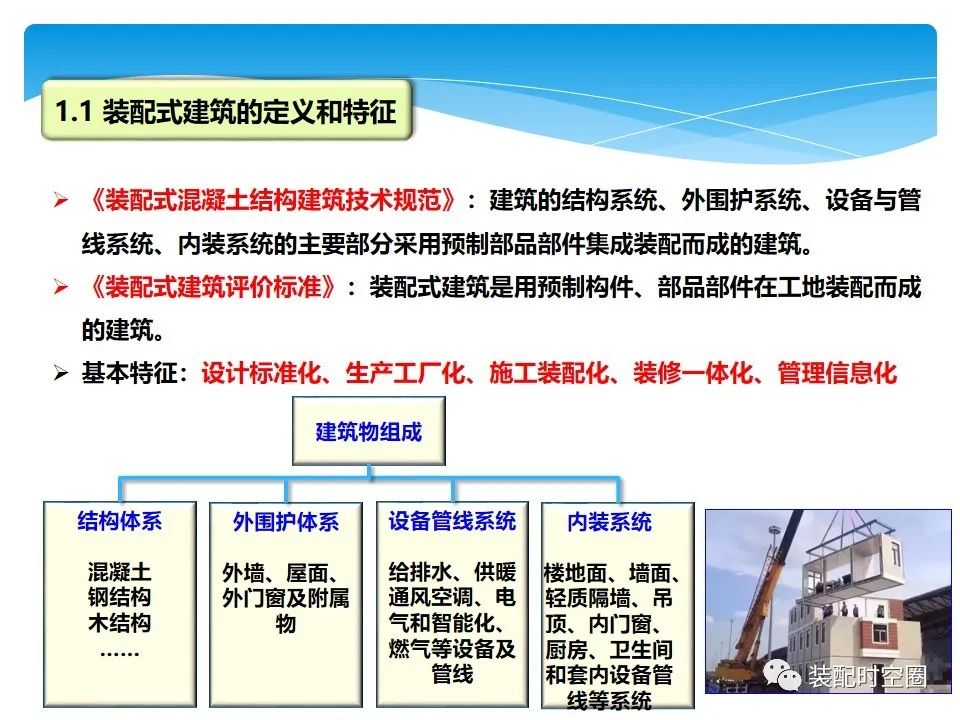
Technical code for precast concrete structure buildings: the main parts of the building’s structural system, peripheral protection system, equipment and pipeline system and interior decoration system are integrated and assembled by precast components.
Evaluation standard for precast buildings: precast buildings are buildings assembled on the construction site with precast components and parts.

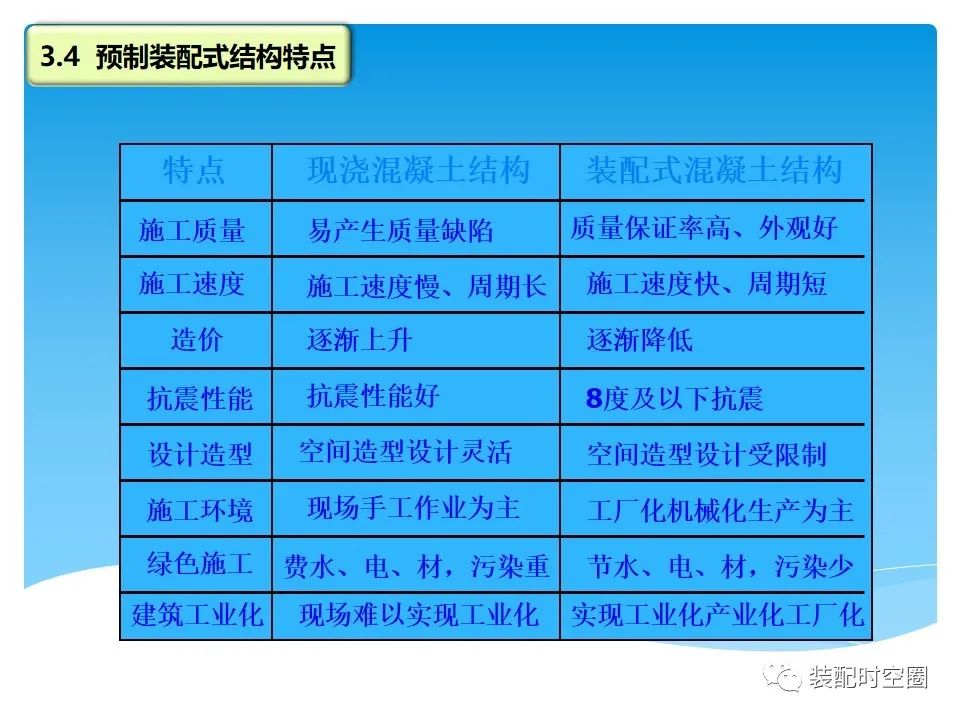
Basic features: design standardization, production industrialization, construction assembly, decoration integration, management informatization, rising labor cost, reducing labor intensity and improving operating conditions; Requirements for energy conservation and environmental protection: greatly reduce construction waste, reduce noise pollution and save water; Technology has gradually matured and economic strength has gradually increased; The requirements for building function and quality are improved.
Precast frame structure refers to that beams, plates and columns are composed of precast concrete components, and structural hoisting is carried out on site: it is mainly used in factories, warehouses, shopping malls, parking lots, office buildings, teaching buildings, medical buildings, business buildings and other buildings requiring open space.

In recent years, it is also gradually applied to residential and other civil buildings.

1.
Coordination of various disciplines in the scheme stage; 2.

Architectural and structural design principles: standardization, modularization, less specifications and more combinations; Structural integrity, durability, high strength and high performance material application; Reasonable prefabrication and disassembly; 3.
Seismic fortification standard; 4.
Detailed design requirements.

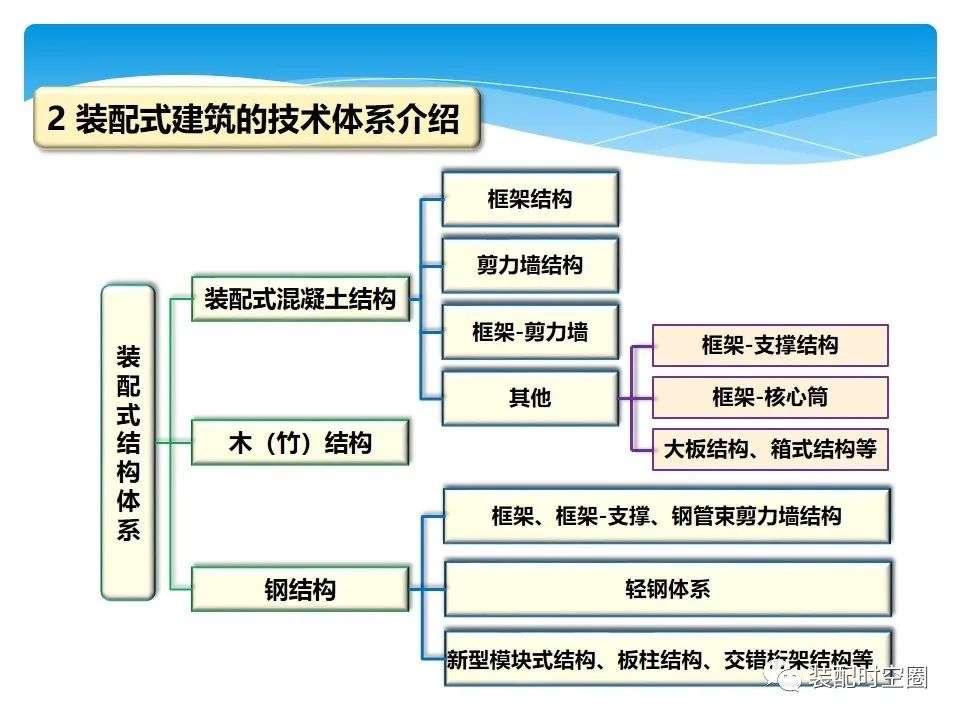
One dimensional component: (precast beams and columns into one-dimensional components and connected by certain methods) advantages: convenient component production and construction, good structural integrity and equivalent to cast-in-situ structure; Disadvantages: the joint is located at the key stress position, and the connection requirements are high.
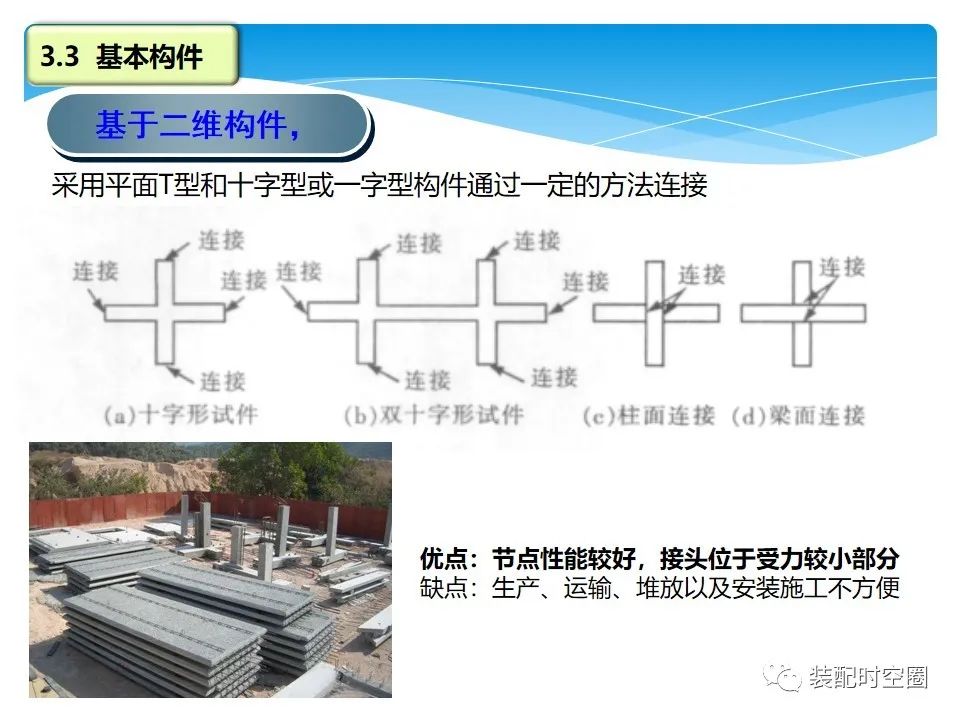
Two dimensional members: (plane T-shaped and cross shaped or I-shaped members are connected by certain methods) advantages: the joint performance is good, and the joint is located in the part with small stress; Disadvantages: inconvenient production, transportation, stacking and installation.

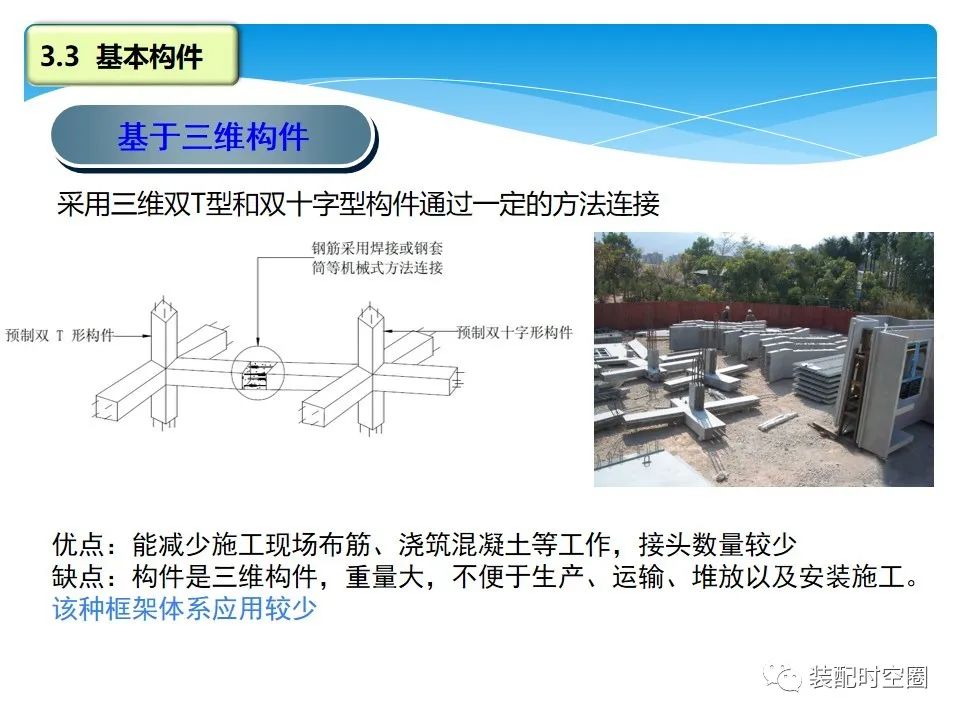
Three dimensional components: (three dimensional double T-shaped and double cross shaped components are connected through certain methods) advantages: it can reduce the work of reinforcement distribution and concrete pouring on the construction site, and the number of joints is less; Disadvantages: the component is a three-dimensional component with large weight, which is not convenient for production, transportation, stacking and installation.

This kind of framework system is rarely used.

Regulations: rough surface and keyway shall be set on the joint surface between precast components and post cast concrete, grouting materials and setting materials.

The rough surface area shall not be less than 80% of the joint surface, the rough surface concave convex depth of precast slab shall not be less than 4mm, and the rough surface concave convex depth of precast beam end, precast column end and precast wall end shall not be less than 6mm.
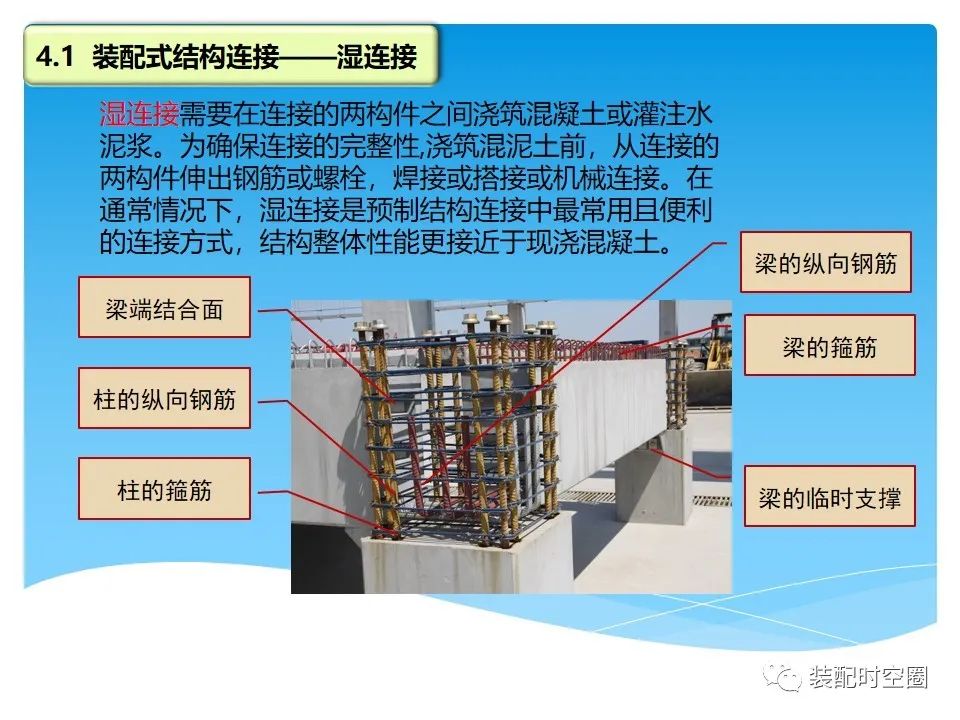
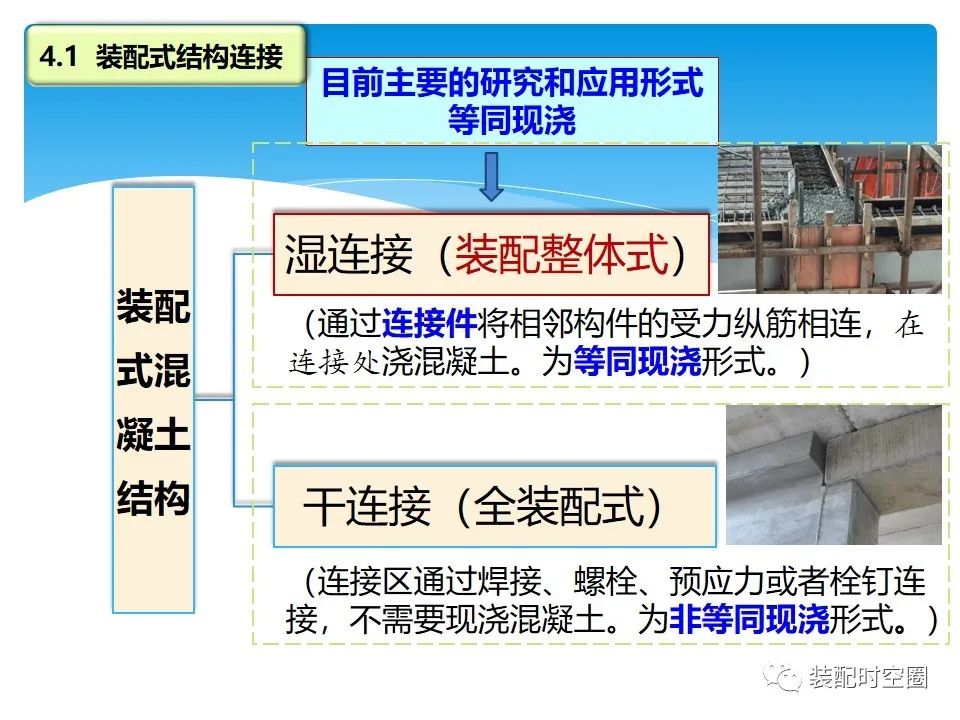
Wet connection requires pouring concrete or pouring cement slurry between the two connected components.

In order to ensure the integrity of the connection, before pouring concrete, the reinforcement or bolt shall be extended from the two connected members, welded or overlapped or mechanically connected.

In general, wet connection is the most common and convenient connection method in precast structure connection, and the overall performance of the structure is closer to that of cast-in-situ concrete.

Dry connection is to achieve the purpose of connection by embedding steel plates or other steel components in the connected components and connecting them by bolts or welding.

Dry connection makes the overall performance of the structure more loose.

Considering the flexural and shear capacity, the correctly constructed dry connection has similar ductility and may have higher energy dissipation than the integral connection.

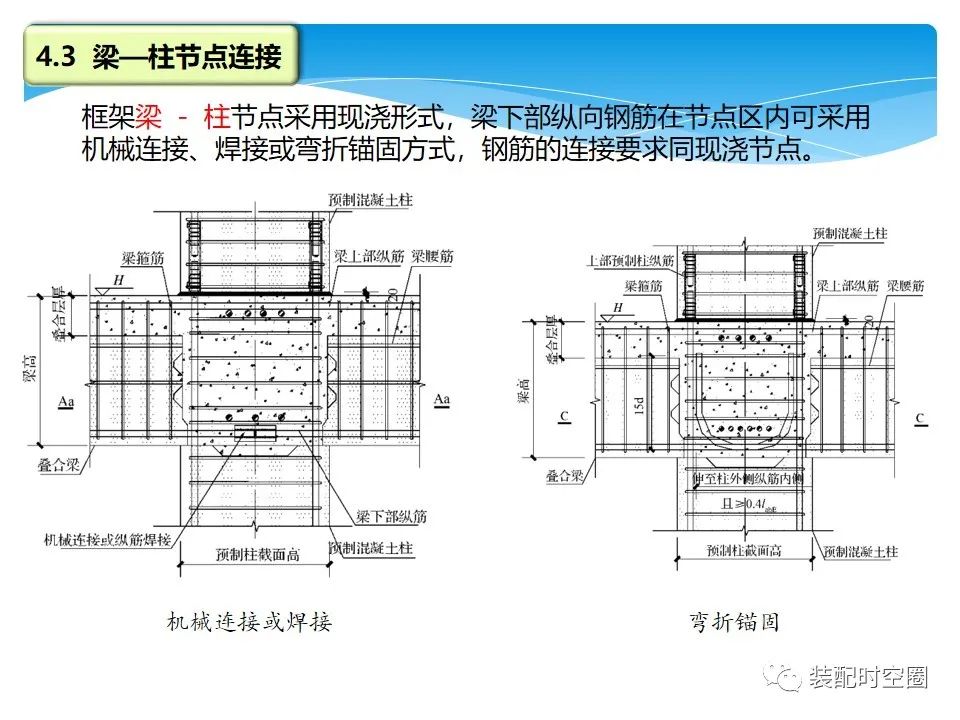
The frame beam column joint adopts the cast-in-situ form.

The longitudinal reinforcement at the lower part of the beam can be mechanically connected, welded or bent and anchored in the joint area.
The connection requirements of the reinforcement are the same as those of the cast-in-situ joint.

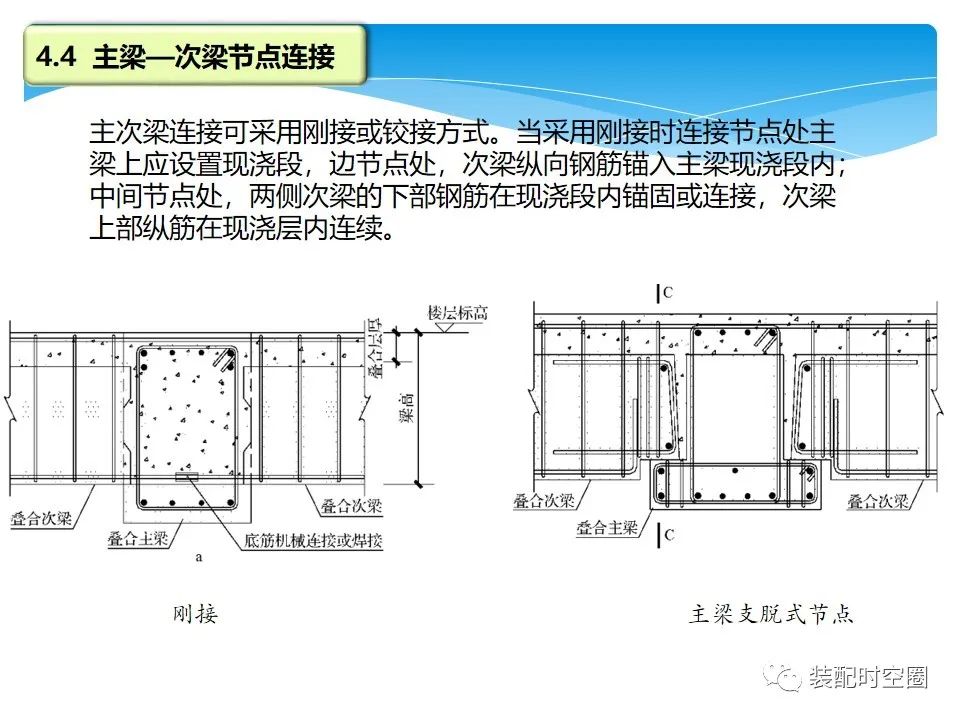
Rigid connection or hinged connection can be adopted for the connection of primary and secondary beams.

When rigid connection is adopted, the cast-in-situ section shall be set on the main beam at the connection node, and the longitudinal reinforcement of the secondary beam shall be anchored into the cast-in-situ section of the main beam at the side node; At the middle node, the lower reinforcement of the secondary beams on both sides is anchored or connected in the cast-in-situ section, and the upper longitudinal reinforcement of the secondary beam is continuous in the cast-in-situ layer.

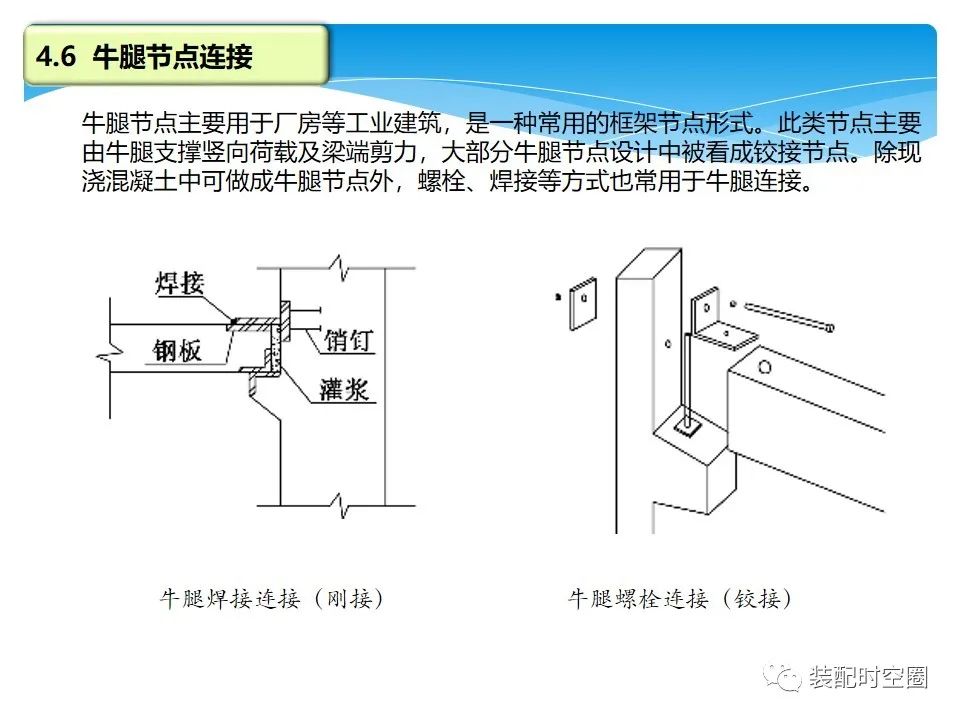
Corbel joint is mainly used in factory buildings and other industrial buildings.

It is a common form of frame joint.

This kind of joint is mainly supported by corbel, vertical load and beam end shear force.
Most corbel joints are regarded as hinged joints in design.
In addition to cast-in-situ concrete can be made into corbel joints, bolts, welding and other methods are also commonly used for corbel connections.

Welded corbel connection: the seismic performance of the welded connection is not ideal, and the weld is prone to brittle failure under repeated seismic load, so its energy dissipation performance is poor.

However, the construction method of welding connection avoids the on-site cast-in-situ concrete and the necessary maintenance, which can save the construction period.

The development of welded connection structure with good deformation performance is also the development direction of dry connection structure at present.

In order to make welding effective and reduce welding residual stress during construction, the welding process of corresponding components should be fully arranged.

Bolted corbel connection: the corbel has good vertical bearing capacity, but needs large building space and affects the building appearance, so it is used in some plant buildings; It can also be made of section steel to connect with dark corbel, which can reduce the use of space.
Bracket connection is matched with welding and bolts to form a variety of joint forms, which can be made into rigid connection form or hinged form, with a wider range of application…