Click “ocean life of streams” above to subscribe.
Introduction the defects of hydraulic structure engineering are a major hidden danger for the safety of hydraulic engineering.
In recent years, with the gradual increase of national investment in water conservancy facilities construction, the number of newly-built and expanded water conservancy and hydropower projects is also increasing.
The operation conditions of these water conservancy and hydropower projects are extremely complex, especially the underwater part of hydraulic structures.
In the process of long-term underwater operation, there will be different degrees of engineering problems and disease hazards.
The common types are mainly the following: sedimentation in the reservoir area and siltation in front of the gate, Corrosion and water leakage of gate, cracks in dam body, uneven settlement, voiding of joints around face slab, collapse of dam slope, leakage of dam body and dam foundation, concrete scouring of stilling basin, underwater side wall, chute and diversion channel, cracks, water leakage and erosion of tunnel concrete lining, etc.

China has the largest number of reservoir dams in the world, with 98000 reservoir dams.

In these water conservancy projects, there are various types of defects in hydraulic concrete structures.
Taking the 32 dams investigated as an example, cracks and leakage account for 100%, followed by scouring and abrasion and cavitation of flood discharge and overflow buildings, accounting for 68.7%.
In addition, cracks can also cause other dangerous diseases, such as leakage corrosion, environmental water erosion, freeze-thaw damage, reinforcement corrosion and so on.
It can be seen that cracks are one of the most important and common forms of diseases.
These cracks of different types, distributions, scales and scales seriously affect the integrity and durability of hydraulic structures.
Therefore, the whole process control and detection of concrete quality is an important measure to ensure the service life of the project.
This drawing comes from China capital construction news II.
Theories and methods the methods of crack detection of hydraulic concrete components are mainly divided into three categories: manual visit method, damage detection method and nondestructive detection method.
The crack width detector method belongs to a kind of artificial visitation method.
This method can automatically collect crack images and interpret the crack width.
It has the advantages of simple, intuitive and easy operation.
The disadvantage is that it can only detect the apparent cracks of concrete components and has no effect on the cracks in components; Drilling video and core sampling are damage detection methods.
The advantages of this method are that it can directly detect the width, depth, direction and other parameters of cracks.
The disadvantages are high cost, destructive to concrete components, and “one hole view” is difficult to realize large-scale plane detection of internal cracks; Ultrasonic method, radar wave method and infrared thermal imaging method belong to non-destructive testing methods.
Their advantages are that they do not damage the original structure of hydraulic concrete components.
Their disadvantages are that they can only be tested qualitatively and can not measure the crack length quantitatively.
⒈ technical route this study focuses on nondestructive testing methods, supplemented by damage detection method and manual visit method.
In view of the influence of external heat source in infrared thermography on the temperature field of concrete components, ultrasonic method and radar wave method are mainly used in this study.
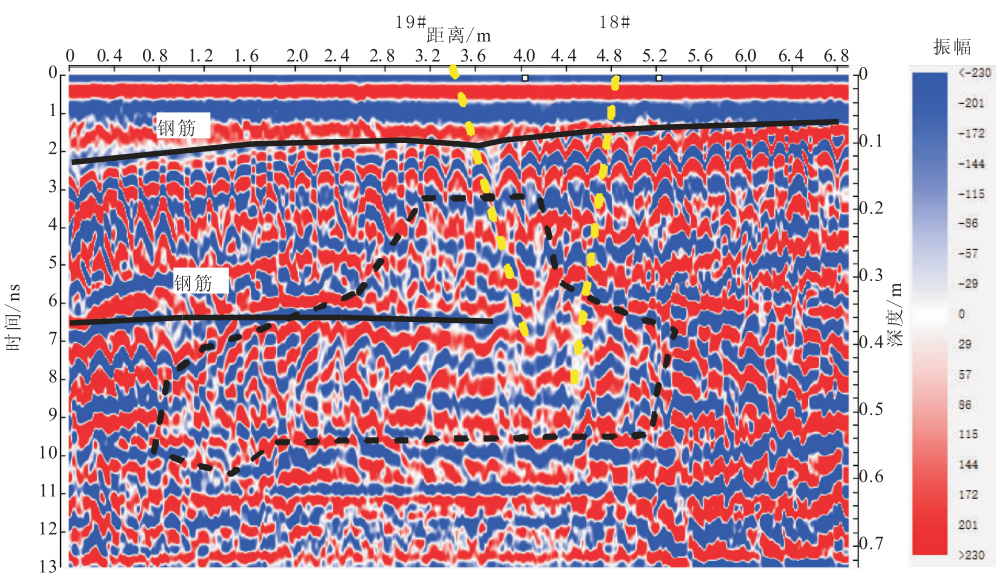
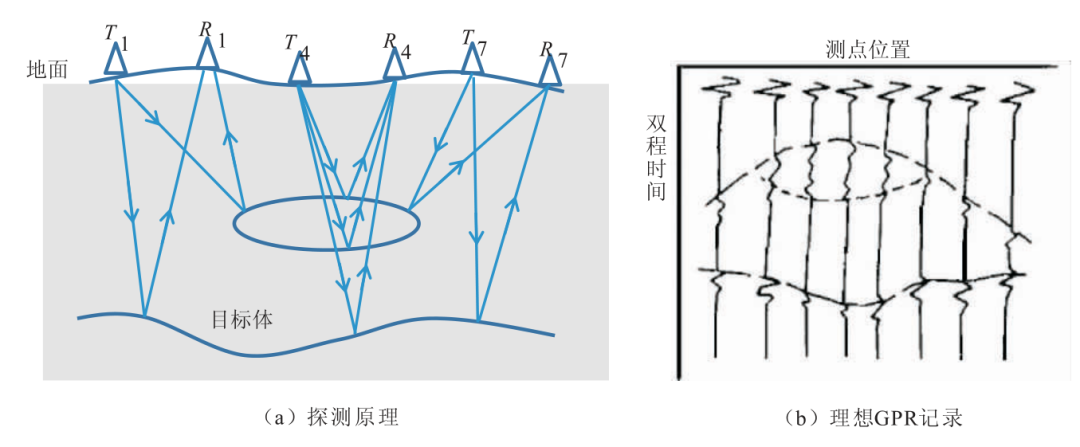
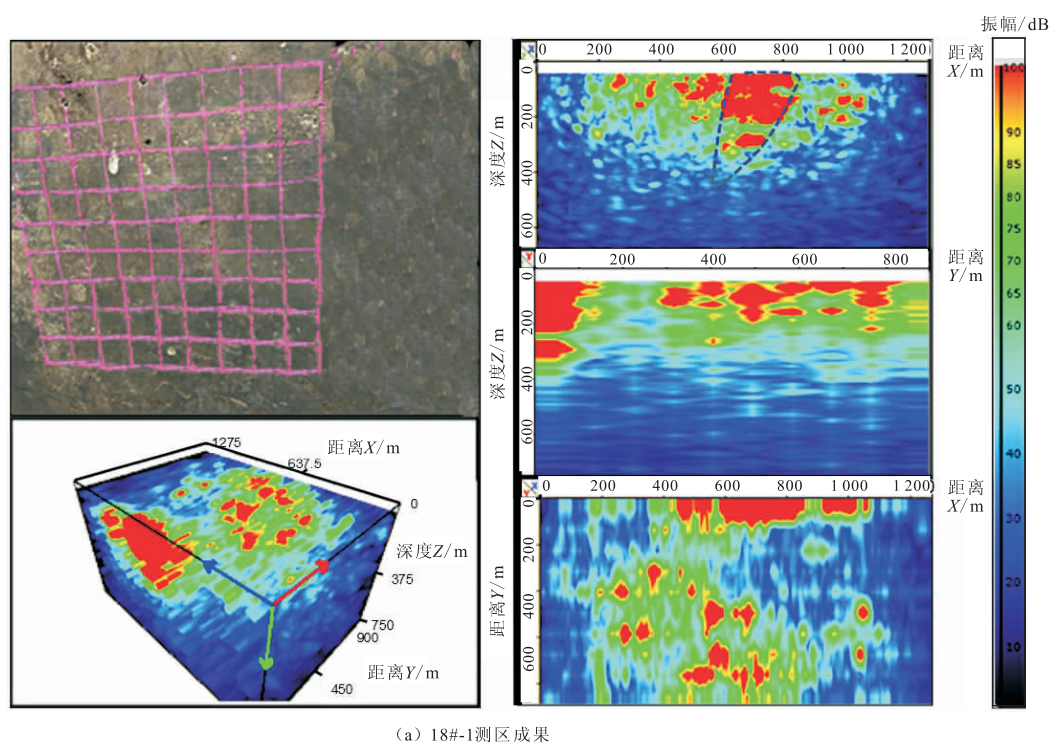
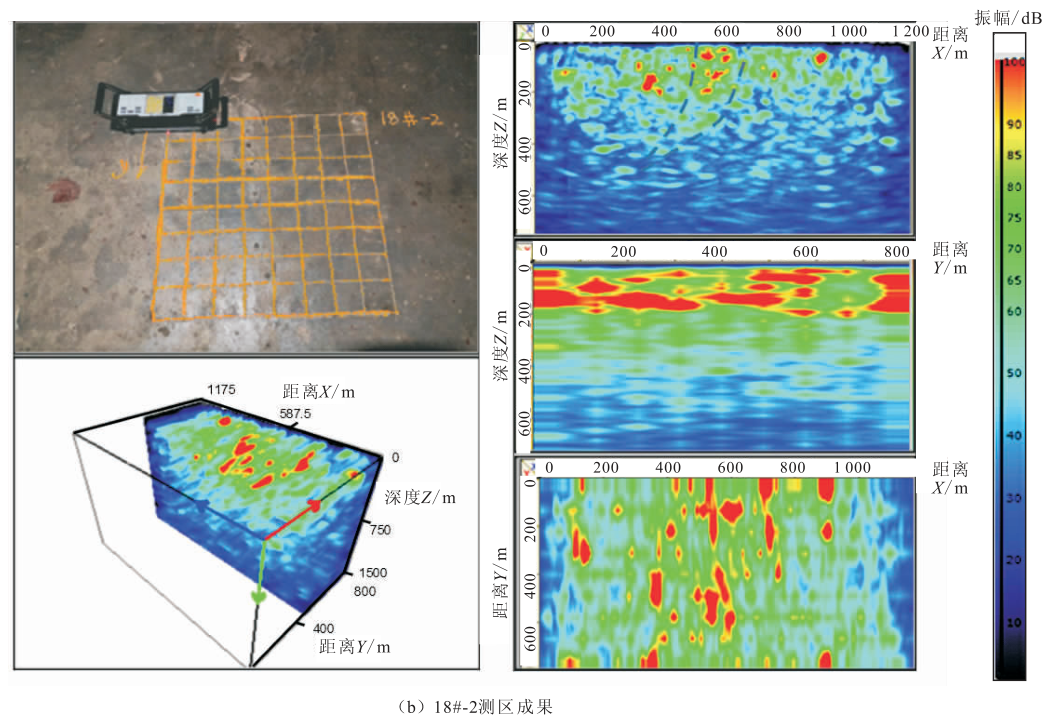
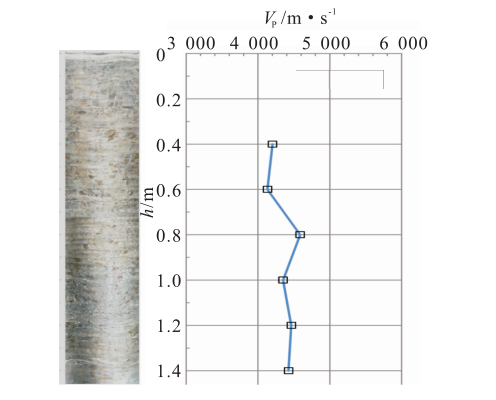
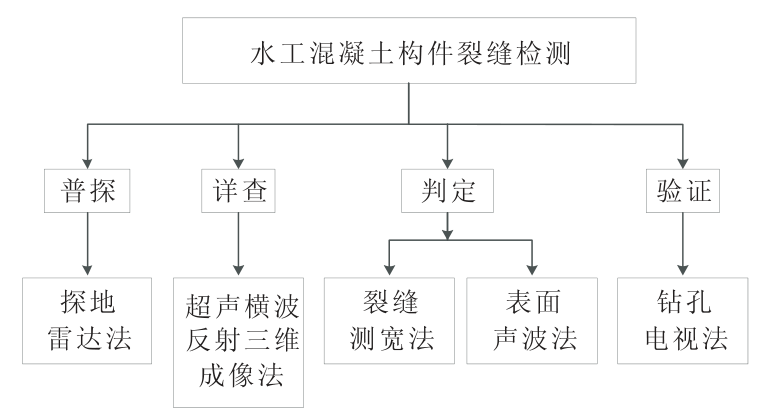
Under the guidance of the integrated detection idea from “qualitative” to “quantitative”, the specific implementation process is divided into four parts (see Figure 1, technical process): in the general exploration stage, the GPR method is used to detect the overall distribution of cracks; In the detailed investigation stage, the method of ultrasonic shear wave reflection three-dimensional imaging is used to investigate the deep distribution of cracks; In the judgment stage, the crack width measurement method and surface acoustic wave method are used to judge the surface width and penetration depth of the crack respectively; In the verification stage, borehole television is used to verify the correctness and accuracy of the detection results.
Figure 1 technical process 2 ground penetrating radar method ground penetrating radar is a geophysical method based on electromagnetic wave propagation theory.
It uses electromagnetic wave theory to detect cracks in hydraulic concrete components.
Its theoretical basis is that when the electromagnetic wave encounters an interface with different electrical properties (dielectric constant, conductivity and permeability), its propagation path, electromagnetic field intensity and waveform will change due to the electrical differences of the interface.
Using ground penetrating radar to detect concrete cracks, according to the principle of electromagnetic wave reflection, it can be seen that when the concrete is uniform and of good quality, only the reflected wave is formed at the interface between concrete lining and surrounding rock; When there are cracks between concrete and surrounding rock, because the void joints are mostly filled with air or water, there will be a large difference in wave impedance and form a strong reflection phenomenon (Fig.
2 (a)).
Fig.
2 Schematic diagram of ground penetrating radar test principle the concrete realization of crack detection of concrete components using ground penetrating radar is as follows (Fig.
2 (b)): firstly, electromagnetic wave is transmitted to underground medium through transmitting antenna; Then, the receiving antenna receives and records the electronic wave signal from the underground; Finally, through data processing, combined with engineering geological conditions, the inference and interpretation of underground media are realized.
In the above process, the propagation characteristics of electromagnetic wave are determined by conductivity σ And dielectric constant, in which the conductivity mainly determines the detection depth of electromagnetic wave; When the conductivity is moderate, the dielectric constant mainly determines the propagation speed of electromagnetic wave in the medium.
Therefore, echo will be generated on the interface of different electrical properties and expressed in the form of travel time, as follows: where h is the crack depth, X is the distance between transmitting antenna and receiving antenna, and V is the propagation speed of electromagnetic wave in the medium.
The propagation speed of electromagnetic wave in the medium is as follows: GPR detection of concrete cracks has the characteristics of fast speed, strong penetration ability and no coupling agent.
It can determine the shape and direction of crack defects.
The disadvantage is that the identification of concrete cracks needs to be carried out with the help of GPR images.
Therefore, the level of inspectors is required.
In addition, this method is suitable for the monitoring of large-scale concrete cracks, It is difficult to identify local small-scale cracks.
3.
Ultrasonic shear wave reflection three-dimensional imaging method ultrasonic is a mechanical wave with frequency greater than 20kHz and propagating in elastic medium in the form of wave..



