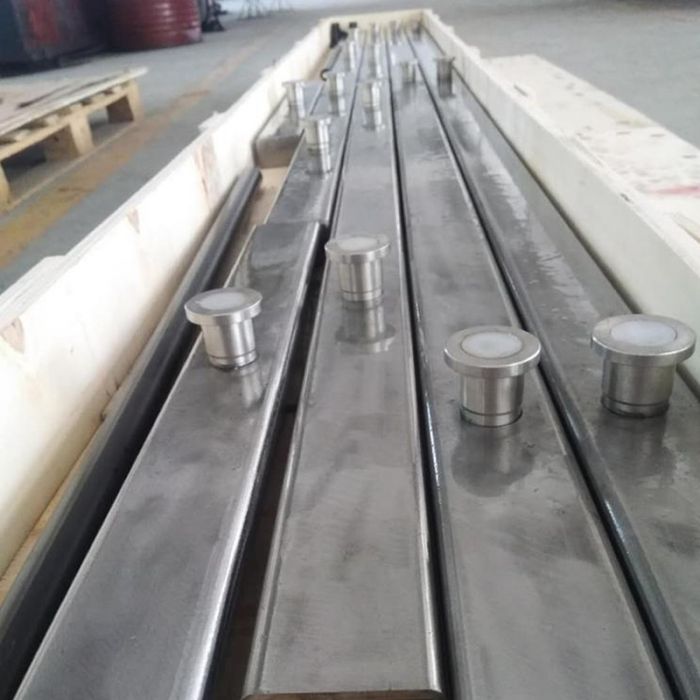
The preform of refractory castable is between fixed and amorphous.
It is the finalization of amorphous refractory castable, which has the advantages of both fixed and amorphous.
It is a new direction of the development of construction and application technology of amorphous refractory.
At present, in the chemical, metallurgical, nonferrous and casting industries, more and more users have chosen to use castable preforms.
At the cement green and energy-saving development seminar held by China Construction Group and Ruitai technology in early December, many branches of Ruitai technology talked about new technologies and products in prefabricated parts.
After finalizing the castable, it is made into prefabricated parts and applied to cement kiln mouth, coal injection pipe and other parts, which not only saves the construction cost, And it also greatly improves the service life of refractory materials, and in the future, this will become a trend of refractory industry.
Fire resistant prefabricated parts are divided into fire-resistant cement bonding, phosphate bonding, water glass bonding, cementless bonding, etc.
According to the material, it can be divided into high alumina, corundum, clay, mullite, etc.
Fire resistant prefabricated parts can be prefabricated into various shapes at will, with good thermal shock stability, high strength and good spalling resistance; The fire resistance can reach 1750 ℃, and it can effectively resist penetration in the application of heavy metal smelting furnace, form an erosion layer, no joint, good air tightness, less heat loss and energy saving; It can quickly repair the kiln and improve the operation rate of the furnace; It can realize direct hoisting, mechanized furnace building and high construction efficiency.
In the previous article, we shared the five common problems of fire-resistant prefabricated parts, such as pulverization, delamination and flashing.
For details, click to view: the five common problems of pulverization, delamination and flashing of fire-resistant prefabricated parts and their solutions.
In addition to the above problems that are easy to appear in the process of use, cracks will also appear in the production process of fire-resistant prefabricated parts, This paper only discusses the causes and control of the cracks in the prefabricated parts of refractory castable in construction.
1.
The production process flow of fire-resistant prefabricated parts is as follows: 2.
Analysis of crack causes.
Most of the cracks occur after curing, demoulding and baking.
There are many reasons for the cracks, mainly including changes in temperature and humidity, brittleness and non-uniformity of castable, unreasonable structure, unqualified raw materials (such as high calcium oxide content in magnesium material), and formwork deformation will also aggravate this phenomenon, During the hardening of castable, the cement releases a large amount of hydration heat, and the internal temperature rises continuously, causing tensile stress on the surface.
Later in the cooling process, due to the constraints of the foundation or bottom castable, tensile stress will appear in the precast block.
The change of temperature will also cause great tensile stress on the concrete surface.
When these tensile stresses exceed the crack resistance of the castable, cracks will appear.
The internal humidity of many castables changes little or slowly, but the surface humidity may change greatly or violently.
For example, if the curing is not complete, the surface shrinkage deformation is constrained by the internal pouring, which often leads to cracks.
According to the formation process of temperature stress, it can be divided into the following three stages: (1) early stage: from the beginning of pouring precast blocks to the basic end of cement heat release.
The two characteristics of this stage are that the cement releases a large amount of hydration heat and the sharp change of elastic modulus on coagulation.
Due to the change of elastic modulus, residual stress is formed in the concrete during this period.
(2) Medium term: from the end of the exothermic effect of cement to the time when the concrete cools to a stable temperature.
During this period, the temperature stress is mainly caused by the cooling of castable and the change of external temperature.
These stresses are superimposed with the residual stress formed in the early stage, and the elastic modulus of concrete changes little during this period.
(3) Late stage: the operation period of precast block baking.
The temperature stress is mainly caused by the change of baking temperature, and these stresses are superimposed with the residual stresses of the first two kinds.
According to the causes of temperature stress, it can be divided into two categories: 1) autogenous stress, mainly on products with relatively large structural size; 2) Constraint stress: the stress caused by the fact that all or part of the boundary of the structure is constrained by the outside world and cannot deform freely.
It is mainly concentrated in the maintenance stage with mold.
3.
Temperature control and measures to reduce cracks in order to prevent cracks and reduce temperature stress, we can start from two aspects: controlling temperature and improving constraint conditions.
The comprehensive control measures are as follows: (1) improve the aggregate gradation and add explosion-proof agents, such as metal aluminum powder and explosion-proof fiber.
In practice, the author summarizes that its main function is: there are a large number of capillary channels in the castable, and the capillary tension is generated in the capillary after water evaporation, but the amount of explosion-proof agent should be strictly controlled, because increasing the capillary diameter can reduce the capillary surface tension, It will reduce the strength of prefabricated parts; (2) During mixing with water, the amount of water added shall be strictly controlled to avoid excessive thickness of slurry overflow layer on the surface during vibration forming, and fine powder floats upward and precipitates in layers; (3) Specify reasonable formwork removal time and methods to avoid rough disassembly and artificially produce or aggravate the size of cracks; (4) Set a reasonable baking curve.
Baking is an important process in the manufacturing process of fire-resistant prefabricated parts.
In the baking process, most of the free water and combined water of the preform itself are discharged and produce high strength, especially the dense and high-strength fire-resistant preform with large volume, which has high density and large size due to the preform itself.
The combined action of water vapor pressure and thermal stress in the baking process can easily lead to the peeling of the preform, and even the explosion of the preform.
In production practice, when baking, several temperature measuring points are arranged in the drying kiln and a baking curve is preset.
The baking curve includes a plurality of heating sections and insulation sections.
By monitoring the temperature of the temperature measuring point, the baking system is carried out according to the preset baking curve.
By strengthening the process control and reducing the cracks of prefabricated parts, it is of great significance to improve the qualified rate of prefabricated products and ensure the use quality..