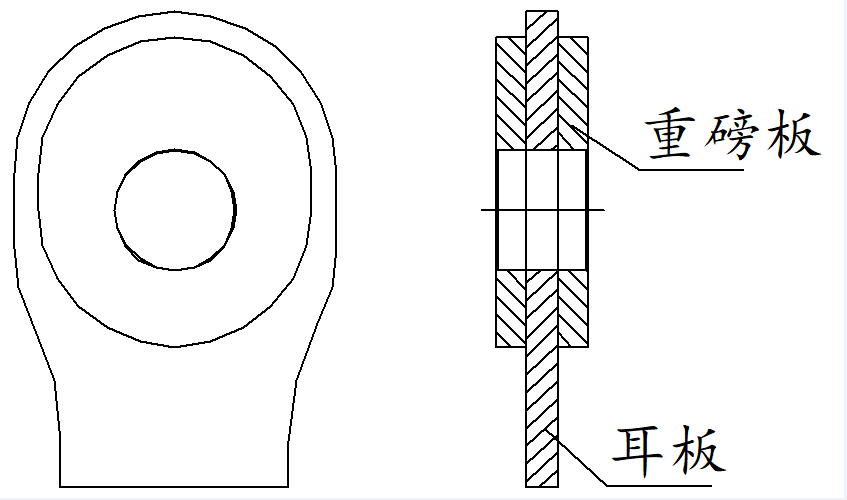
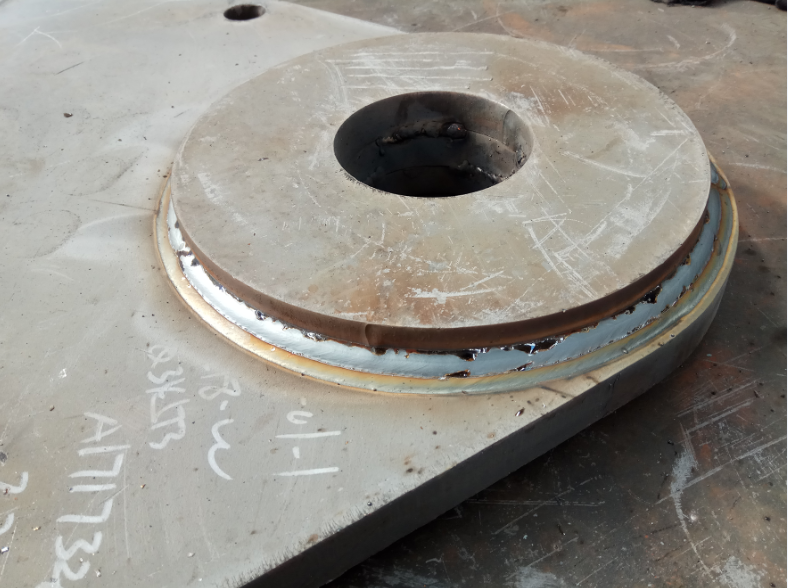
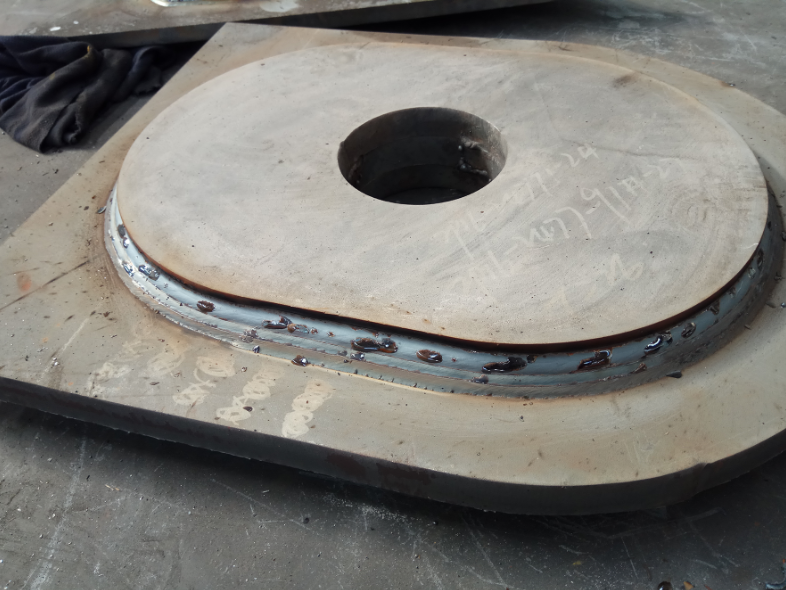
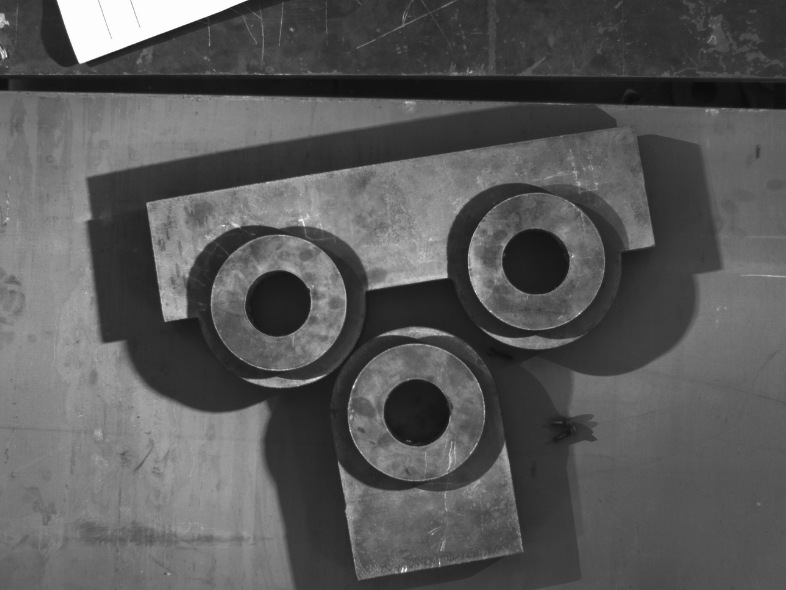
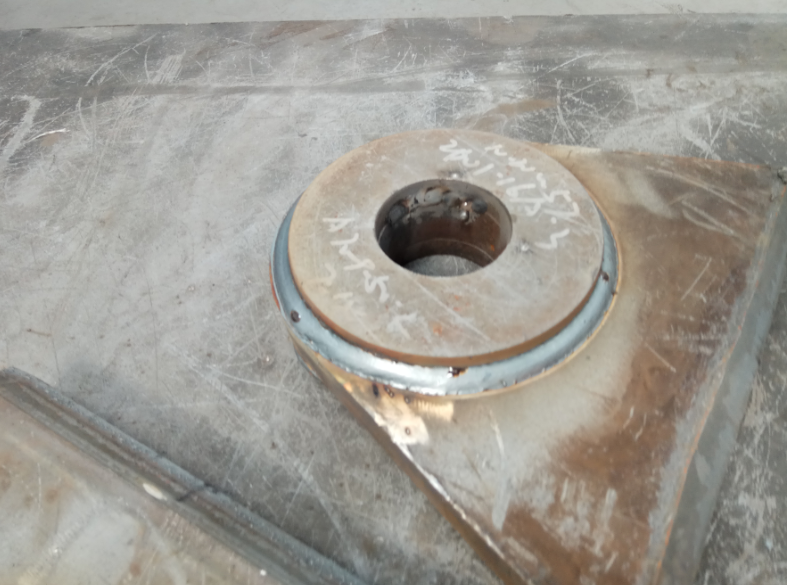
Test content 1.1 test materials and methods the lifting lug component is mainly composed of 1 padeye and 2 heavy plates, which play a reinforcing role.
According to the lifting capacity of the lifting lug, welding grooves of different sizes are set on the heavy plate to improve the stress strength.
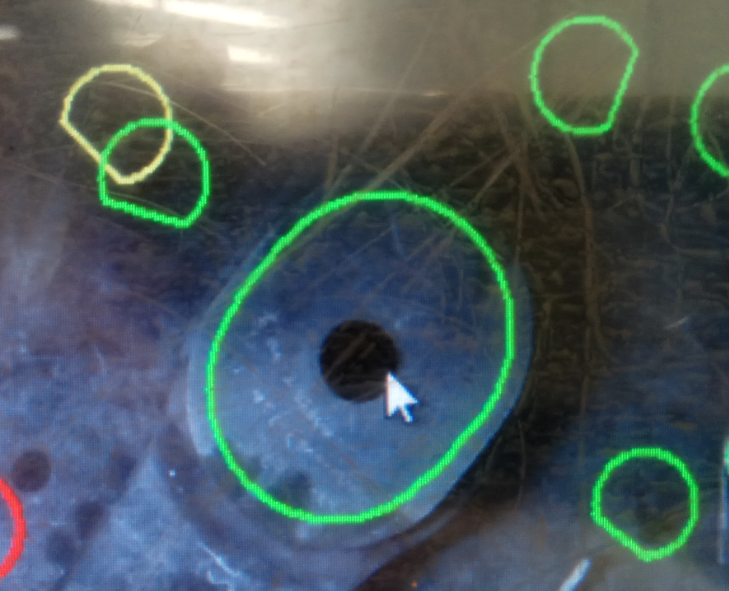
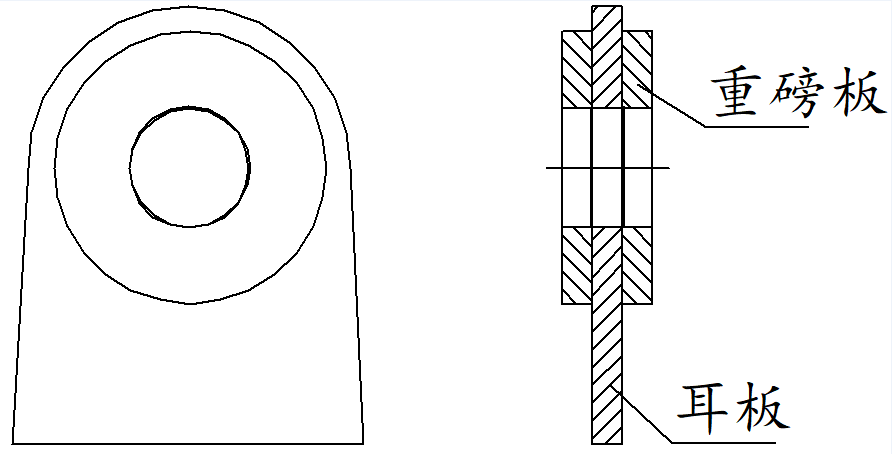
According to different connection positions, there are many structural types of lifting lug components, mainly circular, oval and circular missing lifting lugs, with different sizes.
See Figure 1 for the type of lifting lug components.
(a) Round lifting lug (b) oval lifting lug (c) round missing lifting lug Fig.
1 , the type of lifting lug component is to study the feasibility of the application of 3D vision technology on different types of lifting lug components.
This test is aimed at three types: round, round missing and oval.
The base material of the test is Q345B.
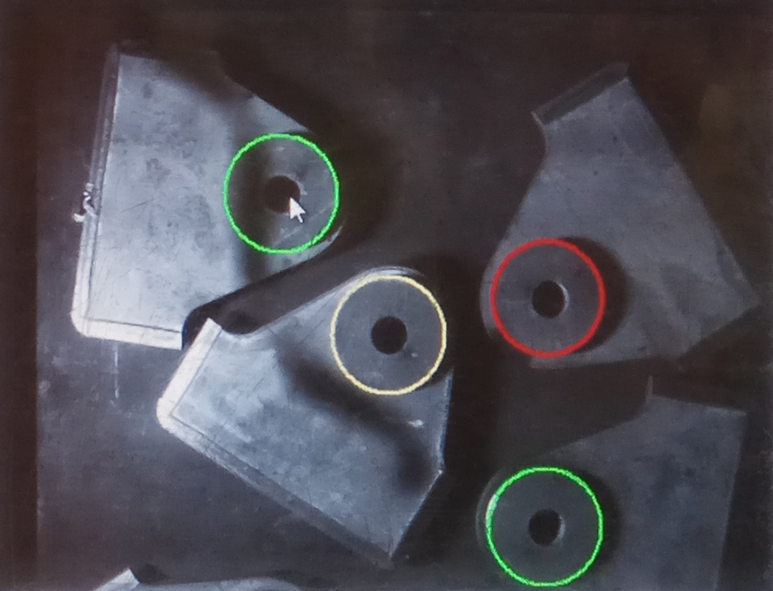
One specification is selected for the comparative test of image recognition and weld positioning function, and according to the groove size of its heavy plate, A comparative test of laser identification, tracking and welding was carried out for grooves of different sizes (0mm, 12mm, 14mm and 16mm).
See Table 1 for the dimension information of shore bridge lifting lug test piece.
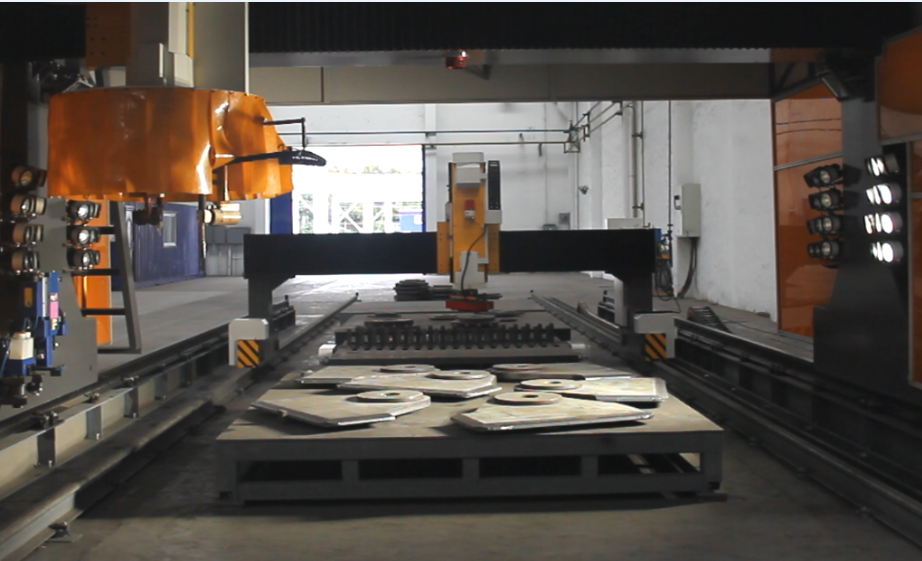
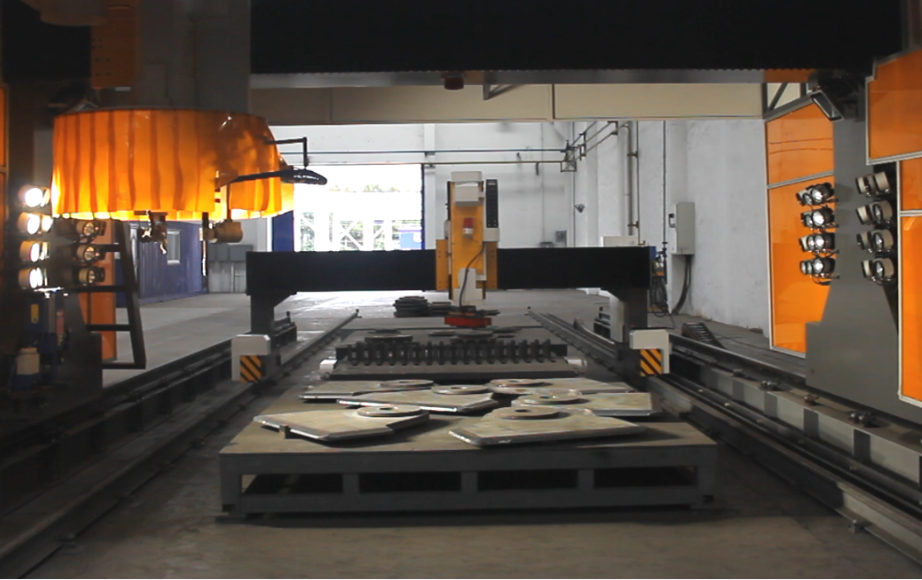
Table 1 size information of lifting lug test piece of shore bridge this test is conducted by using intelligent robot equipment with 3D intelligent image vision and laser recognition function to study the feasibility of the application of visual photographing recognition and laser recognition and tracking technology in actual production.
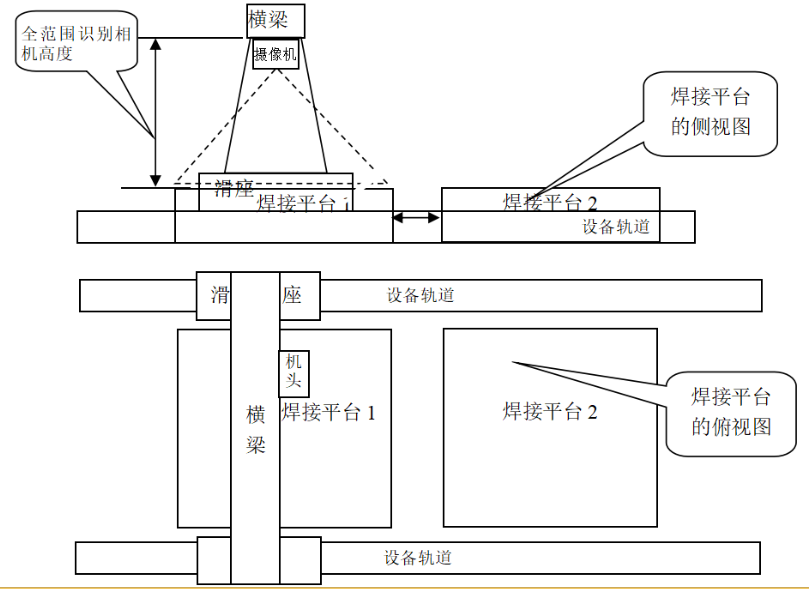
The intelligent visual recognition robot is mainly composed of gantry, equipment track, welding machine head and welding platform.
It mainly relies on the camera installed in the middle under the beam to take overall visual photos and locate the welding platform, and the field of vision just covers the large and small range of a welding platform..


