The most important load-bearing components in the wooden structure of ancient buildings are columns and beams, and the components connecting and stabilizing columns and beams are purlins.
Purlins and braces are widely used, such as spine purlins and metal purlins in the interior, eave purlins and braces exposed in the exterior, hoops and braces in the corner of the building and stable corner columns.
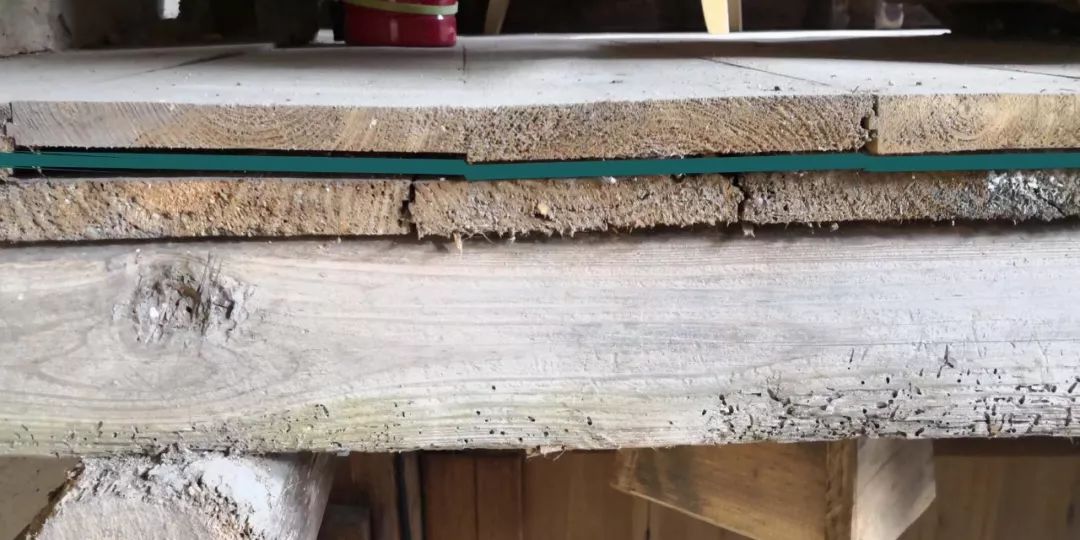

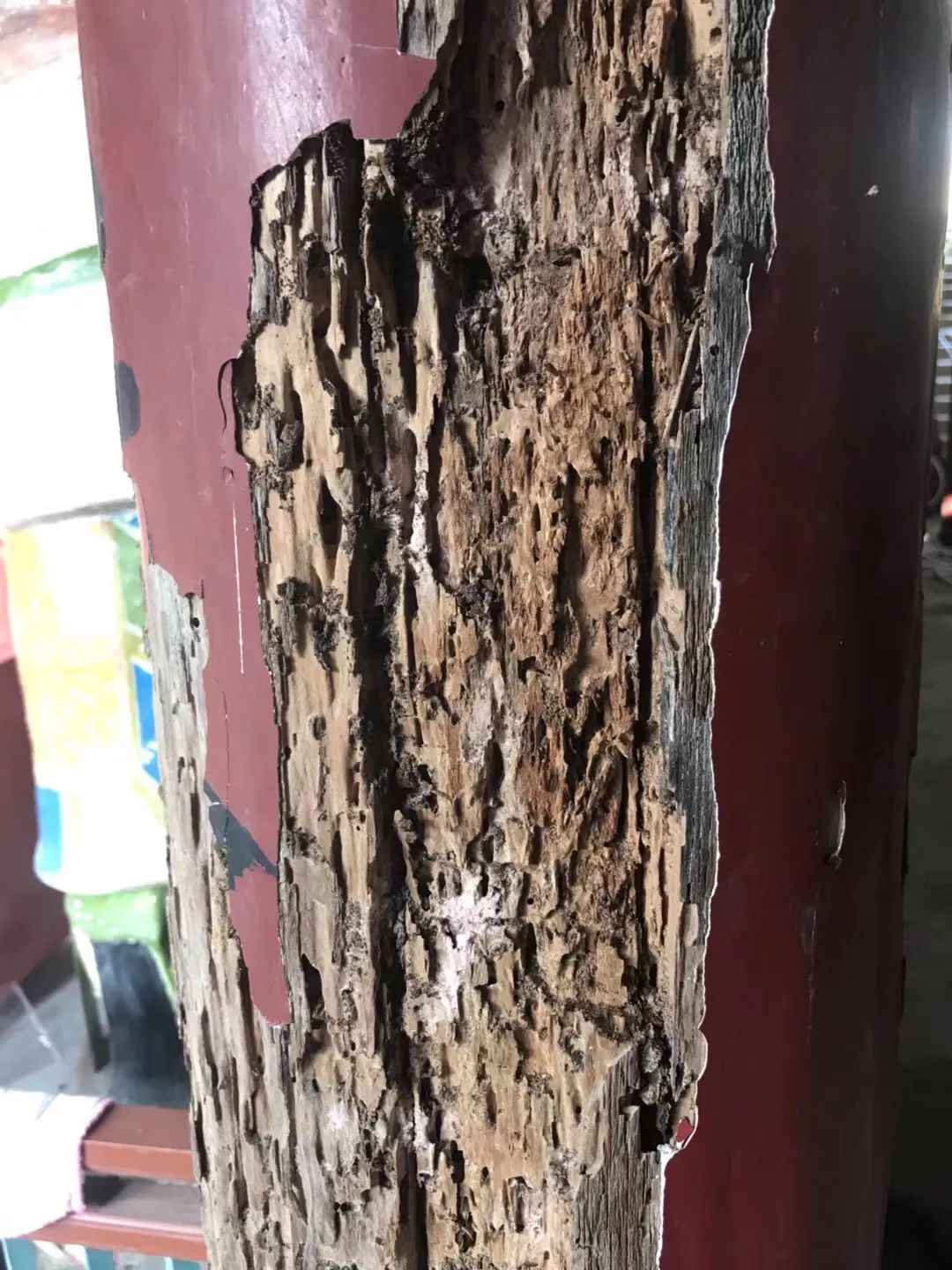
The repair of purlins and braces is also the key to determine the quality and life of ancient buildings.=This push will introduce you some key points of the shape and maintenance of some main purlins and braces.

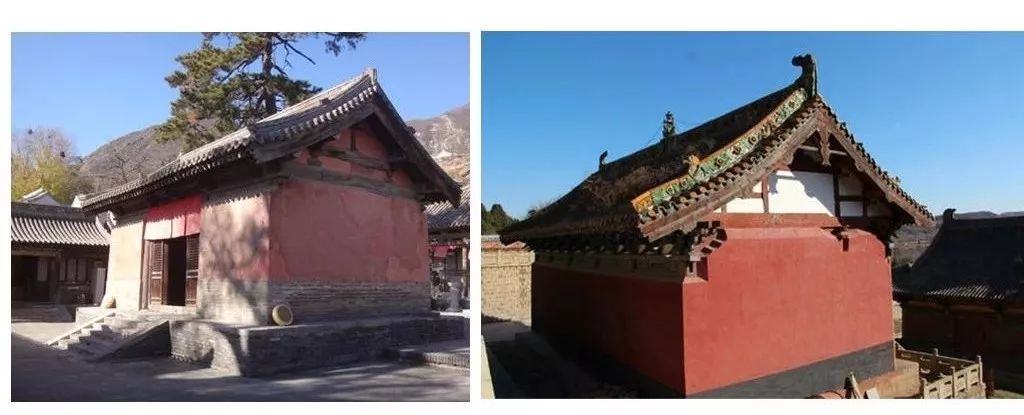
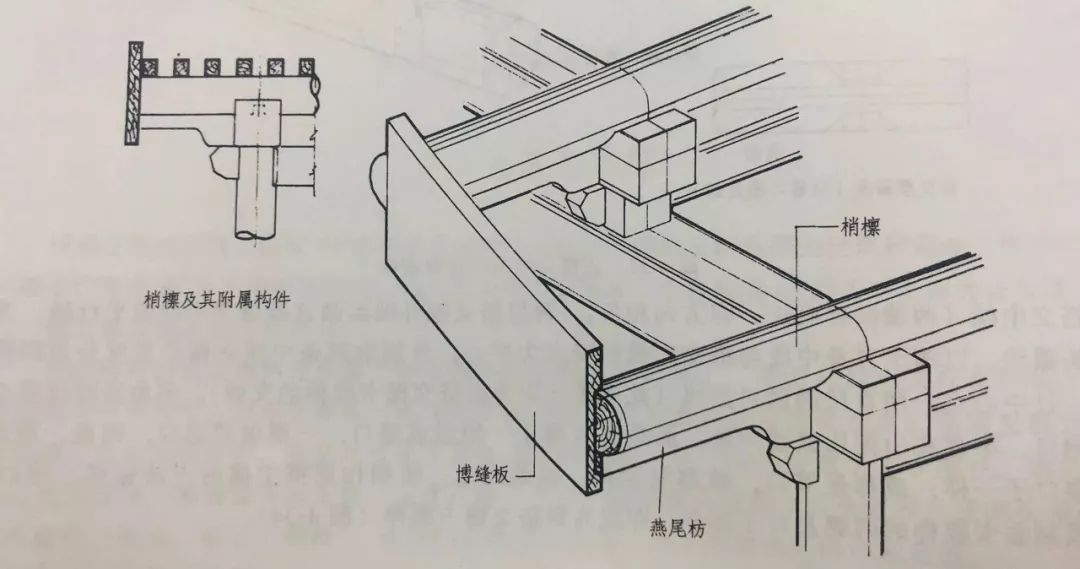
01 Purlin architrave of overhanging mountain building In small buildings, the purlin architrave of overhanging mountain building has some changes due to the coming out of the mountain.
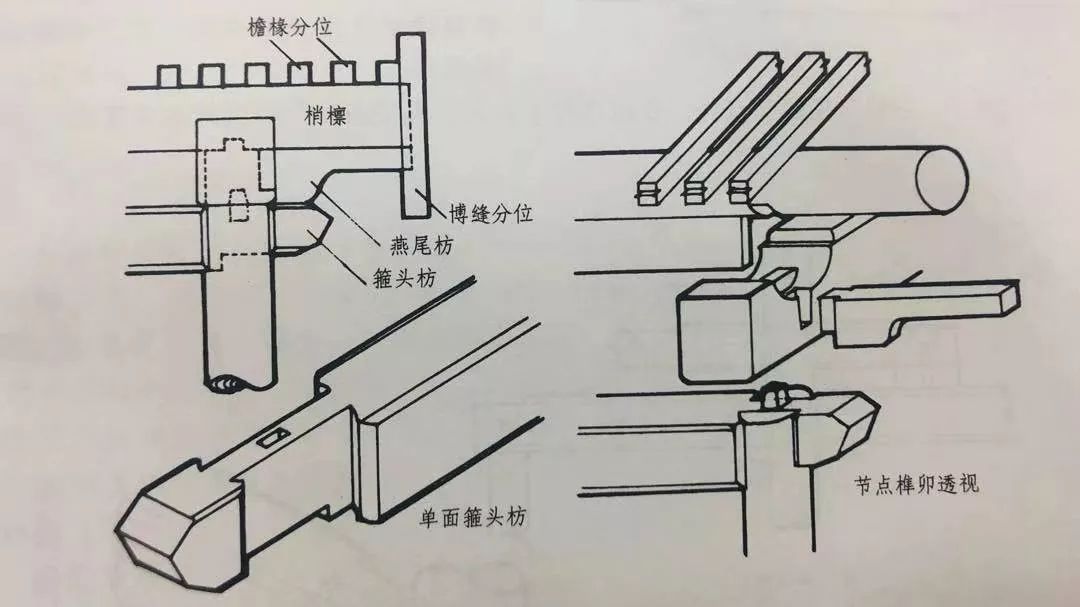
The dovetail architrave is a component of the overhanging mountain building and a foil for the overhanging end of the purlin.

It is mainly used to strengthen the strength of the overhanging purlin and also plays a decorative role.

The length is based on the length of the top purlin.
The purlins projecting from the top to the two sides of the overhanging building are called minor purlins.
The length is the length between the top and the overhanging length.

The overhanging length of the overhanging building is four rafters equal to or equal to the flat size of the eaves.
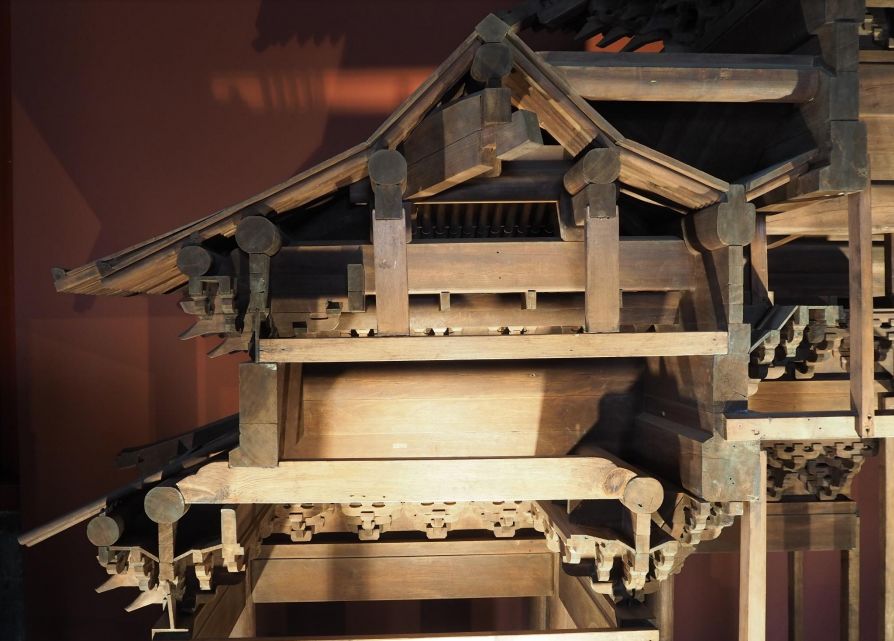

Because the purlin brace bears the load of the overhanging part, the nose with the same height as the purlin bowl cannot be made on the beam frame as the main beam.
To fix the purlin section, the nose tenon section is generally reduced to 1/5 of the purlin diameter.
The height and thickness of the dovetail architrave are the same as the base plate.
Although it is a separate component of the cornice part, it is not integrated with the base plate on the inside.
The architrave under the dovetail architrave is a hoop architrave.
There are also different approaches to the gables that have relations with the dovetail Fang.
One is that the gable is sealed to the top, and only the overhanging part of the purlin and the dovetail brace are exposed.
The other is the “five-flower gable” method, that is, the gable is only built to the bottom of each layer of beam frame, and the masonry on it is built in a ladder shape with the length of the beam frame, and the beam frame is exposed.
This is the unique method of overhanging mountain construction, which can play the role of ventilation and corrosion prevention in ancient times.

There are also a few building gables only built under the girder, all the above wooden structures are exposed, and the empty space is blocked with elephant eye plates.

The method of sealing to the top and the method of five-flowered gable wall.

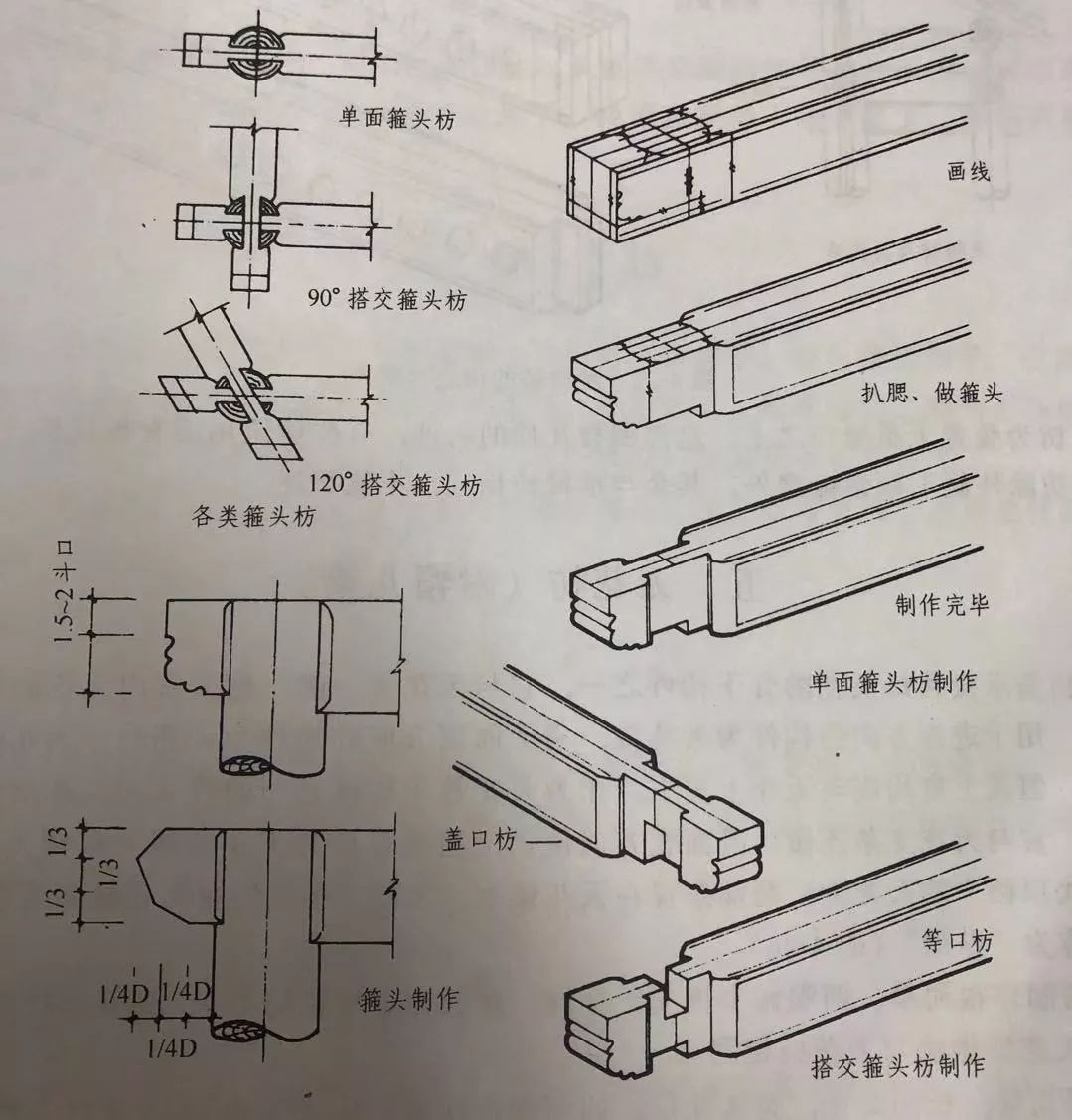
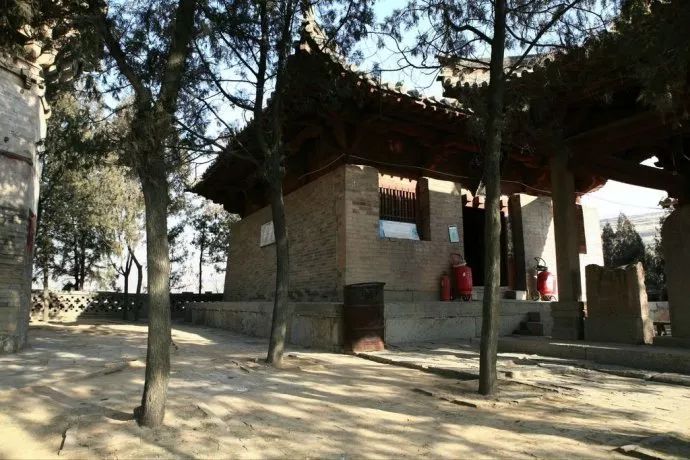
The purlins at the corner of the 02 corner are called hoop-head purlins, which are used at the corner of the top or the mountain.
In addition, the eaves of the polygonal pavilion are hoop-head purlins, which are also different from large and small buildings.
There are two kinds of hoop-head brace: single-sided hoop-head brace and overlapping hoop-head brace.
The hoop-head brace used between the top of the overhanging mountain building is single-sided hoop-head brace; The veranda, Xieshan and pavilions are framed with braces.
There are also two types of single side hoops and cross hoops in overhanging mountain buildings: large and small.
The protruding part of hoops in large buildings with arch of wooden architecture is often made into the shape of “overlord fist”, while the small buildings without arch of wooden architecture are made into the shape of “three forks”.
The width of both kinds of headwear is 8/10 of that of Fangzi, whether it is Bawang Quan or Sancha Tou.
Therefore, both sides of the headwear are cut by 1/10 of the original thickness, and the height is removed by 2/10 of the original height from the bottom.
Skew cross brace refers to purlins and trusses built at 120 degrees, 135 degrees or other angles, which are used for five-square pavilion, six-square pavilion, eight-party pavilion, etc.
In polygonal buildings, there is no problem of the ridge pressing the eave surface, but on the same large wooden member, the direction of the mortise should be consistent.
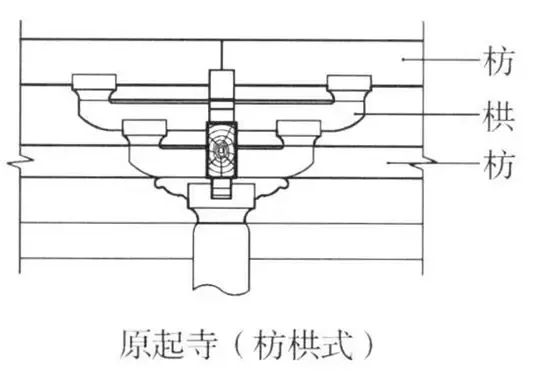
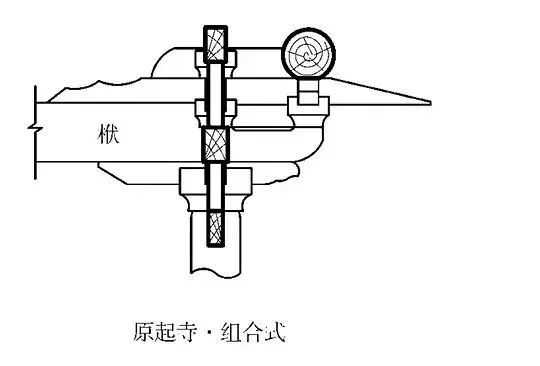
The purlin of Sanchatou 03 large building is the wood component of Foguang Temple in the Tang Dynasty.
The wood component of the Ming and Qing official buildings can also be divided into the early buildings of the Tang and Song dynasties and the official buildings of the Ming and Qing dynasties.
The names of the two components are different, and the relationship between the two components is also different.
Yuanqi Temple in Lucheng, Shanxi Province.
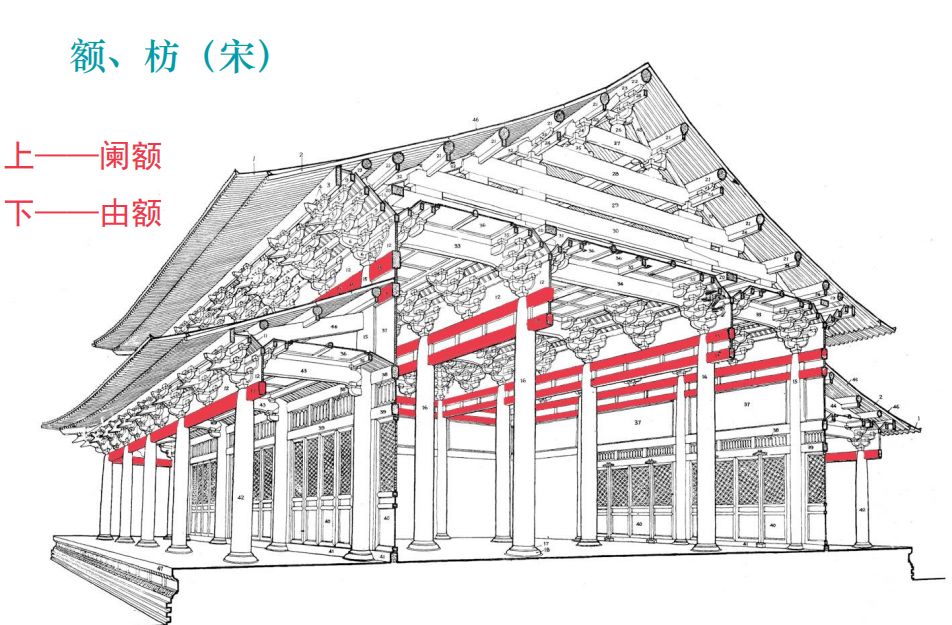
The “beam” of Tang and Song architecture is called “栿”.
The beam intersecting with Dougong is not made of peach pointed beam.
The overhanging eave purlin and central purlin supported by Dougong are also different from the names and shapes of later generations.
In addition, the relationship between purlins and beams in the early buildings is also relatively free.
The beams can be inserted in purlins and beams can also be placed above.
Ding Xuan of the early Xieshan architecture is called “Shun Ba Liang”, which forms a “D” shape with the beam.
Ding Xuan is installed on the arch of wooden architecture or eaves column at one end and the beam at the other end.
The beam is also directly pressed on the purlin of the outer eave.
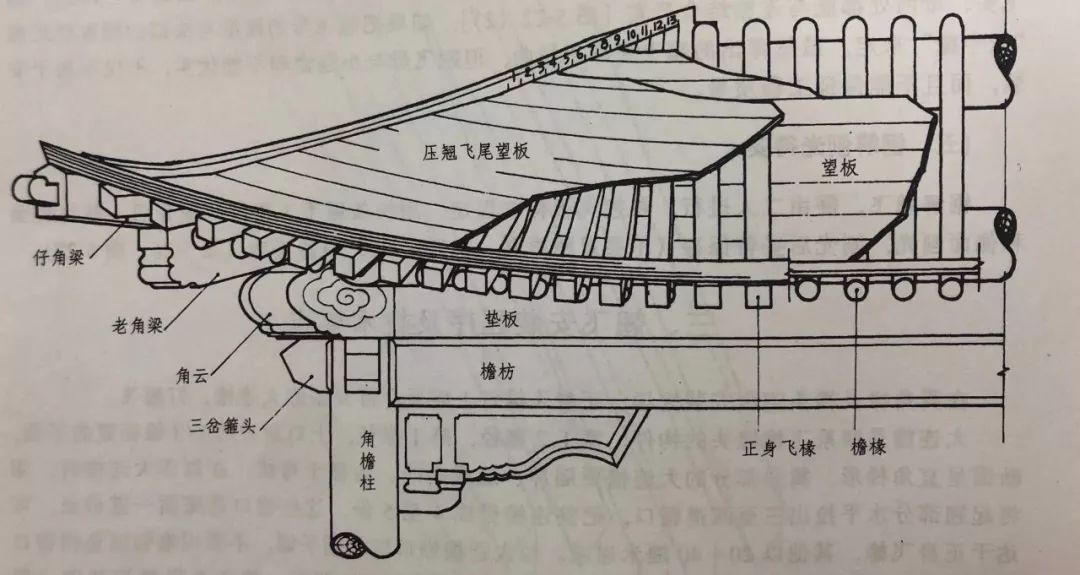
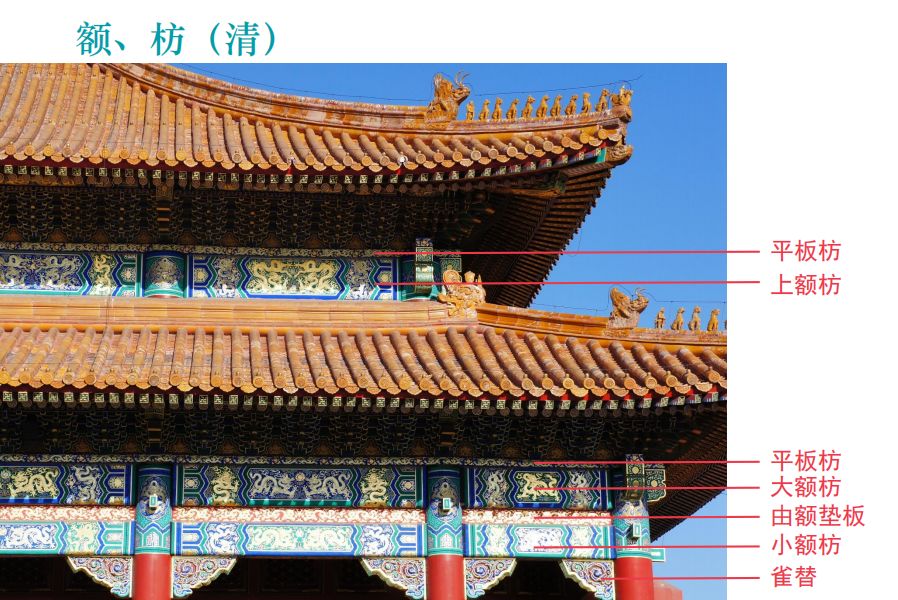
The purlins and architraves of large buildings in the Ming and Qing dynasties are the main load-bearing members, more than the dougong, especially the architraves used in the outer eaves.
The architrave is the name used for large buildings with arch of wooden architecture.
Buildings without arch of wooden architecture are called eaves architrave.
Buildings in the Qing Dynasty have three components: large and small architrave and the front plate.
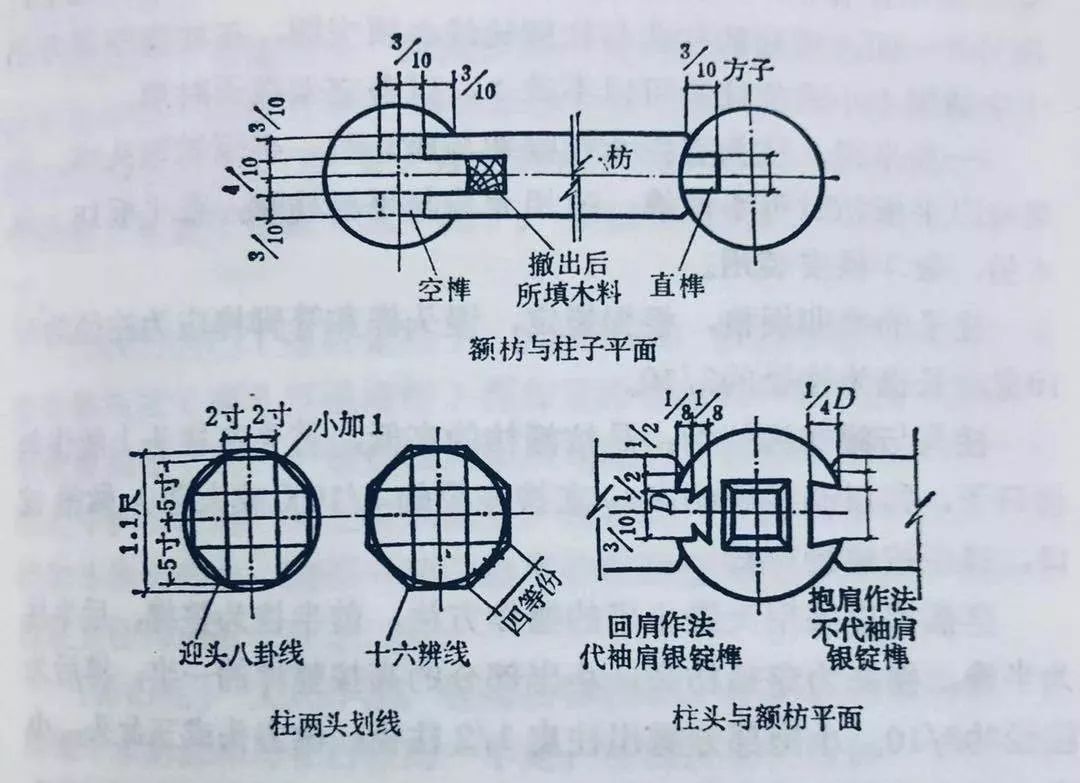
The architrave is a component connecting two columns and supporting the arch of wooden architecture above.
The length of the architrave is determined according to the width of the surface, with a height of 6.6 bucket mouth and a width of 5.4 bucket mouth.
The large architrave intersects with the column head, and the back-off method is used with the measuring rod and the drawing plate.
The tenon is pulled on the architrave according to the size of the architrave hole on the column.
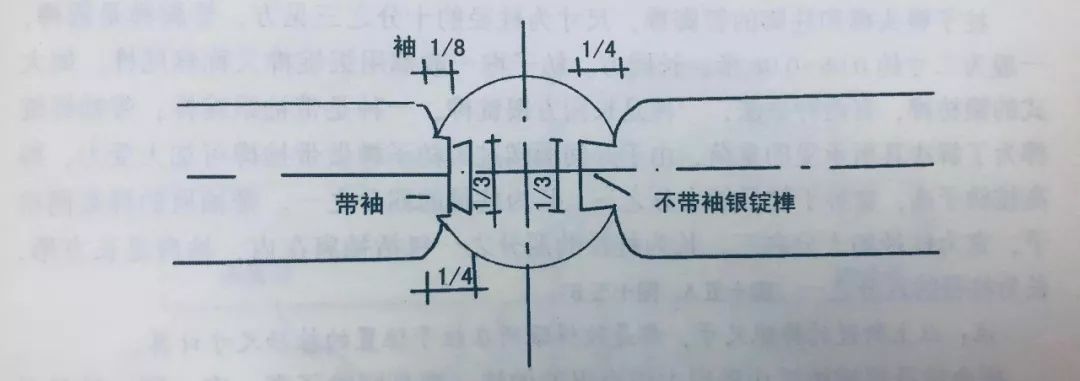
There are also two types of architrave tenon: shoulder with sleeve and shoulder without sleeve.
The small end of the tenon of the architrave accounts for 1/3 of the architrave, the large end accounts for 1/2 of the architrave, each side of the shoulder accounts for 1/4, and the tenon length is 1/4 of the column diameter.
After the tenon is completed, the four sides are chamfered according to 1/10 of the face.
Small architrave is 4.8 bucket high and 4 bucket wide.
The tenon width is 3/10 of the architrave width, and the tenon height is the architrave height.
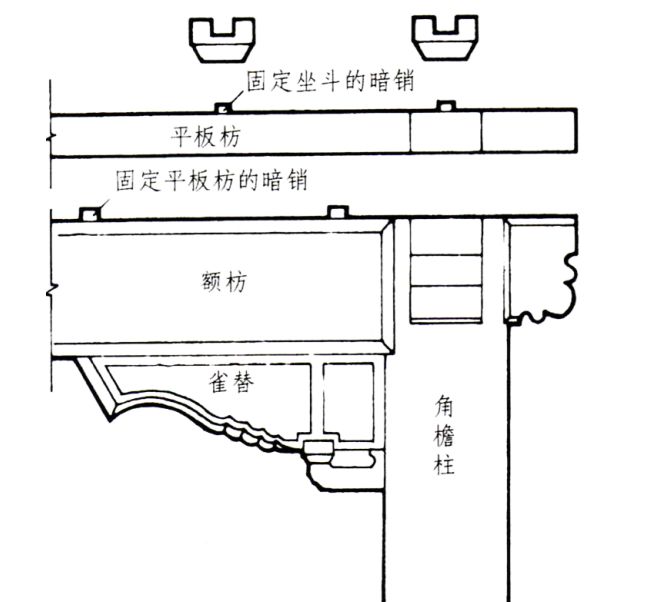
The length of the base plate shall be tenoned according to the net face width, the height shall be the same as the purlin diameter, and the thickness shall be 1 bucket.
The height of the small building base plate is the same as the purlin diameter, and the thickness is 1/5 of the purlin diameter or the same as the plate thickness.
The flat beam has a height of 2 buckets and a width of 3 buckets.
The length is based on the width of each room plus the length of the silver ingot tenon.
The tenon size is 1/2 of the width of the beam.
The lower part is connected with the upper beam by the tip, and the upper part is made by the number of arch of wooden architecture (sitting bucket tenon).
The dowels between the bottom surface of the flat beam and the top beam are generally 2-4 in each room.
The intersection of the flat beam at the corner needs to follow the principle of “mountain surface pressing the eave surface”, that is, the side (mountain surface) component is on the top and the front (eave surface) component is on the bottom.
The eave surface is made into “equal opening”, the mountain surface is made into “cover opening”, and the notch is made into a cover, and the cover depth is 1/10 of the width of the beam.
.



