The reinforcement of the slab is the simplest and easiest to understand in the reinforcement system of the whole building, followed by the wall, and then the column beam.
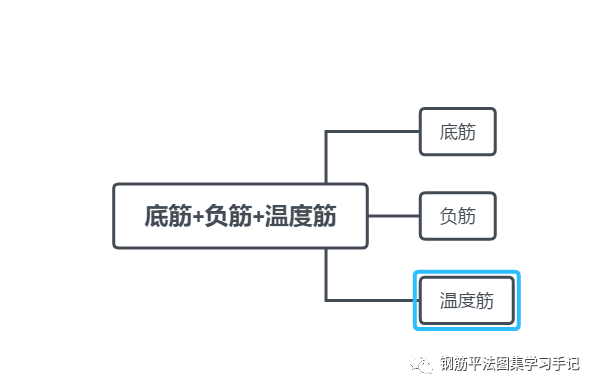
In the floor slab and roof slab, according to the different stress characteristics of the slab, the reinforcement configured is also different, mainly including lower stress reinforcement, bearing negative reinforcement, structural reinforcement, distribution reinforcement and temperature shrinkage stress resistant structural reinforcement.
In Guanglianda gtj, it is divided into bottom reinforcement, gluten reinforcement, temperature reinforcement, negative reinforcement and cross plate stress reinforcement.
The simple classification is as follows; Two way bottom reinforcement + negative reinforcement + bottom reinforcement + negative reinforcement + temperature reinforcement often have several problems.
One is that the slab reinforcement should be drawn in full length.

In line with the principle of being general, it is not necessary to arrange the single plate, which will have more quantities.
Let’s start with the bottom rebar.
The anchoring principle of the bottom rebar is that the anchoring length extending into the support is not less than 5D, and it should extend beyond the center line of the support.
For example: generally, the bottom rebar of the plate is 8 or 10 in diameter, and 5 times the diameter of 10 is 50mm, while the general beam width is 200mm or more, and half of the beam width is 100mm.
Therefore, most of the bottom rebar of the plate should extend to the center of the beam.
It happens that the rebar on the other side also extends to the center of the beam, so they are continuous in space, The effect of most layout is the same as that of single slab layout.
If 5D is much longer than half of the length of the beam center, the amount of reinforcement will be calculated more.
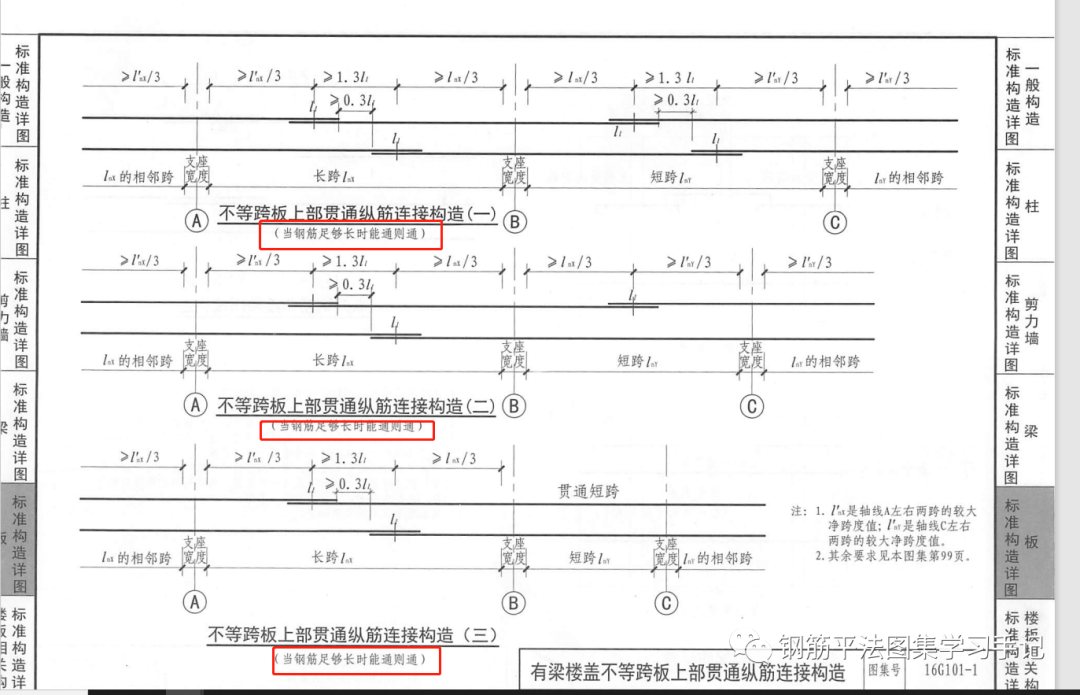
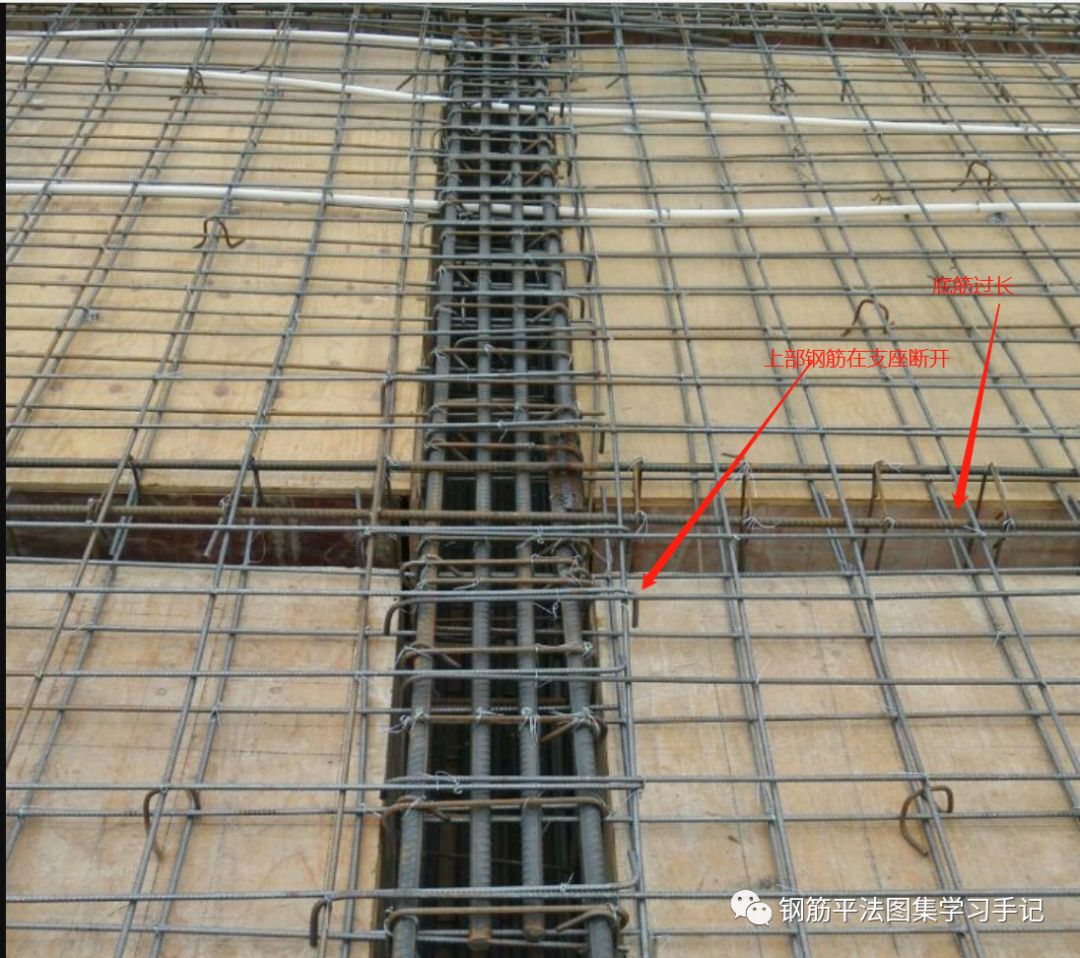
If the plate top reinforcement is arranged in a single plate, it will be anchored around the plate for 15d, which is inconsistent with the actual situation, so it should be pulled through if it can be pulled through.
During the actual construction on site, if the slab top reinforcement is not long enough, it will be overlapped and connected in the middle of the slab span.
Of course, this part is necessary for construction overlapping.
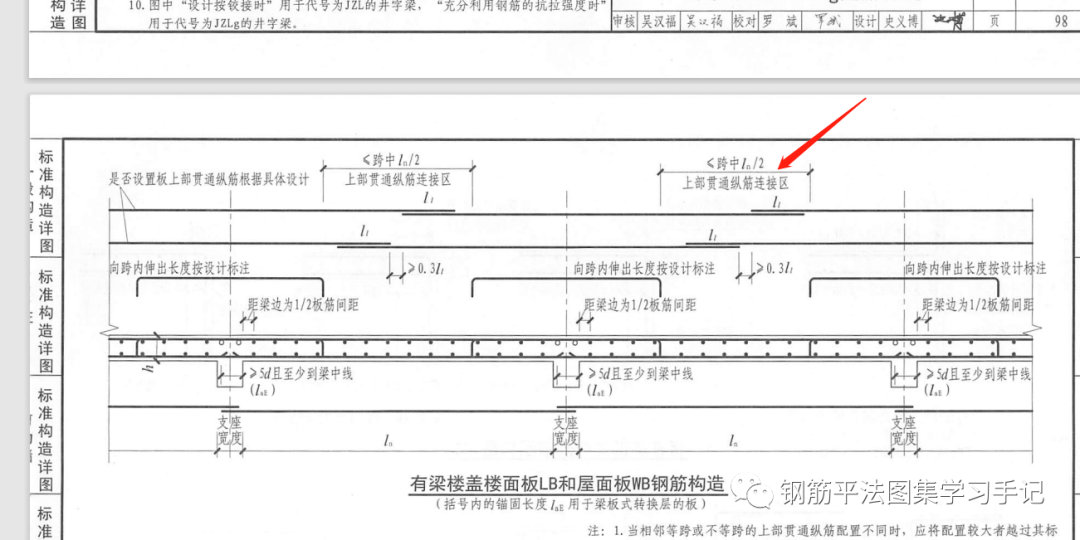
Negative reinforcement and cross slab stress reinforcement have one thing in common, that is, they have their own distribution reinforcement, and cross slab stress reinforcement is the combination of slab reinforcement and negative reinforcement.
Although it is combined, it is still necessary to distinguish which should be used.
If it is gluten, it should be arranged with gluten.
It is not convenient to use cross slab stress reinforcement to adjust the extension length of both ends to 0, because once there is no top reinforcement in the opposite direction, the work quantity of distribution reinforcement will be calculated.
The distribution reinforcement of negative reinforcement shall be overlapped with the stressed reinforcement by 150mm.
Lap joint of temperature reinforcement and stress reinforcement LL.
Finally, add the concept of one-way board and two-way board, which you should have learned at school and review again.
A slab supported on four sides is a two-way slab when the ratio of the long side to the short side is less than or equal to 2; For the slab supported on four sides, when the ratio of long side to short side is greater than 2 but less than 3, it should be considered as a two-way slab; For the plate supported on four sides, when the ratio of long side to short side is greater than or equal to 3, it should be considered as one-way plate; Why mention this, because some drawings really arrange distribution reinforcement for you according to two-way slab and one-way slab.
When you need to check the one-way reinforcement, you only need to check the one-way reinforcement.
When you need to design the one-way reinforcement, you can only know the short reinforcement…



