The House of Philosophers pays close attention to traditional architectural culture and its contemporary value 485 original content official account In traditional Chinese architecture, columns are very important wood members.
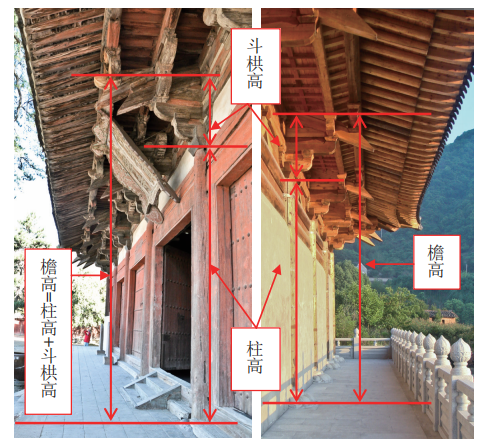
As vertical wood structural members, columns are combined with horizontal wood structural members, such as beams, purlins and braces, to form roof trusses.
It is a vertical component that bears the upper load.
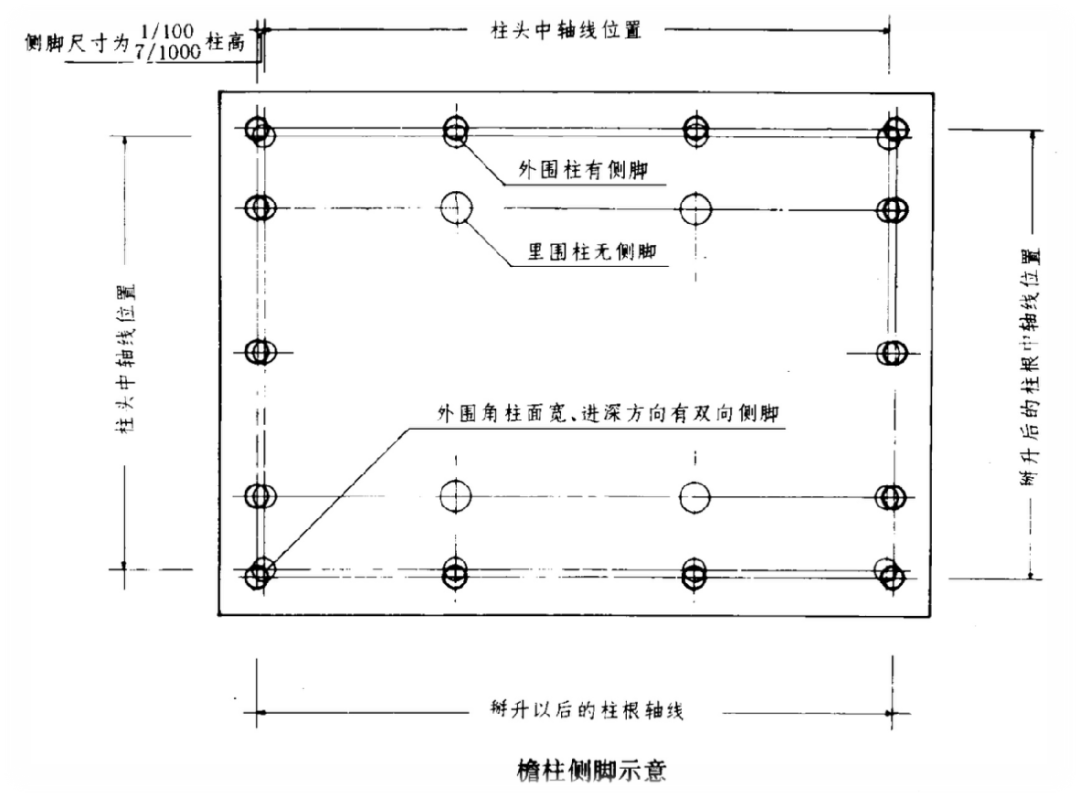
This article introduces columns: their diameter, height, distribution and side legs, and key points for their production.
Column diameter refers to the diameter of the root of the front eave (corridor) column.

In small buildings, large buildings without dougong, and some miscellaneous buildings, this diameter size is usually 1, and other dimensions are multiples of it.
In other words, it can also be said that as long as the size of the “column diameter” is available, the detailed dimensions of various parts and components of small buildings, large buildings without dougong, and some miscellaneous buildings can be calculated based on the weighing rule of the ancient people’s “modulus multiple”.
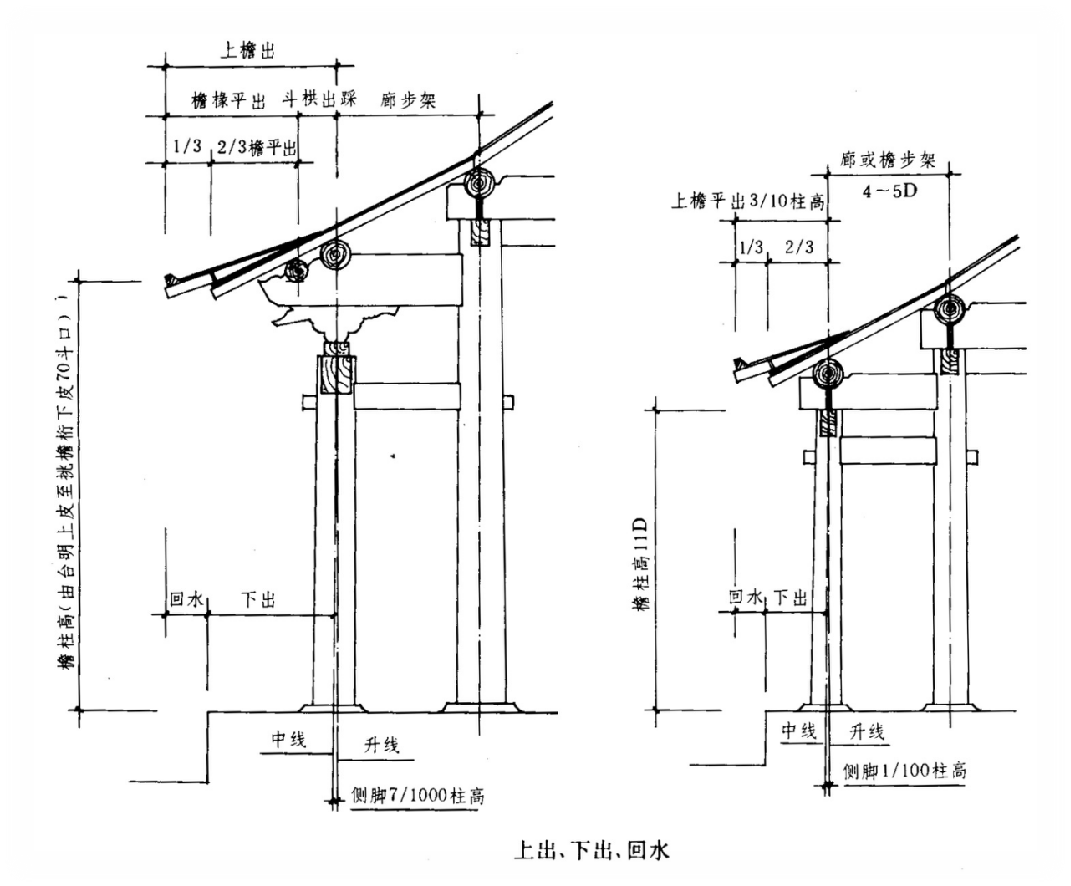
Image source of column diameter diagram: Tang Chongping’s “Introduction to Traditional Chinese Architecture Woodwork Knowledge (Part 1) – Basic Knowledge of Traditional Architecture and the Wood Structure and Dougong Knowledge of Qing Dynasty’s Qing Dynasty Official Architecture” Image source: Tang Chongping’s “Introduction to Traditional Chinese Architecture Woodwork Knowledge (Part 1) – Basic Knowledge of Traditional Architecture and the Wood Structure and Dougong Knowledge of Beijing’s Qing Dynasty Official Architecture” The determination of column diameter in small buildings: the ratio to column height is 1:11 (if the column diameter is 270mm, the column height is 3000mm).
Determination of column diameter for large buildings: According to the Qing style practice, it is specified as 6 bucket openings.
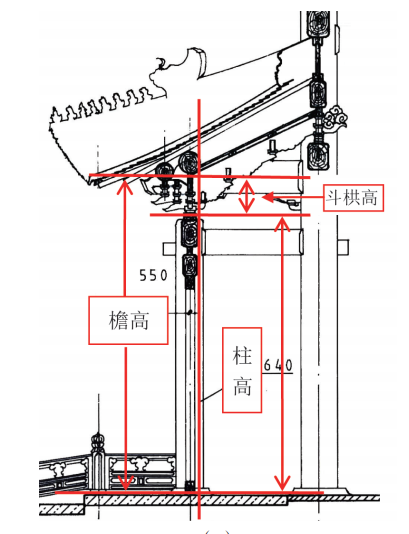
The height of columns varies between large and small buildings.
The column height of a small building is the height from the foundation of the building (Ming) to the column head (lower skin of the beam).
(1) The column height of a small building is the height from the foundation of the building (exposed) to the column head (under the beam), as shown in the following figure.
Image source of column height in Qing style architecture: Tang Chongping’s “Introduction to Traditional Chinese Architecture Woodwork Knowledge (Part 1) – Basic Knowledge of Traditional Architecture and Knowledge of Wood Structures and Dougong in Qing style Architecture in Beijing”.
One thing to note here is that in weighing scales, writings, and design drawings, the column height refers to the entire height from the top of the stone platform to the column head, which actually includes two parts of height.
One is the height of the pure wooden column, The second is the height of the drum diameter part at the top of the stone (occasionally made of other materials) column.
In terms of woodworking construction, column height specifically refers to the height of pure wooden columns.
Whether engaged in design or construction, this difference must be mastered
.



