Chinese architecture happyNewYear is an important special component in the bucket arch of ancient Chinese wooden architecture.

It is called feiang in the construction method.
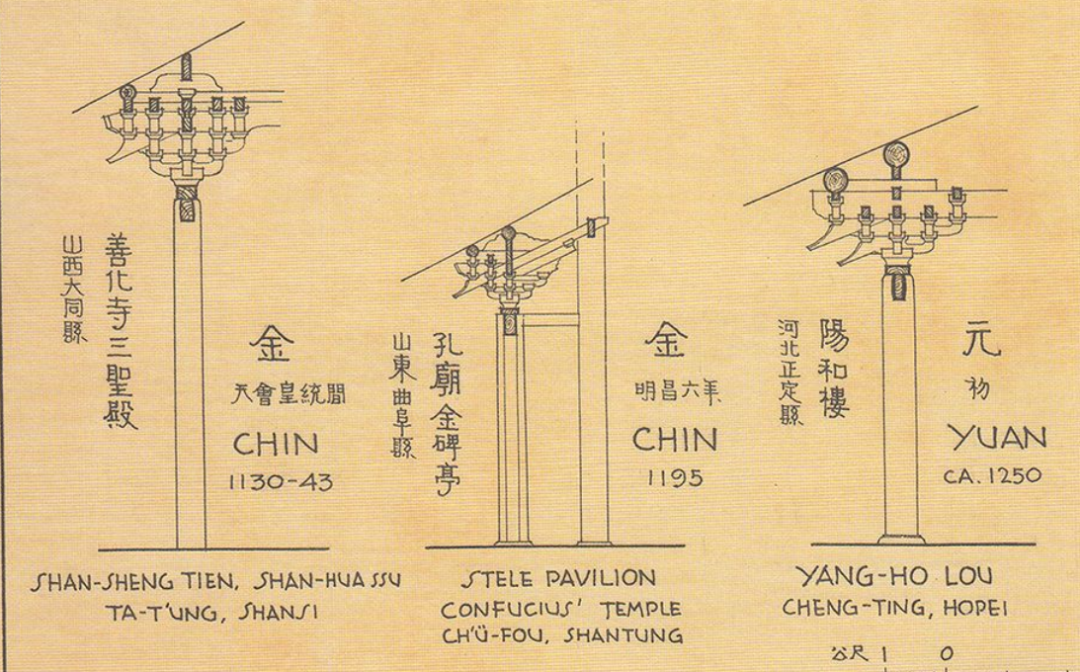
Its name has five, one is Yi (FIR), two is feiang, three is Yingang, four is oblique angle and five is xiaang.
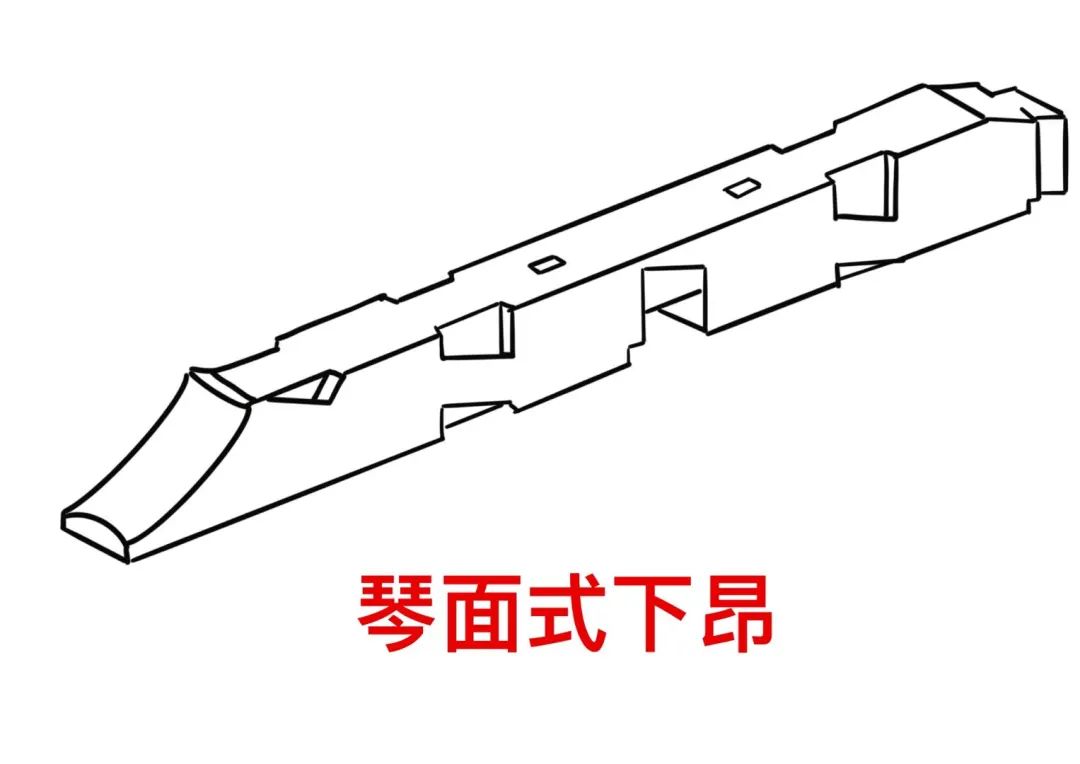
The type names of ang: lower ang, upper ang, true ang, false ang, piano face ang, batch bamboo ang, elephant trunk ang, Ruyi ang, Longtou ang, square head ang, oblique ang, flat out ang, horn ang, insert ang, you ang, head playing ang, etc.
Ang originated from the inclined beam and has taken shape in the architecture of the Han Dynasty.

It was in the development period of Xia ang components in the northern and Southern Dynasties and has been skillfully used in the Sui and Tang Dynasties.
In the early buildings, the head shape of the front end of the ang shaped component was relatively simple, and the ang surface was flat.
Later, it developed into various artistic shapes.
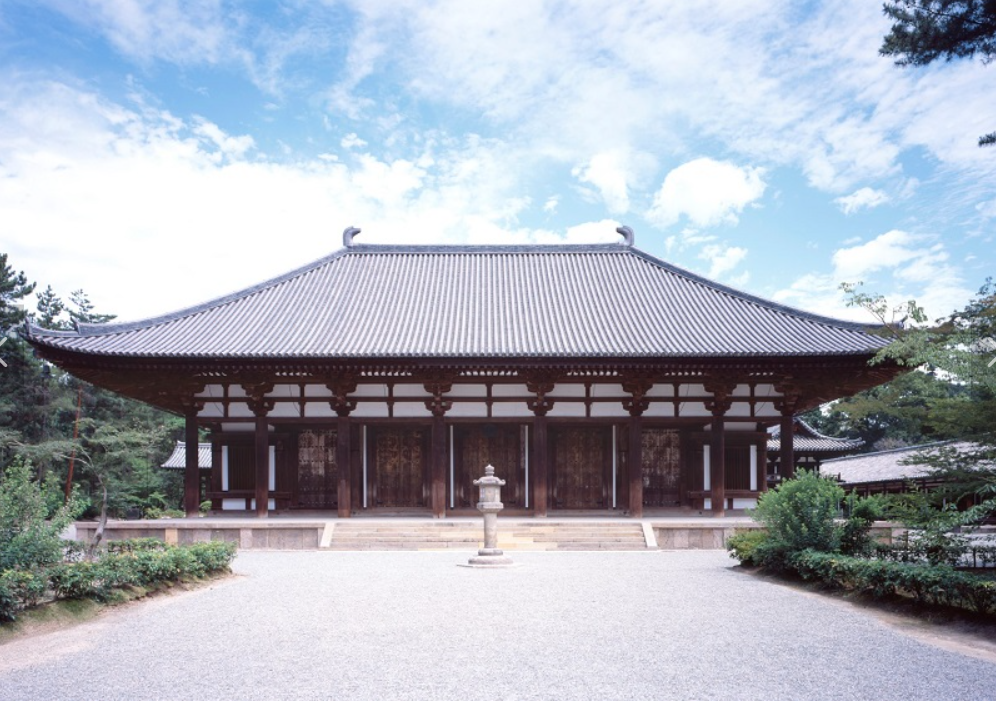

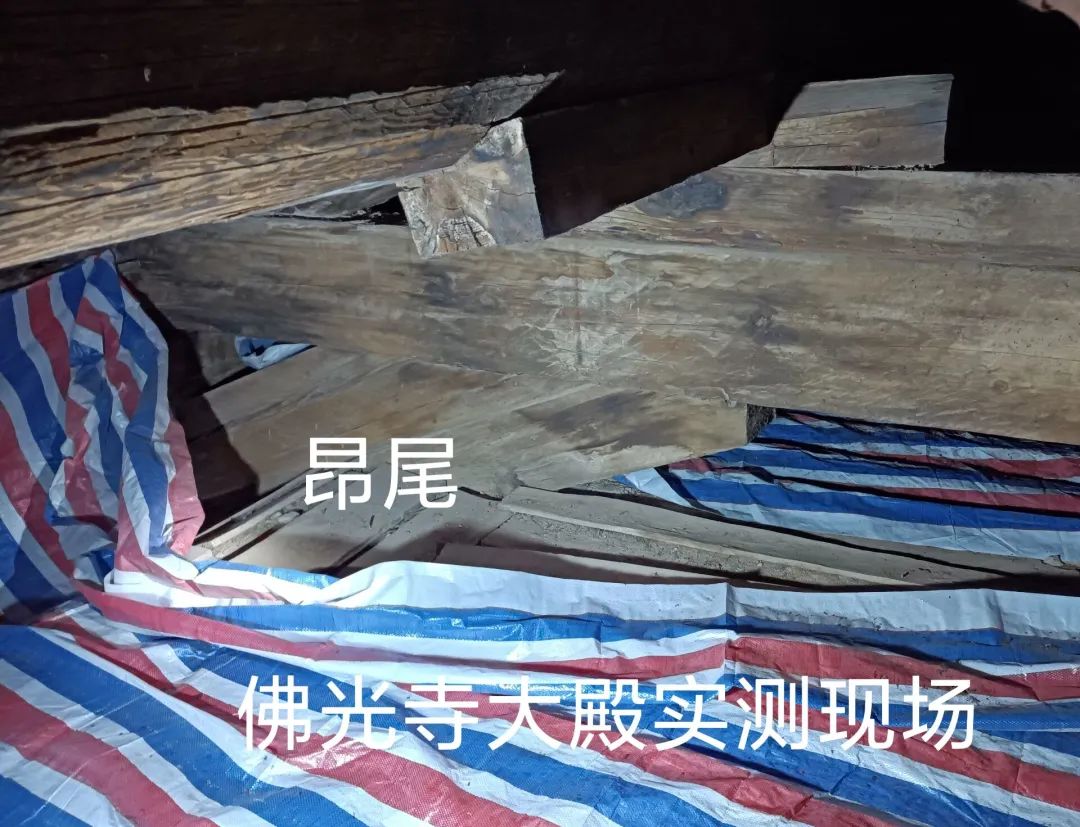
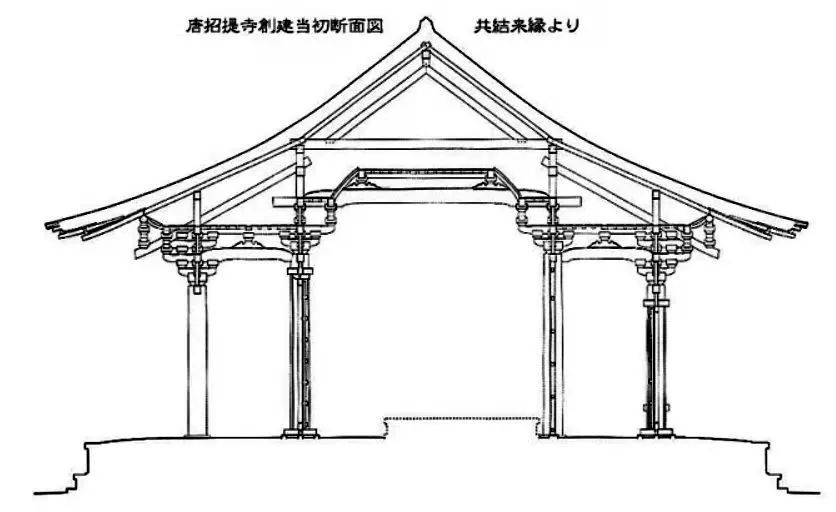
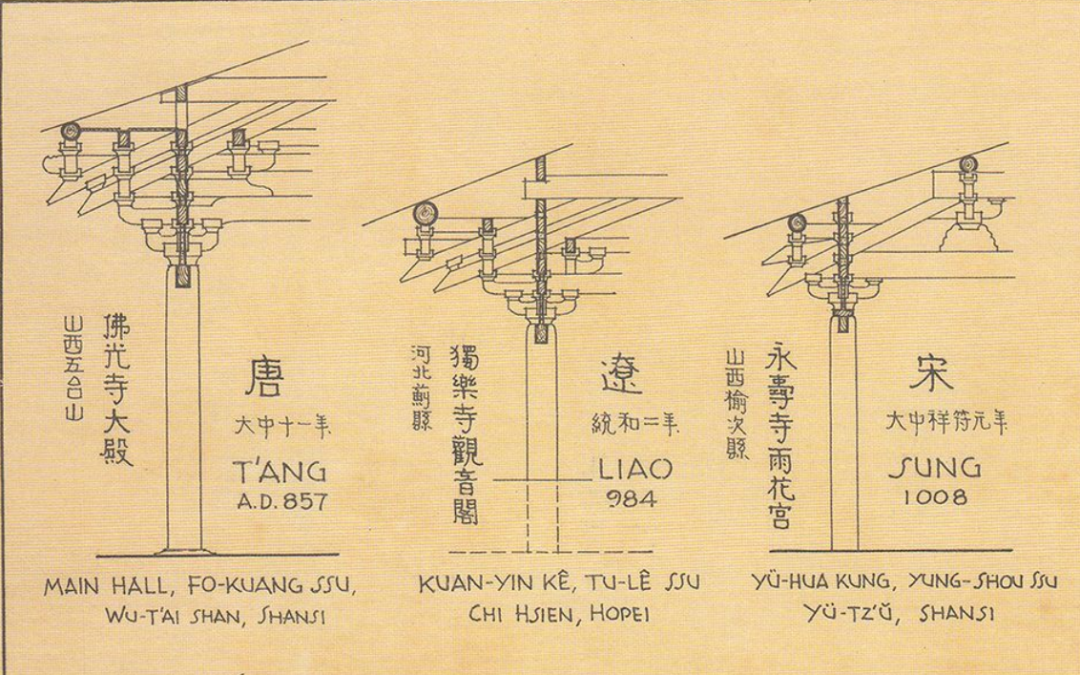
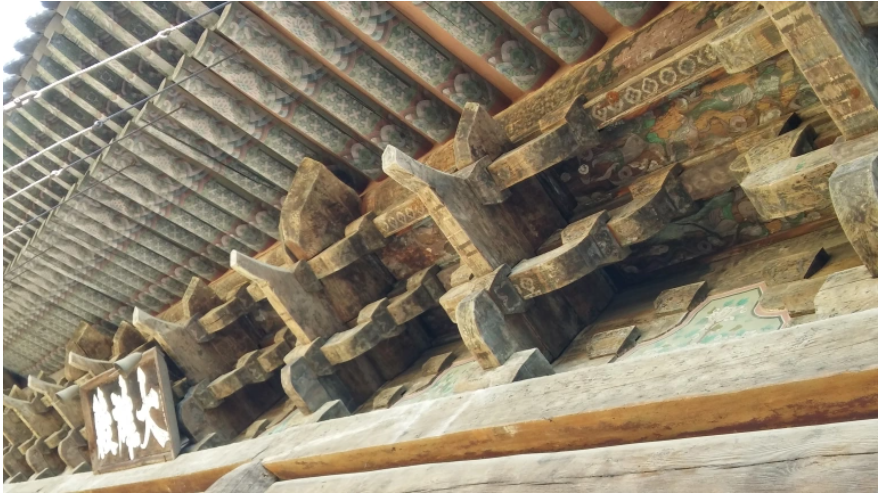
The Tang Dynasty Dougong in the East Hall of Foguang temple in Wutai, Shanxi Province is the earliest existing example of xiaang component in China.
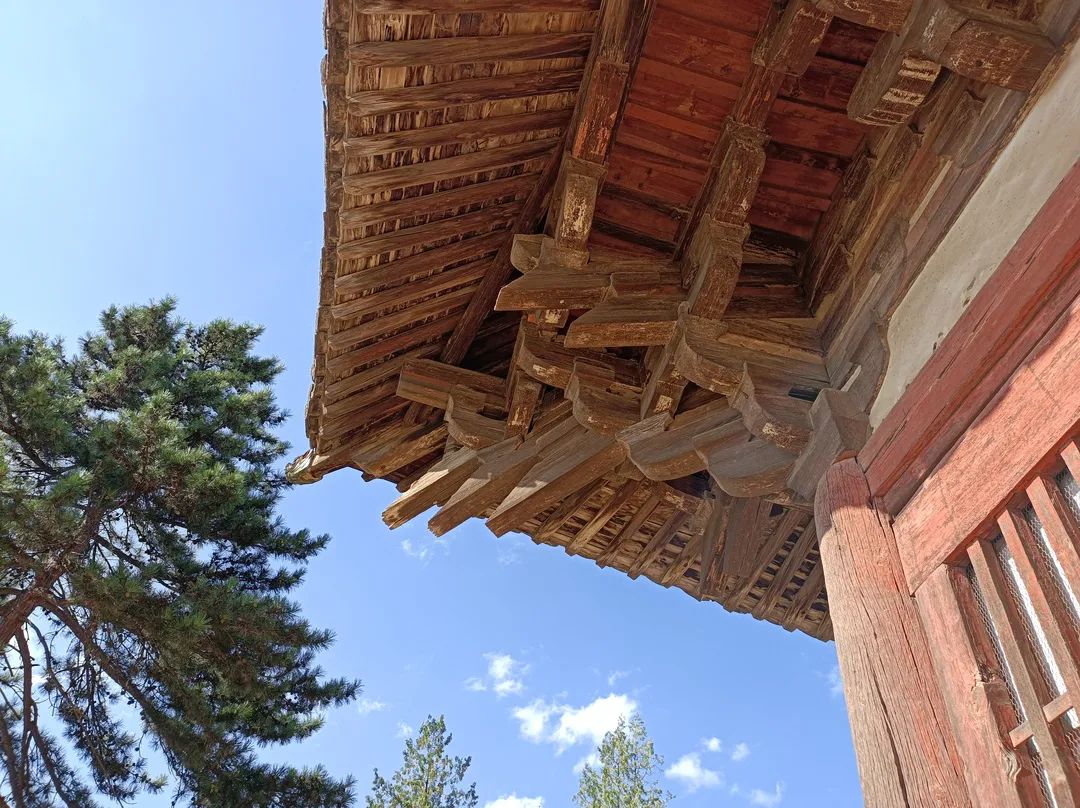

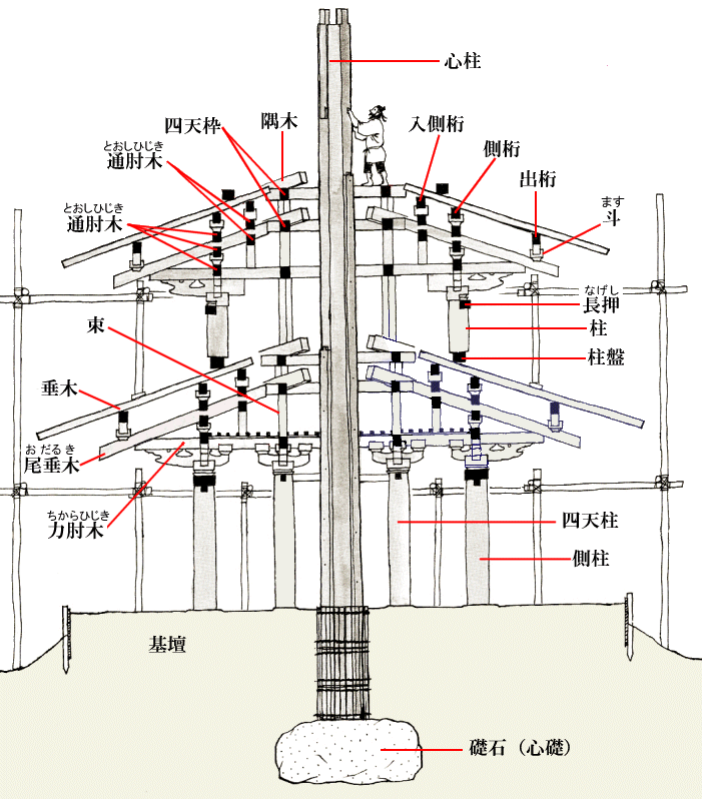
The following figure: the section of the column head bucket arch of the new year Foguang temple.
The buildings in the Sui and Tang Dynasties in Daji mostly use zhenang structure; In the architecture of Song Dynasty, there were some people who made Angs into heads, and some used both real Angs and fake Angs.
Some real Angs were only used for making up rooms, and some made Huagong heads into piano face fake Angs.

The ang shaped components could not play the role of lever structure of zhenang, and the fake Angs gradually occupied a dominant position after the Yuan Dynasty; During the Ming and Qing Dynasties, except for the individual Dougong of Beijing Zhihua temple, zhenang completely disappeared.
All the architectural Dougong had been used with fake ang, which eventually evolved into decorative components.
Throughout the evolution history of Ang, it has the characteristics of changing from large to small, from long to short, from oblique to flat, from true to false, from complex to simple, from function to decoration and so on.

The evolution of Chinese architecture in the new year: Daji II.
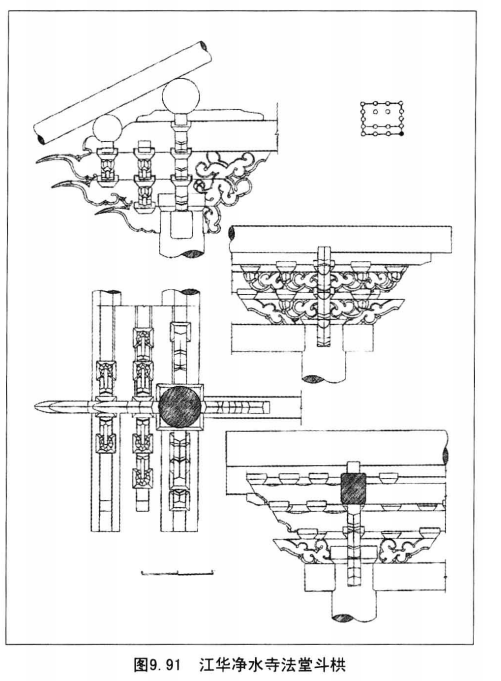
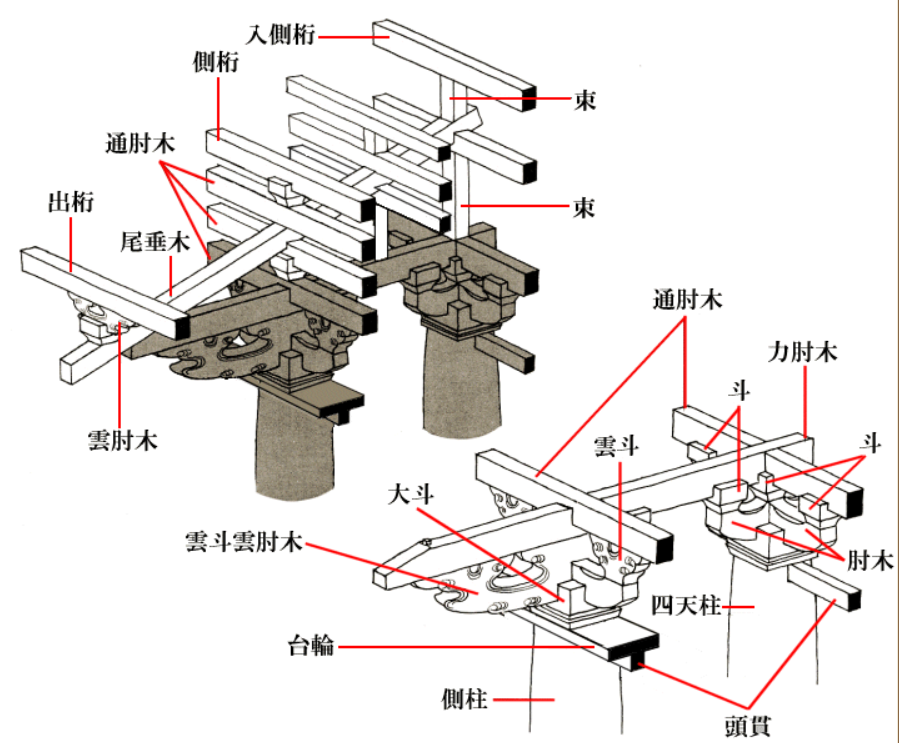
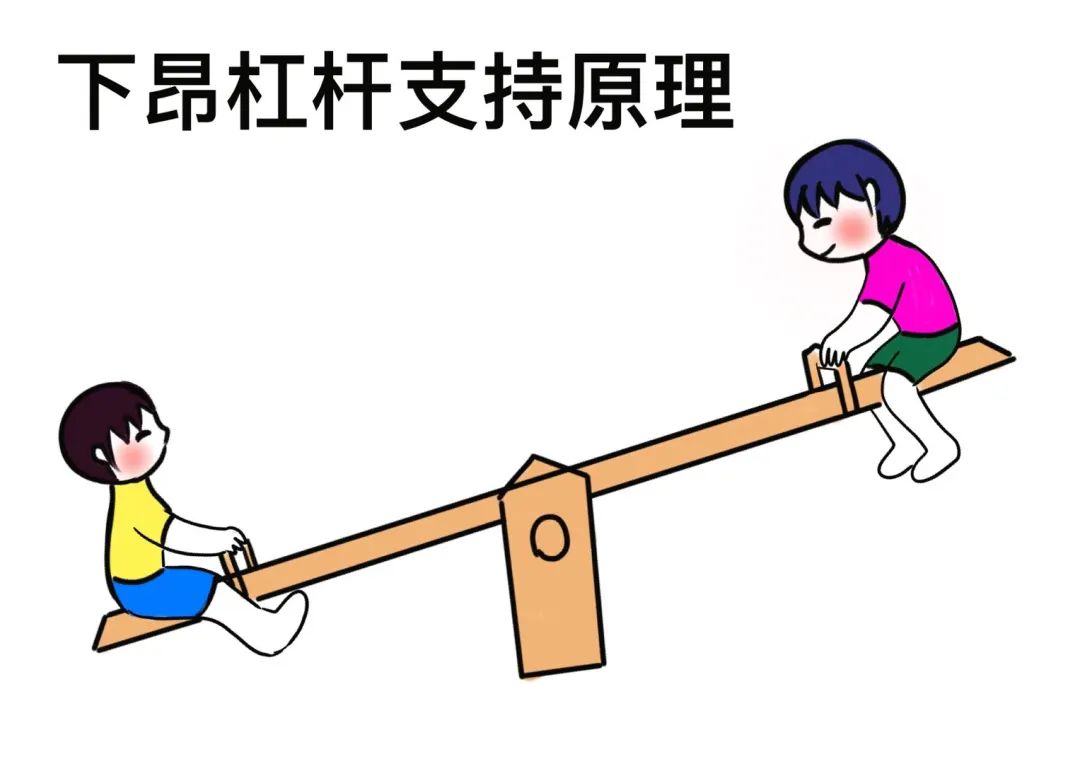
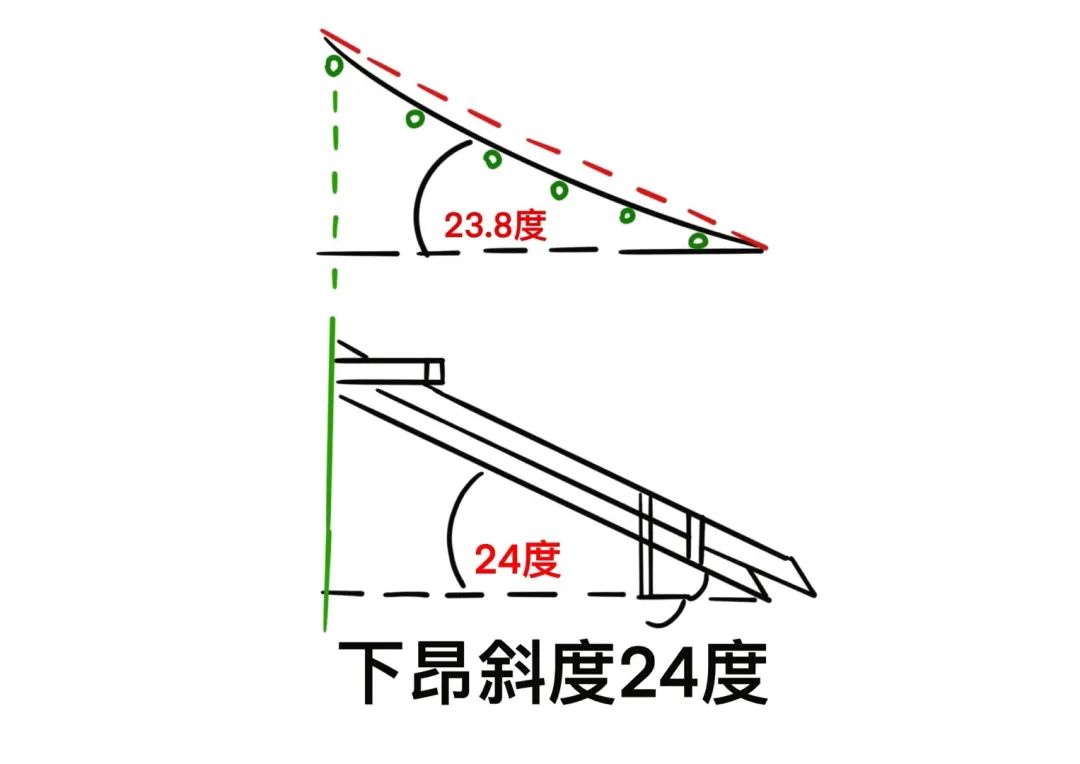
The shape, tail structure and function of zhenang.
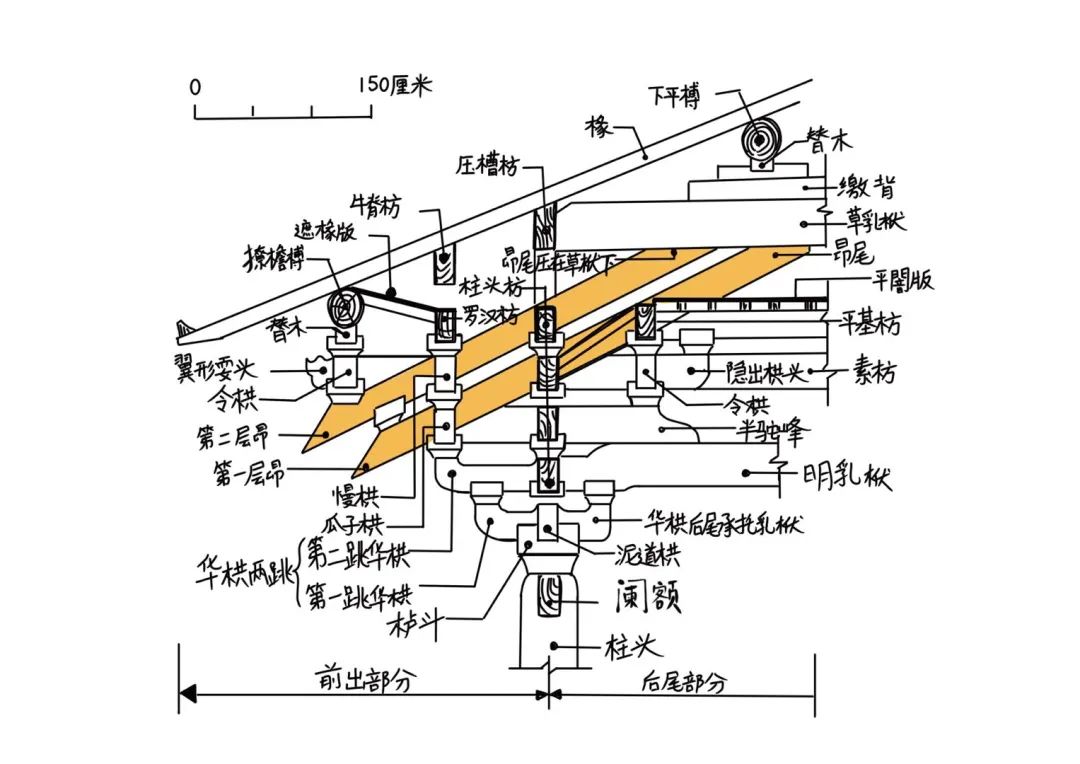
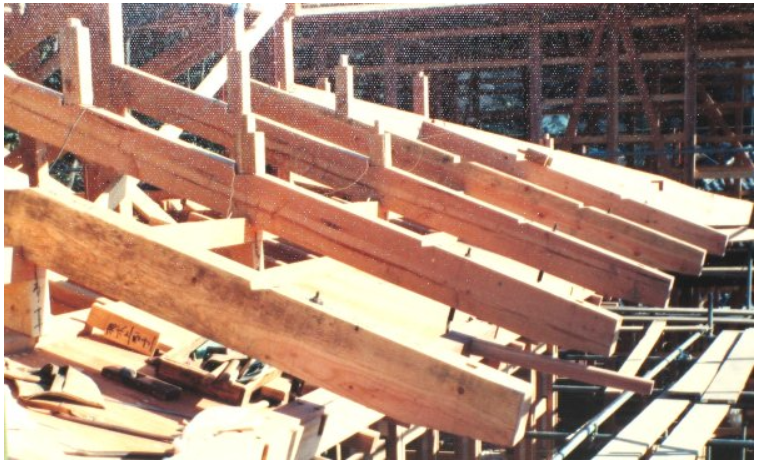
Zhenang has three structures: single lower ang, double lower ang and three lower ang, which overlap with the Huagong up and down, extend in the longitudinal direction and overhang the eaves together.

Zhenang has a long length and is the longest member in a group of bucket arch members.

Examples of zhenang include the East Hall of Foguang temple, the hall of Hualin temple in Fuzhou, the hall of Chongfu temple in Shuozhou, etc.
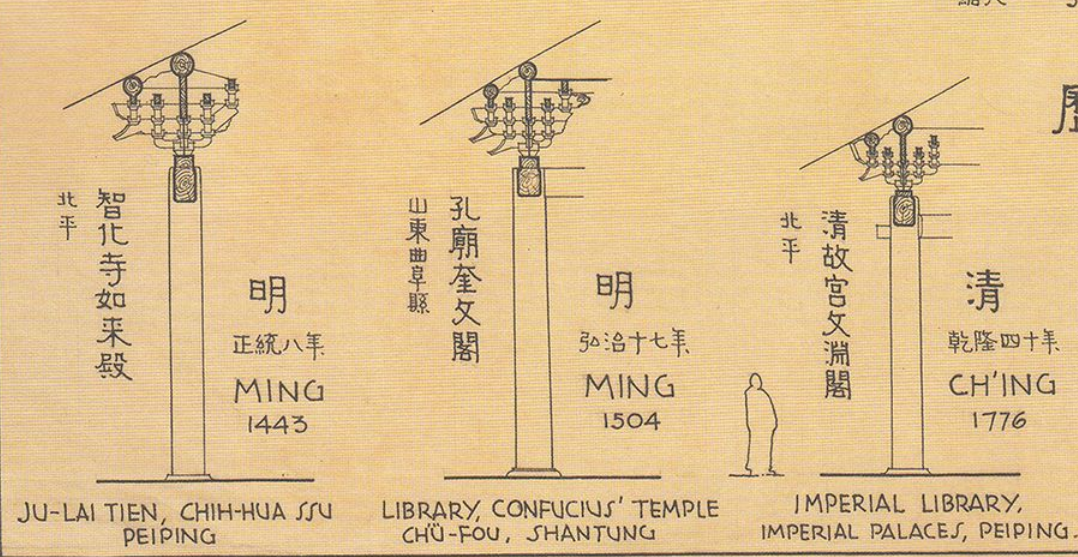
among the bucket arches, its ang is the zhenang extending obliquely below.

Zhenang structure has great technical difficulty, complex calculation and difficult construction.

Zhenang is a structural member.
There are three kinds of lifting tail structures, namely, cantilever type, repressive type and plug-in type.

They are three effective methods to deal with the joints between lifting tail and large wooden frame of inner groove: 1.
Ballasting type, which uses the brackets and braces of inner groove beam frame to press the lifting tail.
For example, in the Dougong of the column head of the East Hall of Foguang temple, the two lower raised tails are pressed with grass.
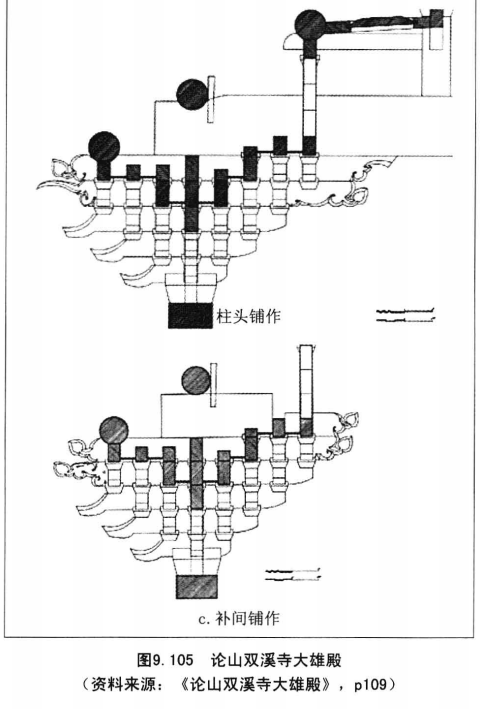
2.
The plug-in type is generally used in hall style buildings.

The raised tail extends obliquely above, and the raised tail is inserted into the short column or gold column between the beams in the form of tenon and mortise to be fixed.
3.
The lifting type is to lift the lower flat in the house obliquely at the lower rear end, and lift the lower flat with a small bucket component of one material and two at the rear end.
The function of the lower hanging can significantly reduce the height of the upper bucket.
At the same time, the external jump of the outer eaves will be reduced accordingly.
The change of the structural slope will inevitably affect the roof slope and the depth of the eaves.
Therefore, the technology of lifting and lowering the upper bucket in the lower lifting components and reducing the part of out jumping is an effective method to adapt to the design requirements of different architectural forms and effectively adjust the roof slope and component nodes.
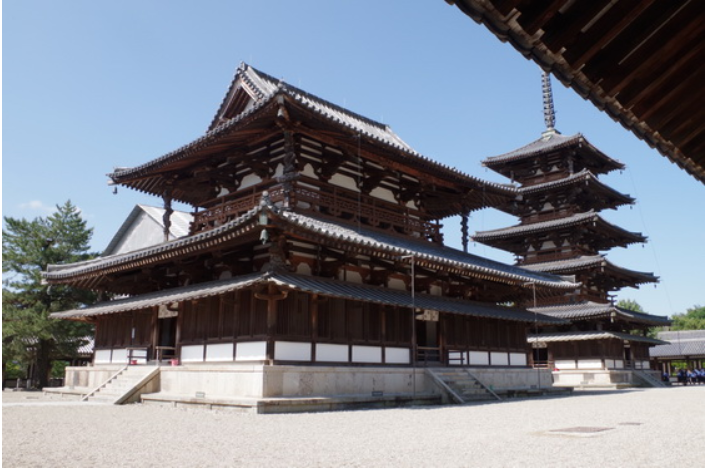
Japanese architecture happyNewYear although the wooden buildings before the Mid Tang Dynasty in China have disappeared, they can still be compared and referenced from the buildings in the period of Japanese birds.
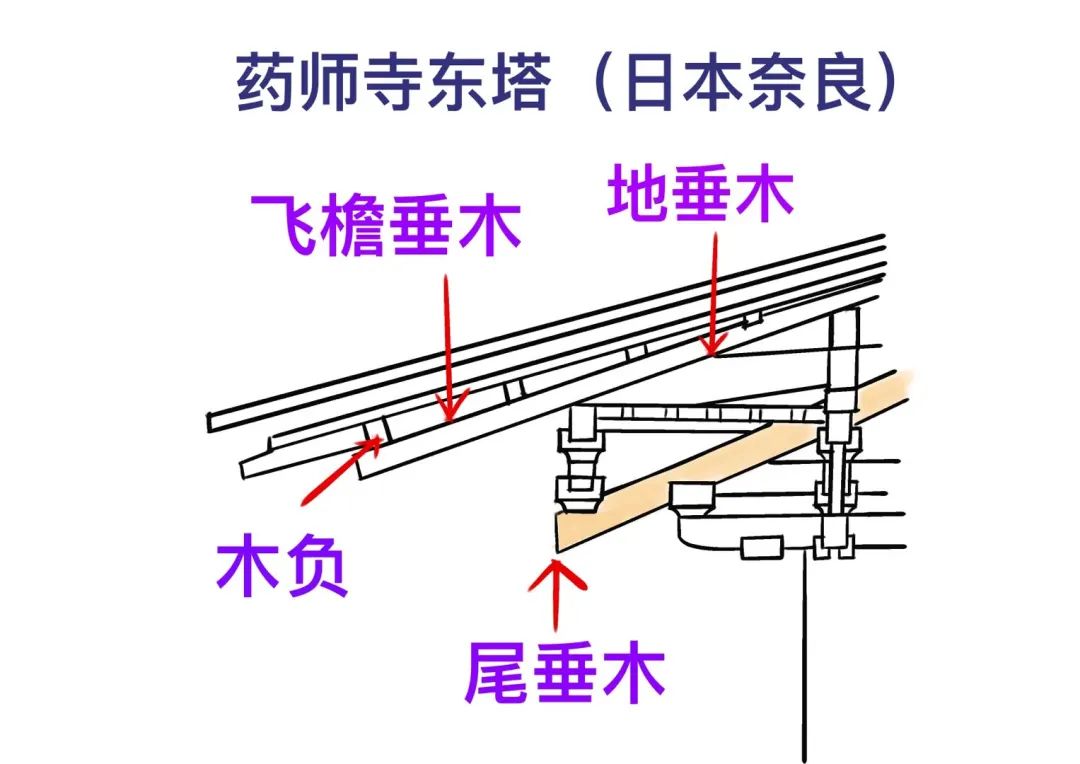
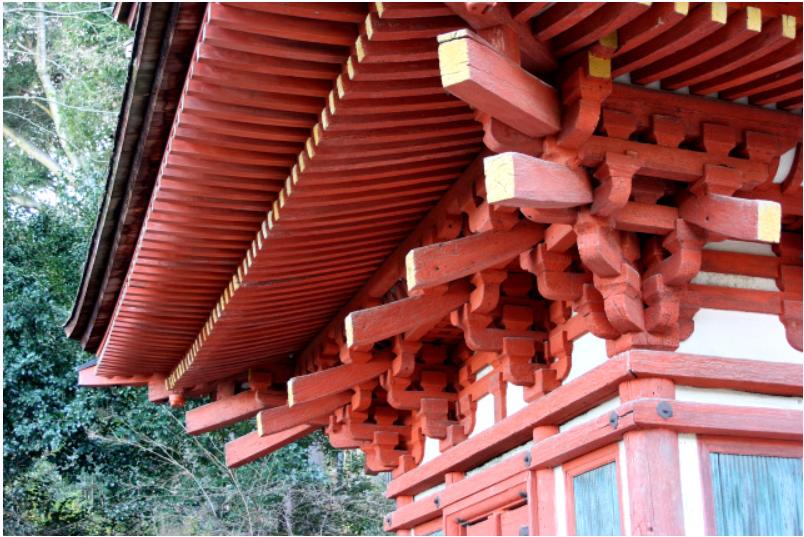
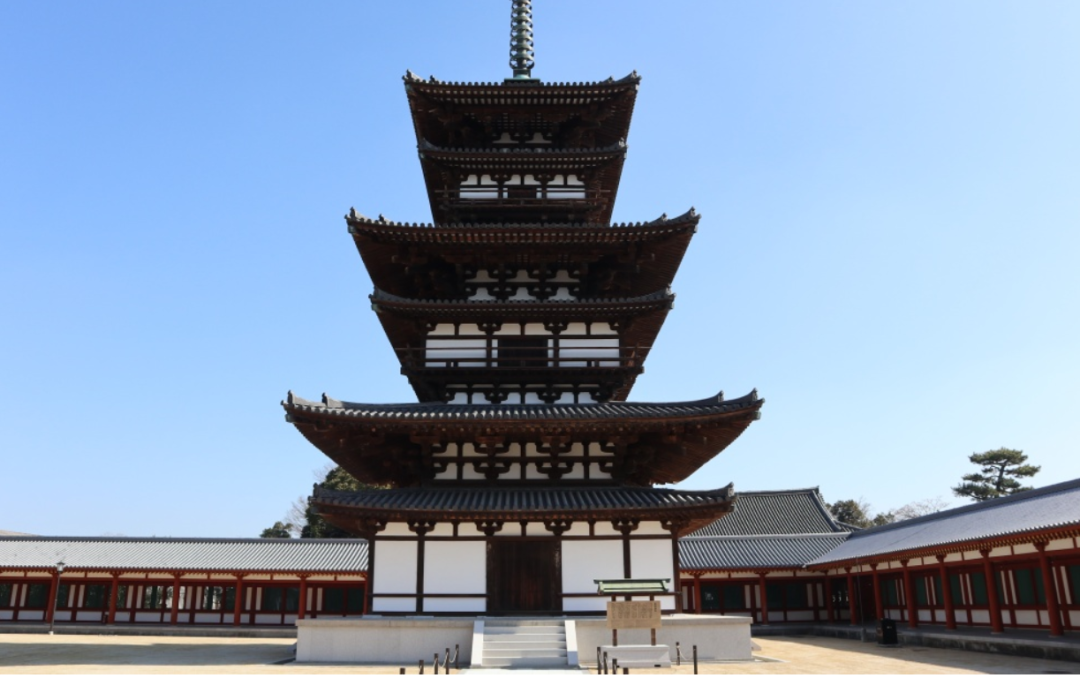
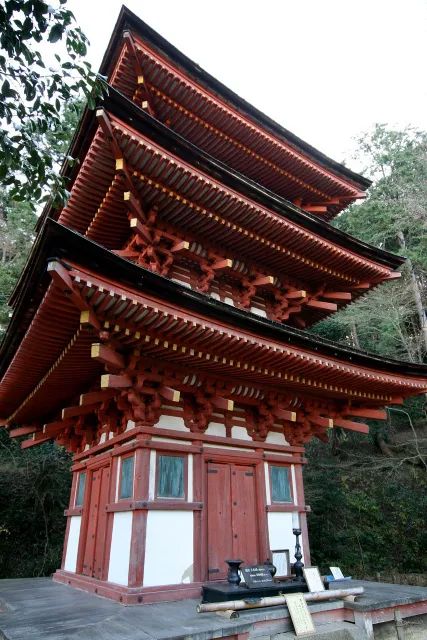
For example, the quintuple tower of FaLong temple in Japan, the East Tower of pharmacist temple and the Golden Hall of zhaoti temple in Tang Dynasty use an inclined cantilever component of “tail hanging wood” under the eaves.
The bucket arch is huge and the eaves are quite far-reaching and elegant.
It is very similar to ang in Chinese architecture and has a certain reference value.
The traditional wooden structure buildings in Japan are kept very clean and feel very new, because every time they go through a period of falling frame overhaul, dismantle many components such as columns and beams for refitting, save the damaged component numbers into the warehouse, and replace a batch of new components.
This fundamental repair method is still inherited today.
This is the most different place from the repair methods of Chinese buildings.
It is a major feature of the repair of wooden buildings in Japan.
For example, the buildings of Feiniao temple, sitianwang temple and FaLong temple in the era of flying birds were repaired in this way.
Nara FaLong Temple Nara era: pharmacist temple, Tang zhaoti temple.
The Golden Hall of the Tang zhaoti temple was established at the end of the 8th century and was repaired on a large scale during the Edo period and the Meiji period.
Disassembly and repair is not only the preservation of buildings, but also the reconfirmation of the ancient technology.
In the middle of Ping’an, Japanese craftsmen constantly transformed xiaang and incorporated local techniques into the triple tower of Jingli temple.
Korean architecture has a close relationship with Chinese architecture and Japanese architecture.
From the cultural exchange in the Han and Wei dynasties, the wooden architecture technology in the Tang Dynasty was more mature.
With the change of dynasties, after the Koryo Period, Korean architecture integrated some characteristics of Chinese architecture in song, Liao, Jin and Ming Dynasties.
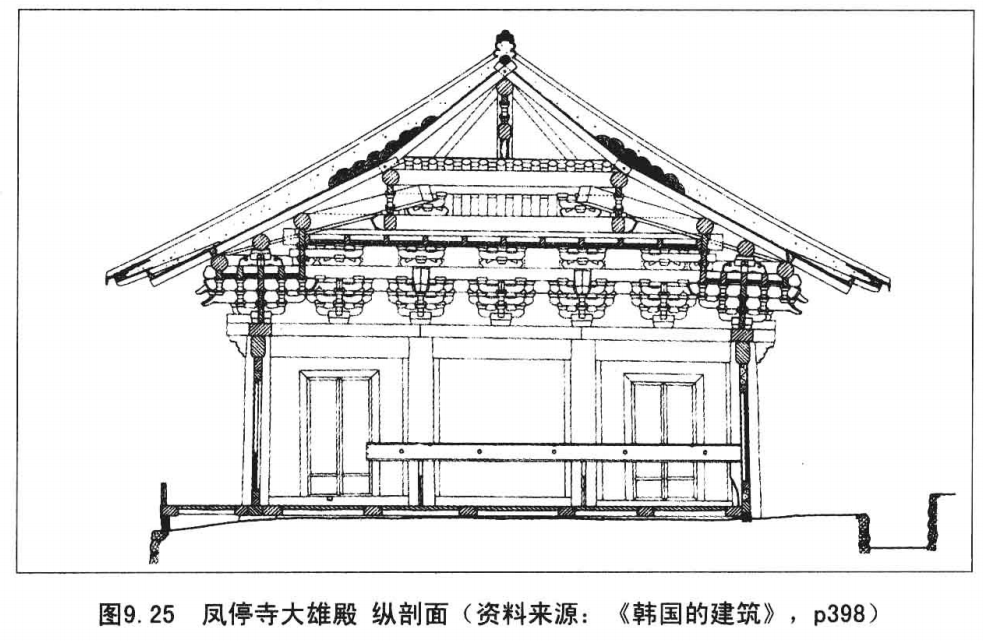
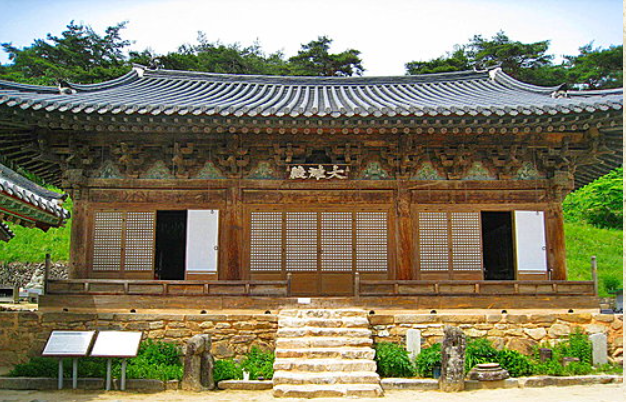
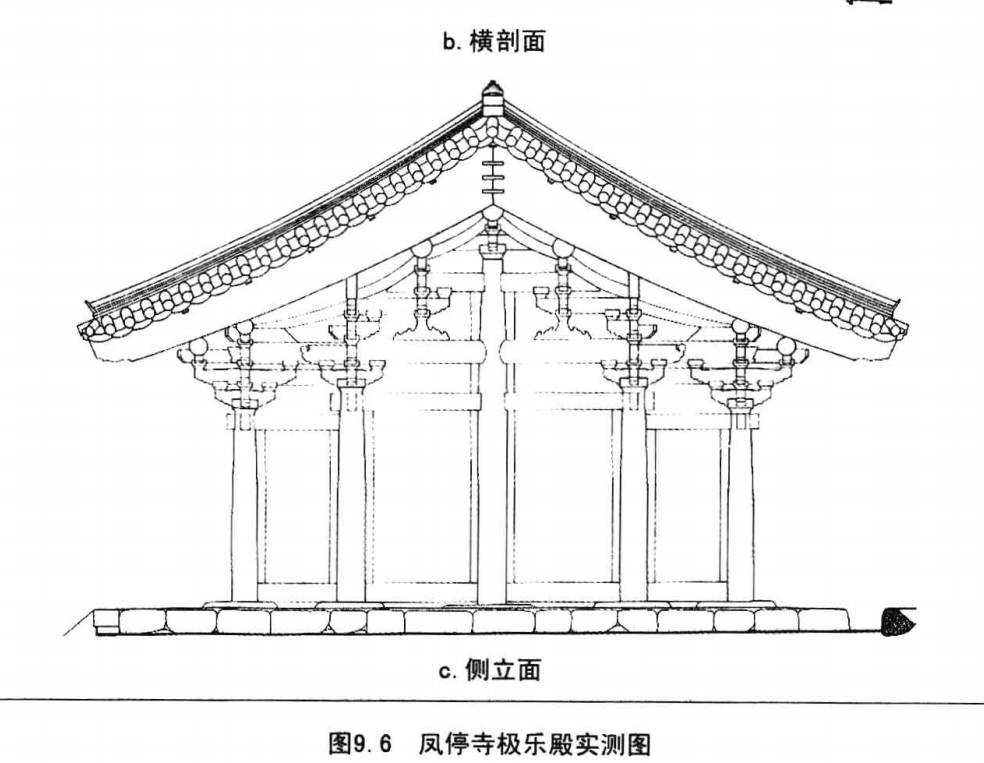
The blissful hall in Andong Fengting temple is the oldest existing wooden building in South Korea.
It is speculated that it was built in the early 13th century and has a history of about 800 years.
The architectural framework retains the Chinese style components such as fork hands, supporting feet and herringbone arches.
The interior is made from the top and the top.
The girder is very similar to the Chinese moon beam, but the bucket arch has changed significantly.
The lower arch will be made into the shape of ox tongue, which is only a simple decoration and no longer used as a support cantilever.
The ancient architecture, culture and Museum data sharing exchange group regularly shares ancient architecture, culture and Museum data.
Please read the group rules before joining the group.
(students who are already in the group should not add groups repeatedly.
Each group shares the same data) if the QR code expires, you can add me to the group via wechat: dougong68 remarks: enter the group..



