The most important bearing and reconstructing components in the wood structure of ancient buildings are columns and beams, and the component connecting and stabilizing columns and beams is purlin.

Purlins and braces are widely used, such as ridge purlins and gold purlins indoors, eaves and braces exposed outdoors, corner parts of buildings, hoop head braces for stabilizing corner columns, etc.
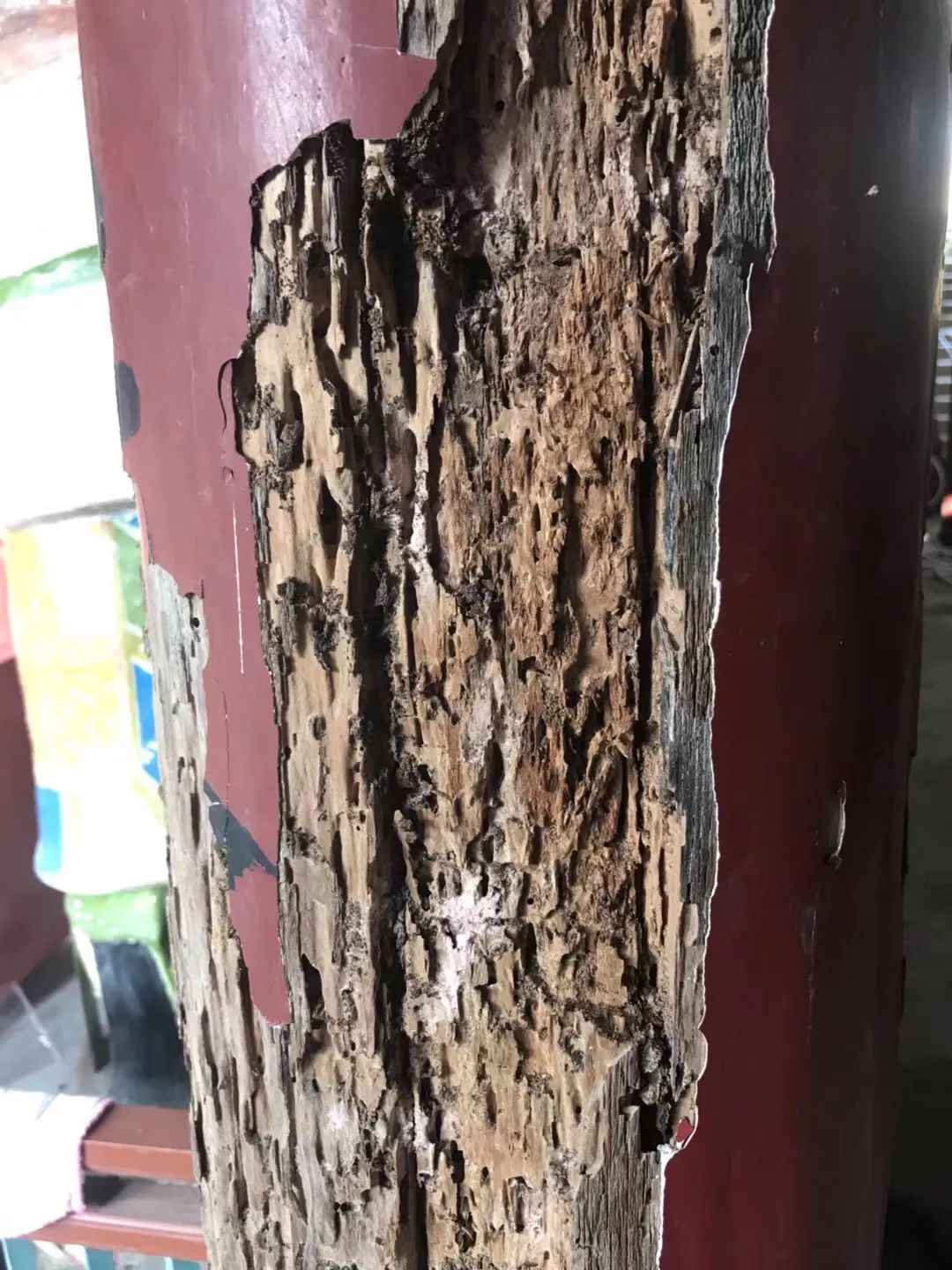

The repair and construction of purlins and braces is also the key to determine the quality and service life of ancient buildings.
This issue will introduce some key points of the shape and maintenance of some main purlins and braces.
01 purlin and brace of Xuanshan building in small buildings, there are some changes in the purlin and brace of Xuanshan building due to coming out of the mountain.

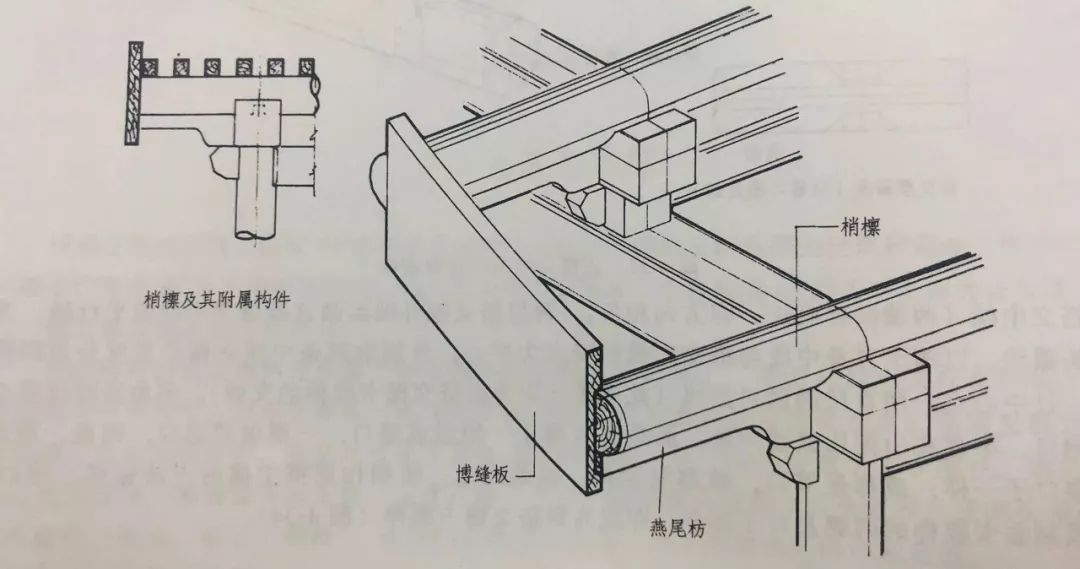
Dovetail brace is the component of Xuanshan building and the backing wood at the cantilevered end of purlin wood.

It is mainly to strengthen the strength of cantilevered purlin wood and play a decorative role.
The length shall be based on the extension length of the tip purlin.
The purlin overhanging from the top to the two mountain surfaces of Xuanshan building is called slightly purlin.
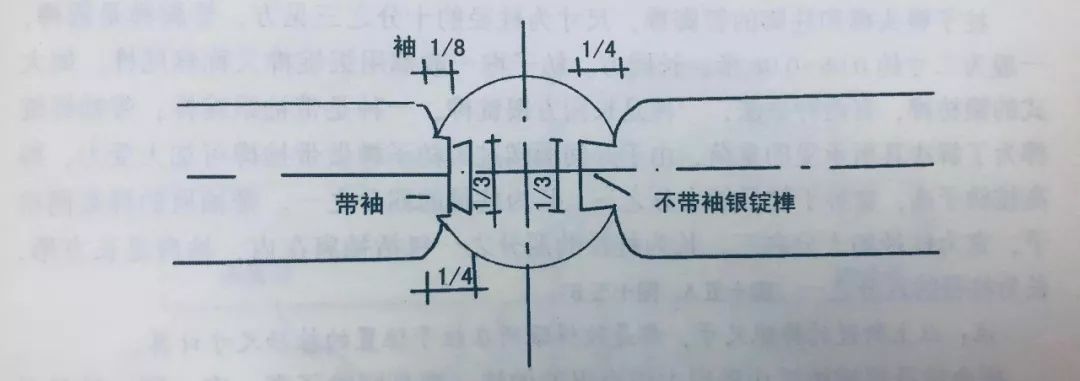
The length is the length between the tips plus the overhanging length.
The overhanging length of Xuanshan is four rafters or equal to the flat size of the eaves.

Because the purlin brace should bear the load of the overhanging part, the nose with the same height as the purlin bowl cannot be made on the beam frame as the main beam.
In order to fix the purlin section, the nose tenon section is generally reduced to 1 / 5 of the purlin diameter.

The height and thickness of the dovetail brace are the same as the base plate.

Although it is a separate component of the eaves, it is not integrated with the base plate on the inner side.
The brace below the dovetail brace is a hoop head brace.
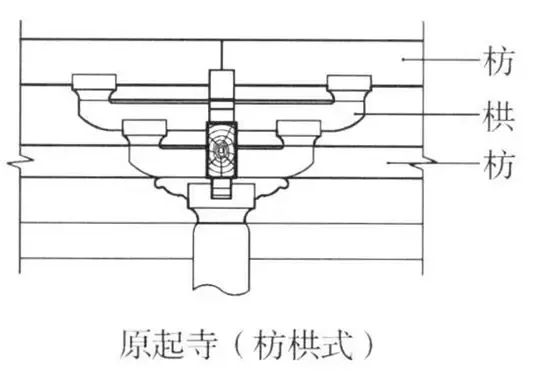
The gables related to swallow tail Fang also have different practices.
One is that the gable is always sealed to the top, and only the slightly overhanging purlin and dovetail brace are exposed.
The other is the practice of “five flower gable”, that is, the gable is only built to the lower batch of each layer of beam frame, and the masonry on it is built into a ladder shape with the length of beam frame to expose the beam frame.

This is a unique practice of suspended mountain construction, which can play the role of ventilation and anti-corrosion in ancient times.
In a few buildings, the gables are only built under the big roof, all the above wooden structures are exposed, and the empty places are blocked with elephant eye plates.
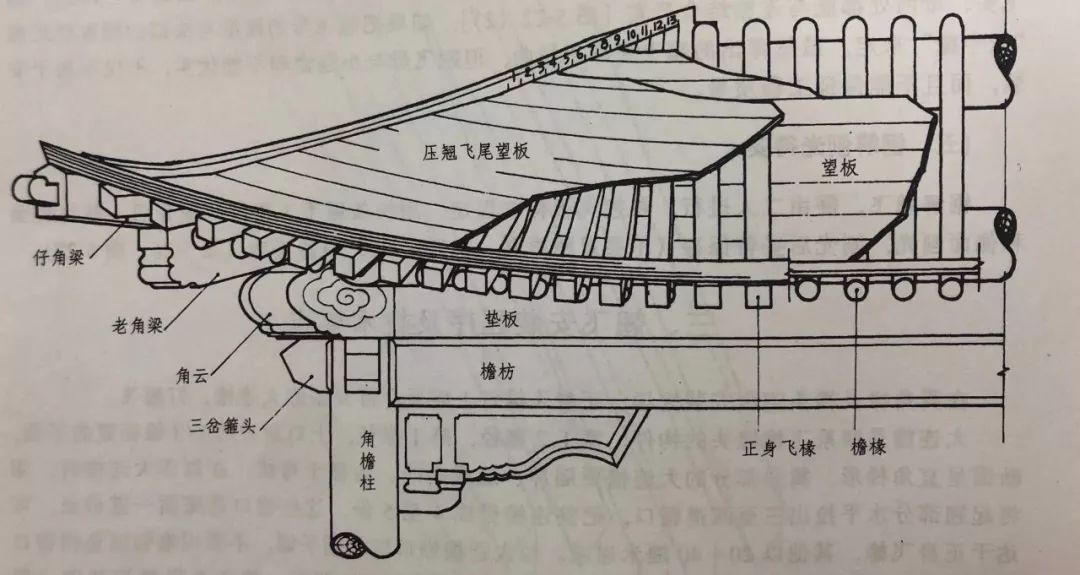
The method of sealing to the top and the method of five flower gable are the purlin brace at the corner of 02.

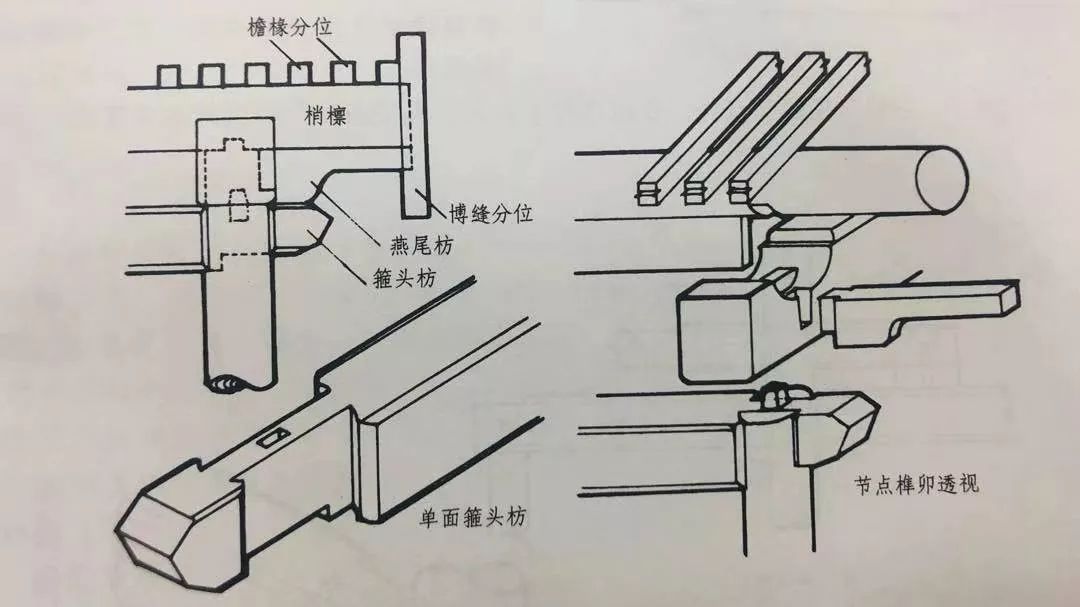
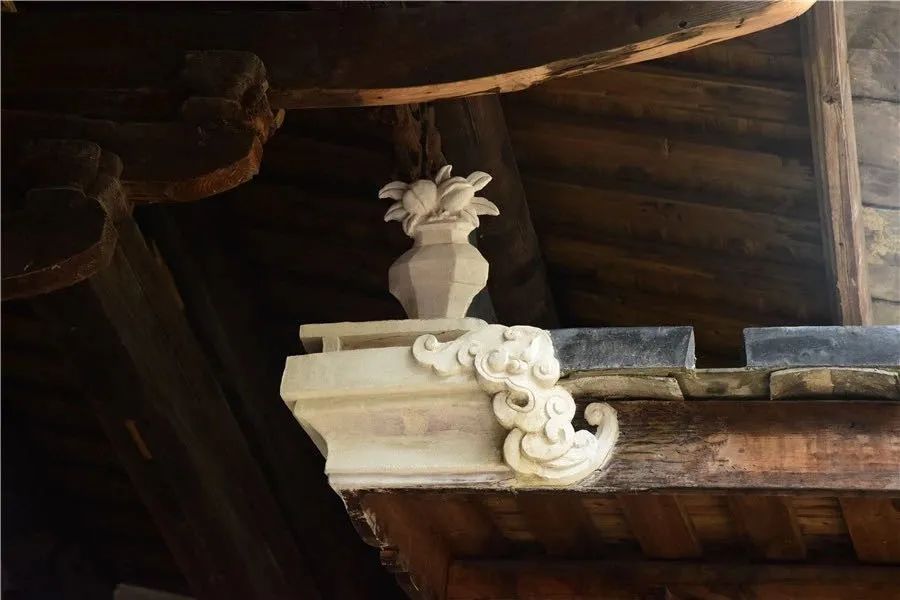
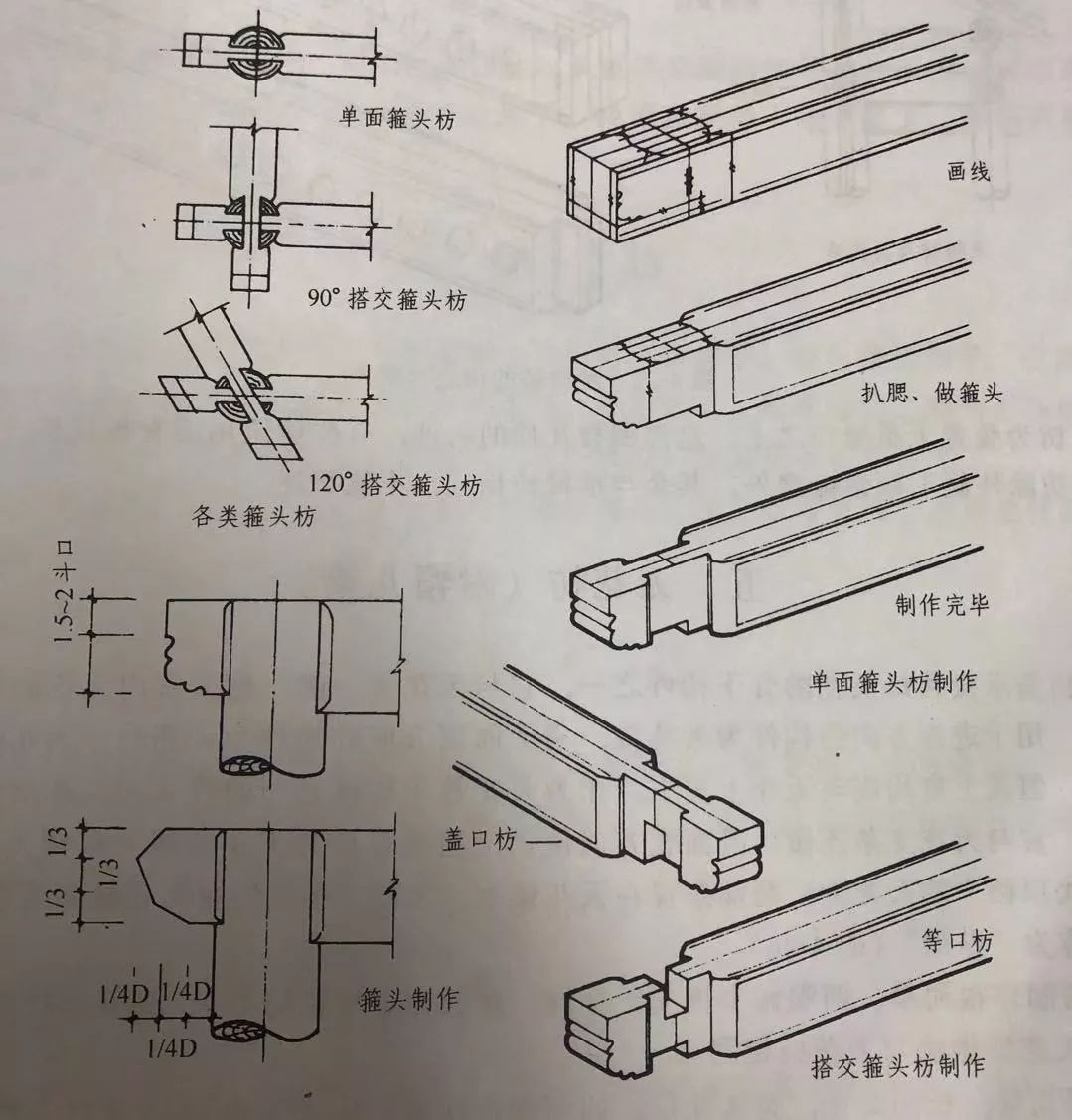
The purlin brace at the corner is called hoop brace, which is used at the corner between the tips or on the mountain surface.
In addition, the eaves brace of polygonal pavilions are hoop brace, which is also different from large-scale buildings and small-scale buildings.
Hoop head brace includes single-sided hoop head brace and overlapping hoop head brace.
The hoop head brace used between the tops of suspended mountain buildings is single-sided hoop head brace; Veranda, Xieshan and pavilions are covered with cross hoops.
There are also two types of single-sided hoop head brace and cross hoop head brace in Xuanshan buildings.
The first part of the hoop head brace of large buildings with bucket arch is often made into the shape of “overlord fist”, and the small buildings without bucket arch are made into the shape of “three fork head”.
Whether it is bawangquan or sanchatou, the width of the two headdresses is 8 / 10 of the square.
Therefore, the two sides of the hoop square headdress are cut off by 1 / 10 of the original thickness, and the height is removed by 2 / 10 of the original height from the bottom.
Oblique overlapping hoop head brace refers to purlin truss overlapped at 120 degrees, 135 degrees or other angles, which is used for five Square Pavilion, six square Pavilion, eight square Pavilion, etc.
in polygonal buildings, there is no problem of pressing eaves on mountain surface, but on the same large wooden member, the direction of sockets should be consistent.
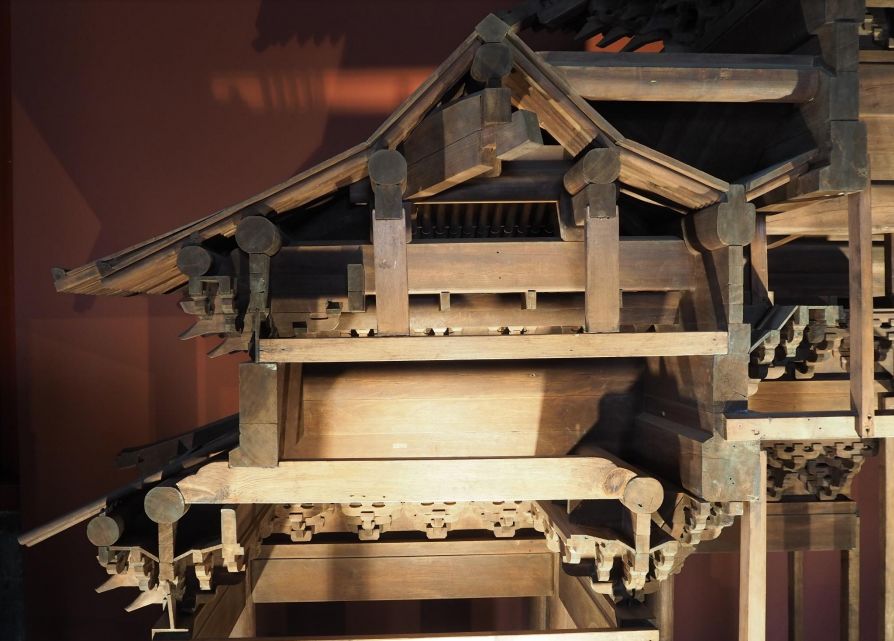
The purlins and braces of sanchatou 03 large-scale building are the wooden components of Foguang temple in the Tang Dynasty, the official buildings in the Ming and Qing Dynasties, and the large-scale buildings can also be divided into early buildings in the Tang and Song Dynasties and official buildings in the Ming and Qing Dynasties.
They have different component names and different relationships with Dougong and other components.
Yuanqi temple in Lucheng, Shanxi Province, was built in the Tang Dynasty.
The “beam” of the buildings in the Tang and Song Dynasties was called “Xi”.
The beam intersecting Dougong was not made into a peach pointed beam.
The cornice purlin and Zhengxin purlin supported by Dougong were also different from the names and shapes of future generations.
In addition, the relationship between purlin brace and beam frame in early buildings is also relatively free.
Beams can be inserted in purlin brace or overlapped above.
In the early Xieshan architecture, the “Ding” is “along the beam”, which forms a “t” shape with the beam.
The ding is installed on the bucket arch or eaves column at one end and on the beam at the other end.
The beam is also directly pressed on the outer eaves purlin.
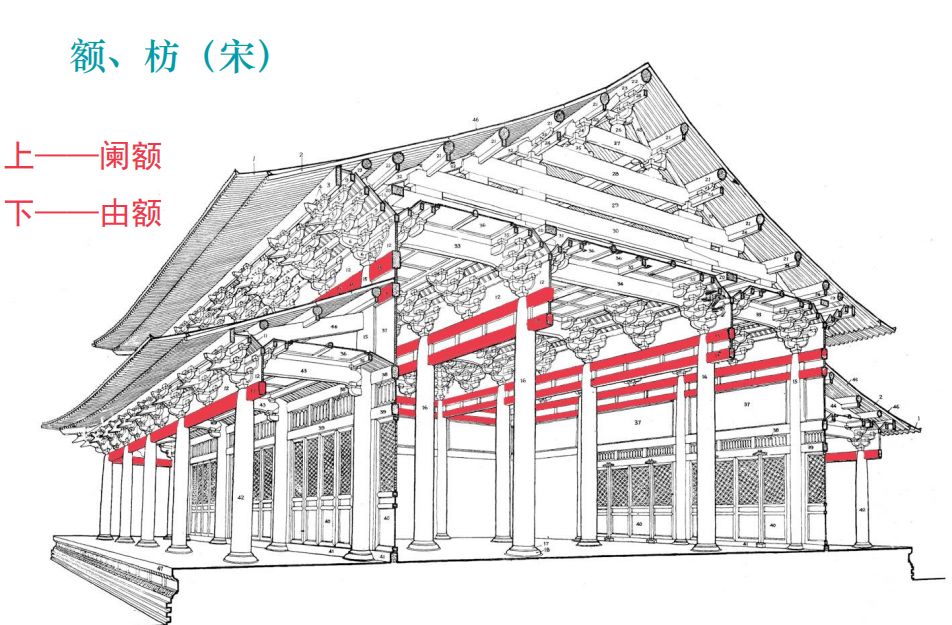
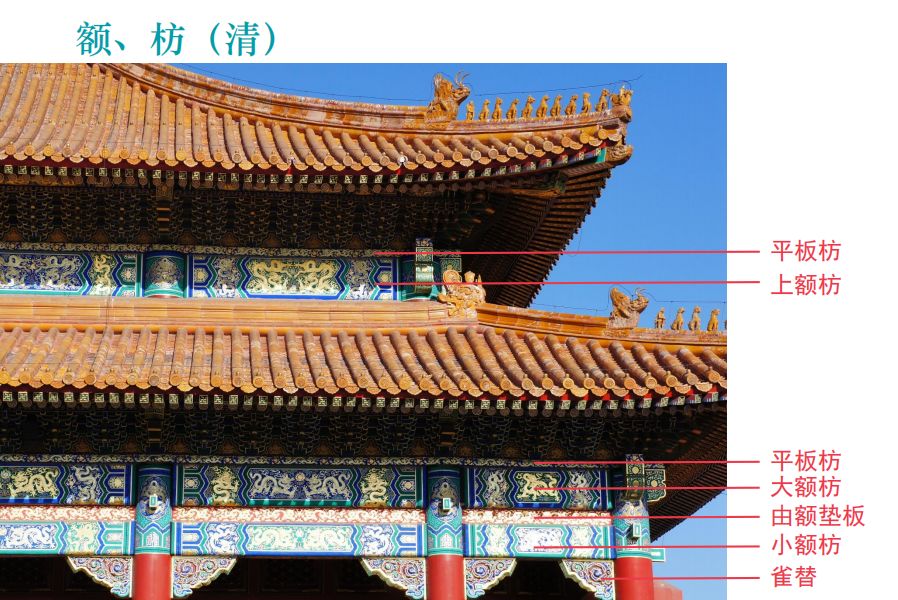
Purlins and braces of large-scale buildings in the Ming and Qing Dynasties are the main load-bearing components, more than Dougong, especially the architrave used in the outer eaves.
Architrave is the name used for large-scale buildings with bucket arches.
Buildings without bucket arches are called eaves architraves.
Buildings in the Qing Dynasty have three components: large and small architraves and cushion plates.
The architrave is a component connecting two columns and supporting the upper bucket arch.
The length of the architrave is determined according to the width of the surface, with a height of 6.6 bucket mouth and a width of 5.4 bucket mouth.
The large architrave intersects with the column head, and the tenon is pulled on the architrave according to the size of the architrave opening on the column by using the Zhang rod and the extraction plate.
There are also two kinds of architrave tenon with sleeve shoulder and without sleeve shoulder, as well as holding shoulder and back shoulder.
The small end of the architrave tenon accounts for 1 / 3 of the architrave, the large end is 1 / 2 of the architrave, and each side of the shoulder accounts for 1 / 4.
The tenon length is 1 / 4 of the column diameter.
After the tenon is completed, the four sides are inverted according to 1 / 10 of the face.
The small brace has a height of 4.8 bucket mouth and a width of 4 bucket mouth.
The tenon width is 3 / 10 of the brace width and the tenon height is according to the brace height.
The base plate shall be tenoned according to the clear surface width, the height shall be the same as the purlin diameter, and the thickness shall be 1 bucket mouth.
The height of small building base plate is the same as the purlin diameter, and the thickness is 1 / 5 of the purlin diameter or the thickness of the viewing plate.
The flat brace has a height of 2 bucket openings and a width of 3 bucket openings.
The length is based on the face width of each room plus the length of silver ingot tenon.
The size of tenon is based on 1 / 2 of the brace width.
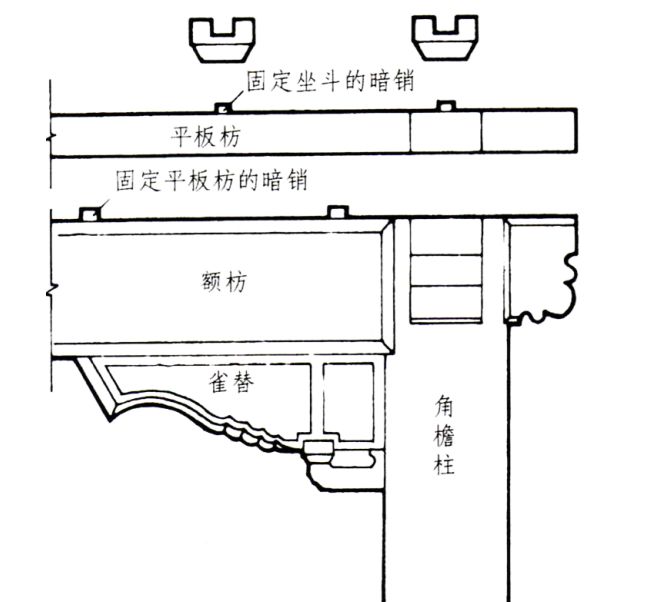
The lower part is connected with the front brace according to the tip, The dowels (sitting dowels) are made according to the number of bucket arches on the top.
Generally, there are 2-4 dowel pins between the bottom surface of the flat brace and the front brace, and the overlapping flat brace at the corner intersects cross.
It is necessary to follow the principle of “mountain surface pressing the eaves surface”, that is, the side (mountain surface) components are on the top and the front (eaves surface) components are on the bottom.
The eaves surface is made into “equal opening” and the mountain surface is made into “cover opening” A covering is made at the notch, and the covering depth is 1 / 10 of the brace width.
The purlins and braces in large-scale buildings are also more rigorous and huge.
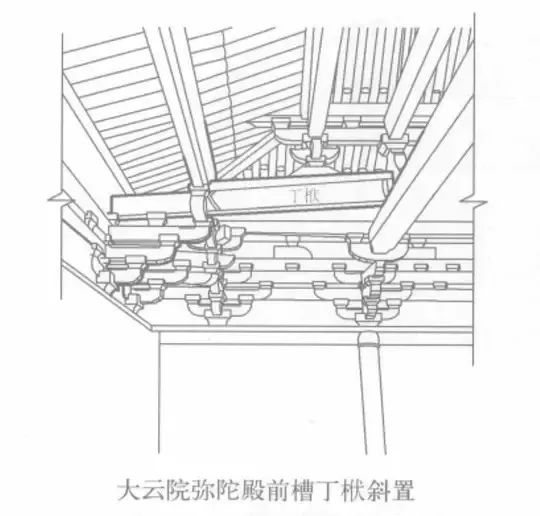
In order to undertake the Shun lying beam, generally, one end of the Shun lying beam as shown in the figure is inserted on the golden melon column on the five beams, and one end is on the golden purlin under the mountain.
The longitudinal beam is overlapped on the lower golden purlin and falls on the golden melon column, and the corner beam is buckled on the overlapped lower golden purlin.
04 repair and protective transformation of purlins and braces general spine purlins and gold purlins cannot be buttressed after decay, because these purlins are load-bearing points as a whole and shoulder the weight of all rafters, watchboards, gray backs, etc.
in the upper part.
However, the eaves purlin is different.
It is built directly above the wall.
Below it, there are not only the wall, eaves column, but also the bucket arch to share the gravity, so the eaves purlin can be buttressed in sections.
When the pier is connected to the eaves purlin, attention should be paid to the overlapping method.
Generally, the simplest knot tenon is used instead of hand tenon and palm tenon.
However, the tenon insertion part should be lengthened as much as possible, not less than 40 cm, and the pier joint must be set directly above the Dougong square, so as to disperse the bearing force and combine the two sections of wood parts as much as possible to balance the force.
During pier connection, white glue shall be added at the joint of tenon and mortise, and iron hoops can also be added at the pier connection.
The repair method of patching can also be used, that is, the rotten part in the middle of the wood parts can be hollowed out, cut to the non rotten part, and then the new wood parts can be inlaid with glue.
At the same time, there are color paintings on the beams of many buildings in the Ming and Qing Dynasties.
How to protect the color paintings while maintaining the wood structure is also a problem that needs attention.
It is a basic principle that all ancient builders must adhere to.
For the gold purlins that are seriously rotten and need to be replaced, the splicing and patching method is generally adopted.
The so-called inlay filling method is to cut a part of the rotten gold purlin that can be completely cut off, cut it down as a whole, then cut a new gold purlin of the same size according to the size of the old color painted gold purlin, patch the old gold purlin, add glue in the middle, and reinforce it with different numbers of concealed nails according to the length, so as to retain the color paintings with historical and artistic value..


